The pectoral girdle and upper limb, also known as the shoulder and arm, play a crucial role in the movement and function of the human body. The pectoral girdle consists of the clavicle (collarbone) and the scapula (shoulder blade), which form a joint with the humerus (upper arm bone) to create the shoulder joint. This joint allows for a wide range of movement, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction.
The muscles of the pectoral girdle and upper limb work together to provide the necessary strength and stability for movements such as lifting, reaching, and throwing. The pectoral muscles, located in the chest, are responsible for moving the arm across the front of the body. The deltoid muscles, located in the shoulder, are responsible for rotating and lifting the arm. The biceps and triceps muscles, located in the upper arm, are responsible for flexing and extending the arm, respectively.
In addition to these major muscle groups, there are also numerous smaller muscles that contribute to the movement and stability of the shoulder and arm. The rotator cuff muscles, for example, are responsible for rotating the shoulder joint and stabilizing the shoulder blade. The wrist and hand are also essential for a wide range of movements, including grasping and manipulating objects.
Overall, the pectoral girdle and upper limb play a vital role in the movement and function of the human body. From lifting and carrying to reaching and grasping, these body parts allow us to perform a wide range of activities that are essential for daily living.
11.5 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs

The hypothenar muscles, which are located on the medial part of the palm, are the abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, and opponens digiti minimi. The subacromial bursaand the sub-coracoid bursa,as the names suggest, are locatedbetween the joint capsule and the acromion and coracoid processes, respectively. GLENOHUMERAL JOINT Articulating Surface and Type of Joint This joint is formed by the head of the humerus and the glenoid fossa of the scapula. You can easily palpate, or feel with your fingers, the entire length of your clavicle. The broad, triangular latissimus dorsi is located on the inferior part of the back and has multiple points of origin including the lumbosacral fascia attached to the inferior 6 thoracic vertebrae, the inferior 3 ribs, the iliac crest and inferior angle of the scapula.
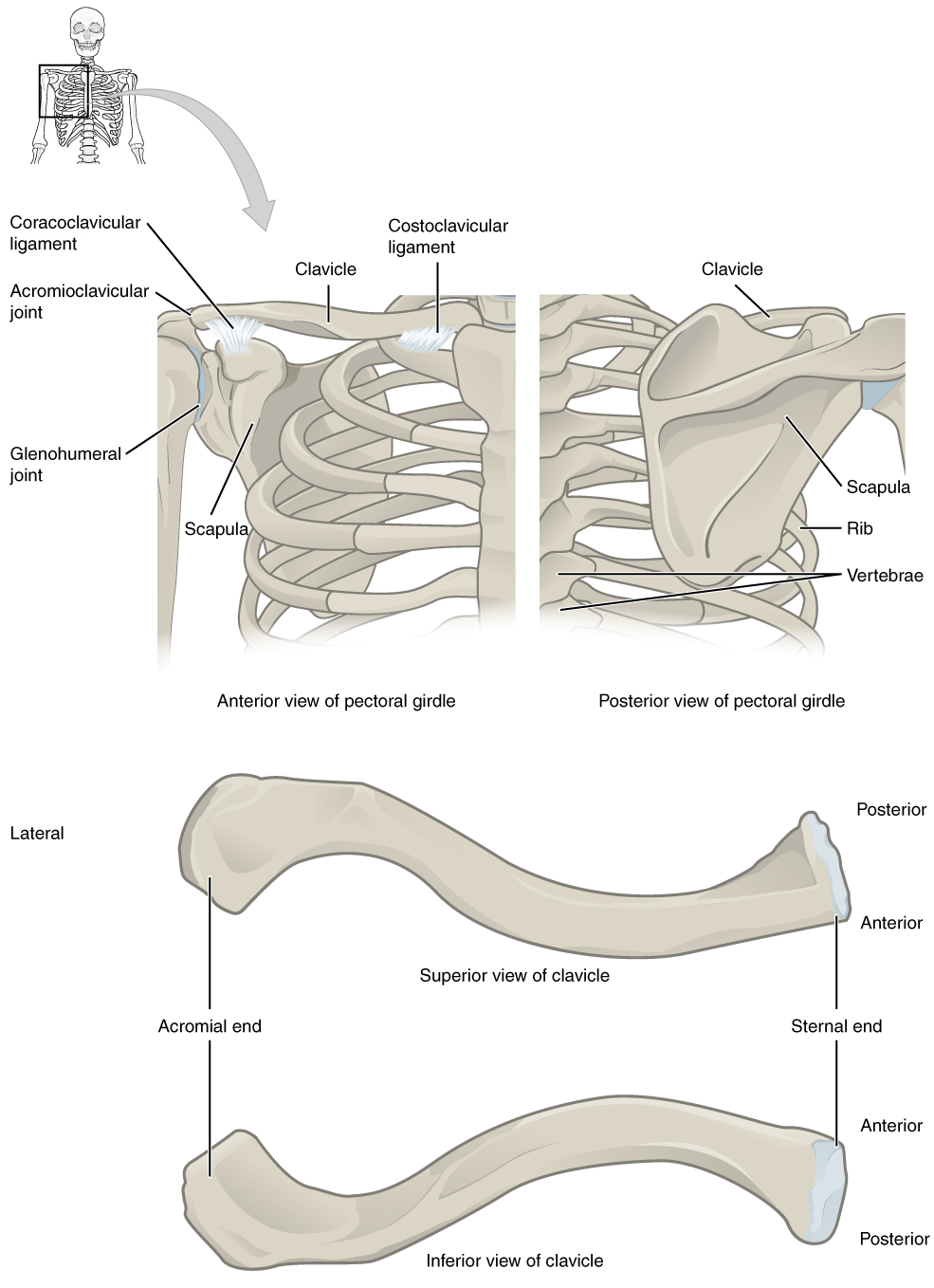
Joints of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb
The ones that originate on the axial skeleton are the pectoralis major and the latissimus dorsi. The muscles that move the shoulder also move this joint. The tendons of the deep subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor connect the scapula to the humerus, forming the rotator cuff musculotendinous cuff , the circle of tendons around the shoulder joint. The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. These are the flexor pollicis longus and the flexor digitorum profundus. Because the sternoclavicular joint is strong and rarely dislocated, excessive force results in the breaking of the clavicle, usually between the middle and lateral portions of the bone. The scapula is located on the posterior side of the shoulder.
11.6 Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs

