Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart's Symphony No. 40 in G minor is a work of extraordinary musical depth and complexity. The first movement, marked "Molto allegro," is a prime example of Mozart's innovative use of form, harmony, and melody to convey a wide range of emotions and musical ideas.
The movement begins with a dramatic and tense opening theme, played by the strings in unison. This theme is characterized by its angular melody, which features a series of leaps and intervals that create a sense of unease and dissonance. The theme is then repeated and developed by the woodwinds, adding to the sense of tension and drama.
As the movement progresses, Mozart introduces a second theme, which is characterized by its more lyrical and expressive melody. This theme is played by the strings and woodwinds in a more legato style, creating a contrast with the first theme and providing a sense of relief and release from the tension.
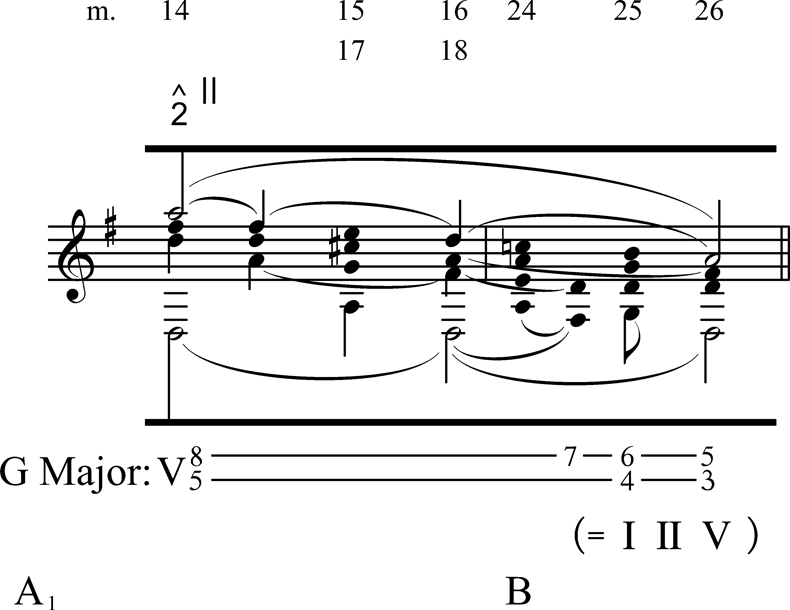
One of the most striking features of the first movement is its use of harmony. Mozart employs a variety of chord progressions and modulation techniques to create a sense of instability and dissonance, which adds to the overall sense of drama and tension. He also uses chromaticism, or the use of notes outside the diatonic scale, to add to the sense of dissonance and instability.
Another important aspect of the first movement is its form. Mozart uses a sonata form structure, which consists of three main sections: the exposition, development, and recapitulation. In the exposition, he presents the two main themes, which are then developed and transformed in the development section. In the recapitulation, he brings the two themes back, often in altered form, to create a sense of resolution and closure.
Overall, the first movement of Mozart's Symphony No. 40 is a masterful example of musical craftsmanship and emotional depth. Its innovative use of form, harmony, and melody creates a sense of tension, drama, and resolution that continues to captivate and inspire listeners to this day.