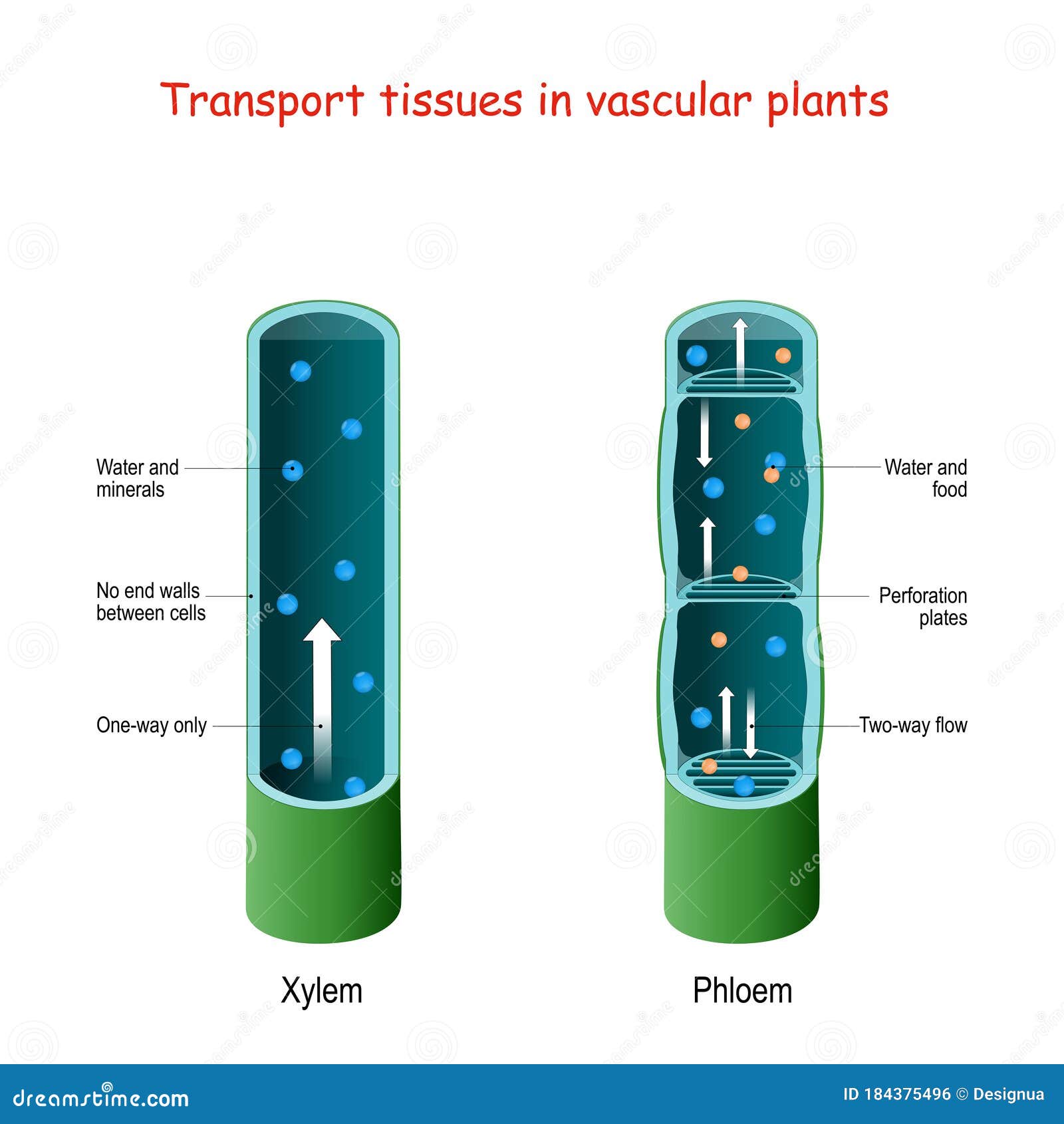
Xylem and phloem vessels are two types of tubes found in plants that play critical roles in the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. Both types of vessels are made up of cells that are specialized for their respective functions and are essential for the proper functioning and growth of a plant.