However, poor ergonomics can irritate the tendons of these muscles as they slide back and forth with the carpal tunnel of the anterior wrist and pinch the median nerve, which also travels through the tunnel, causing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Click for larger image. The key difference between pelvis and pelvic girdle is that the pelvis is a lower part of the trunk that composes several bones such as a pair of bones, sacrum and coccyx while the pelvic girdle is one of the two parts of the bony pelvis that composes two appendicular hip bones oriented in a ring. Deep to the biceps brachii, the brachial is a synergist in forearm flexion. The superficial anterior compartment of the forearm produces flexion. Muscles That Move the Humerus a, c The muscles that move the humerus anteriorly are generally located on the anterior side of the body and originate from the sternum e. The biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis flex the forearm.
What is the three parts of the pectoral girdle?
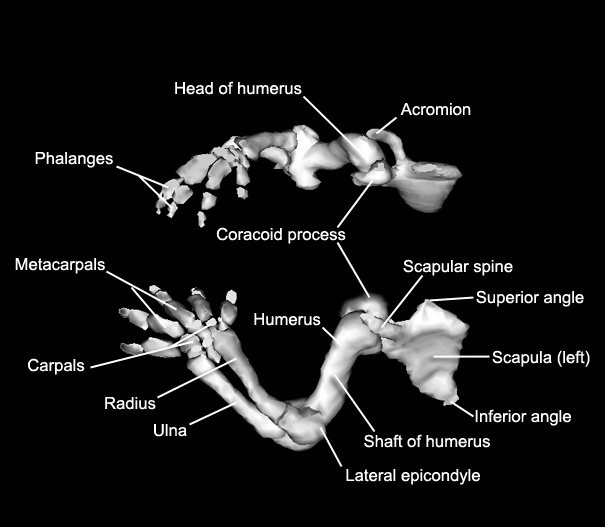
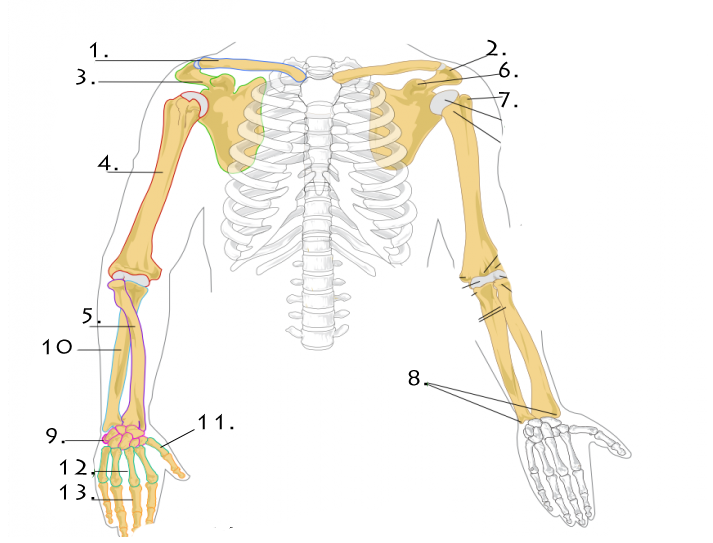
In men, the clavicle is heavier and longer, and has a greater curvature and rougher surfaces where muscles attach, features that are more pronounced in manual workers. Ligaments The glenohumeral ligamentconsists of three thick-ened sets of fibers on the anterior side of the capsule and extends from the humerus to the margin of the glenoid cavity. Finally, the coracobrachialis flexes and adducts the arm. Muscles That Position the Pectoral Girdle The pectoral girdle, or shoulder girdle, consists of the lateral ends of the clavicle and scapula, along with the proximal end of the humerus, and the muscles covering these three bones to stabilize the shoulder joint. Superior to the spine is the narrow supraspinous fossa, and inferior to the spine is the broad infraspinous fossa. The pronators are the pronator teres and the pronator quadratus, and the supinator is the only one that turns the forearm anteriorly.
Pectoral Girdle: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment

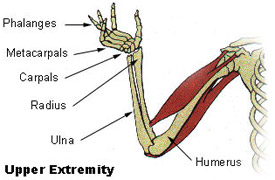
These muscles and their associated blood vessels and nerves form the anterior compartment of the arm anterior flexor compartment of the arm Figure 11. Upper extremity bones: The 64 upper extremity bones consist of 10 shoulder and arm, 16 wrist and 38 hand bones. These make up the bulk of the forearm. DISTAL INFERIOR RADIOULNAR JOINT This pivot joint anchors the distal radius and ulna and participates in supination and pronation. From lateral to medial, the superficial anterior compartment of the forearm includes the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, and flexor digitorum superficialis.