A perfectly competitive market is a hypothetical market structure in which several key conditions are met. These conditions include a large number of buyers and sellers, homogenous products, and easy entry and exit for firms. In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price takers, meaning they have no control over the price of the goods or services they sell and must accept the market price.
One of the main conditions for a perfectly competitive market is a large number of buyers and sellers. This means that no single buyer or seller has the ability to influence the market price. With a large number of participants, the market price is determined by the interactions of all buyers and sellers, rather than being influenced by any single actor.
Another key condition for a perfectly competitive market is homogenous products. This means that the goods or services being sold are identical or nearly identical, making it easy for buyers to switch between sellers without incurring any additional costs. In this type of market, there is no brand loyalty or product differentiation, as all firms are selling the same product.
Easy entry and exit for firms is also a crucial condition for a perfectly competitive market. This means that it is easy for new firms to enter the market and start selling the same product, and it is also easy for existing firms to exit the market if they are not profitable. This helps to ensure that there is a constant influx of new firms and keeps the market competitive.
In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price takers, meaning they do not have the ability to influence the market price. Instead, they must accept the market price and adjust their production accordingly. This means that firms in a perfectly competitive market must operate at the lowest possible cost in order to be profitable.
Overall, the conditions for a perfectly competitive market include a large number of buyers and sellers, homogenous products, and easy entry and exit for firms. In such a market, firms are price takers and must operate at the lowest possible cost in order to be profitable.
The conditions for a perfectly competitive market include which one of the following? A) Firms behave as price takers. B) Profits are zero in the short run. C) New entrants cannot threaten the position of existing firms. D) Firms can control prices. E) Fi

The information regarding the availability, cost, price, quantity, nature of the factor or product, etc. Although the sellers are few, the goods offered are varied. Answer and Explanation: 1. The producer surplus equals the profit from trading minus the profit or loss from not trading, revenue minus variable costs. Which is the best example of perfect competition? It is easier to maximize profit than to maximize revenue. If an entrepreneur sees profits being made in a perfectly competitive market, he's able to enter that market immediately and begin competing profits away from the firms in the market.
Describe the conditions for a perfectly competitive market.
Here are four conditions to make a perfect competition. On account of innumerable transactors, each seller produces a very small portion of the total quantity offered in the market and each buyer has an inappreciable portion of the total demand of the market. Finally, it is assumed that raw materials and other resources are not monopolised. Although some goods are entirely homogenous, they aren't necessarily always produced by firms with the same production technologies. This website includes study notes, research papers, essays, articles and other allied information submitted by visitors like YOU. A regular at Starbucks does not influence the price of a latte. This is obviously not always the case in many markets, because many markets are dominated by one firm or a small group of firms.
Chapter 12 Flashcards

But in the long period, the firms can come and go, i. Absence of Transportation and Selling Costs: Under perfect competition, there is no transportation cost for either the movement of factors or products between different parts of the market. Instead, all must be selling the same, indistinguishable product. If you fail to find any of these conditions holding in a given market, the market is not perfectly competitive. Some animal rights activists were pushing for the USDA to enact stricter guidelines than many egg farmers were following voluntarily. Further, any type of Government intervention into the free interplay of market forces is assumed to be absent.
7 Assumptions or Conditions of Perfect Competition Market
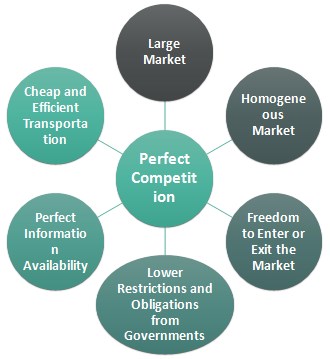
A number of factors are required for a gi","noIndex":0,"noFollow":0},"content":"Following are some of the conditions that determine which markets are oh so perfect and which fall below the standard. Free entry and exit by strengthening the competitive process ensures that in the long run economic profit cannot deviate from zero that is, normal profit. He received his PhD from Yale University. Take commodities, which are defined by their homogeneity: Gold is either gold or something else. If the firm shuts down, it loses the fixed costs.