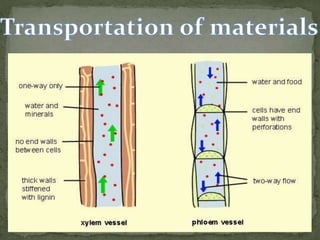
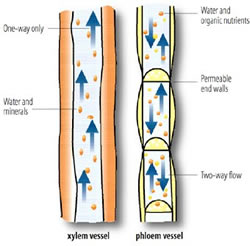
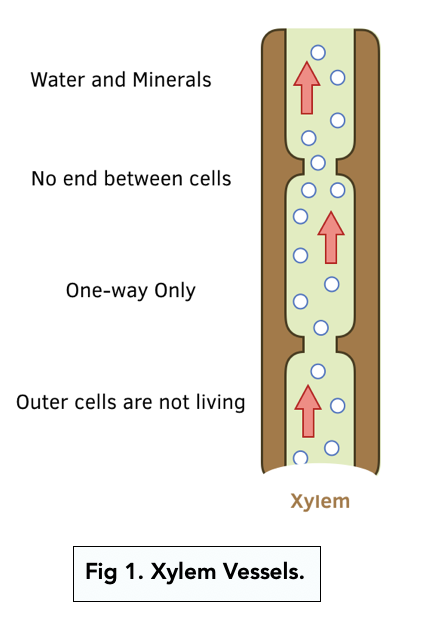
Xylem vessels are responsible for the transport of water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. These tubes are made up of cells with thick walls that have collapsed, forming long, narrow tubes. The cells of the xylem are arranged in such a way as to create a continuous tube from the roots to the top of the plant. Xylem vessels are equipped with a system of valves called "pit membranes" that allow for the flow of water in one direction only, from the roots to the leaves. This helps to prevent the loss of water through evaporation and helps to maintain proper water balance in the plant.
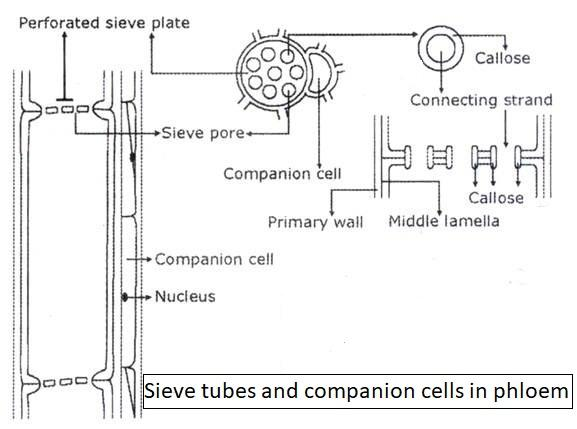
Phloem vessels, on the other hand, are responsible for the transport of sugars and other nutrients throughout the plant. These tubes are made up of living cells that have thin walls and are arranged in a way that allows for the flow of sugars in both directions. Phloem vessels are equipped with a system of "sieve tubes" that allow for the movement of sugars and other nutrients through the tubes. The sieve tubes are connected by small pores called "sieve plates," which allow for the movement of sugars and other nutrients from one cell to the next.
Both xylem and phloem vessels are essential for the proper functioning and growth of a plant. Without the xylem, plants would not be able to transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, leading to dehydration and death. Similarly, without the phloem, plants would not be able to transport sugars and other nutrients to different parts of the plant, leading to stunted growth and reduced reproductive success.
In conclusion, xylem and phloem vessels are two types of tubes found in plants that play critical roles in the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. Both types of vessels are essential for the proper functioning and growth of a plant and are made up of specialized cells that are adapted for their respective functions.