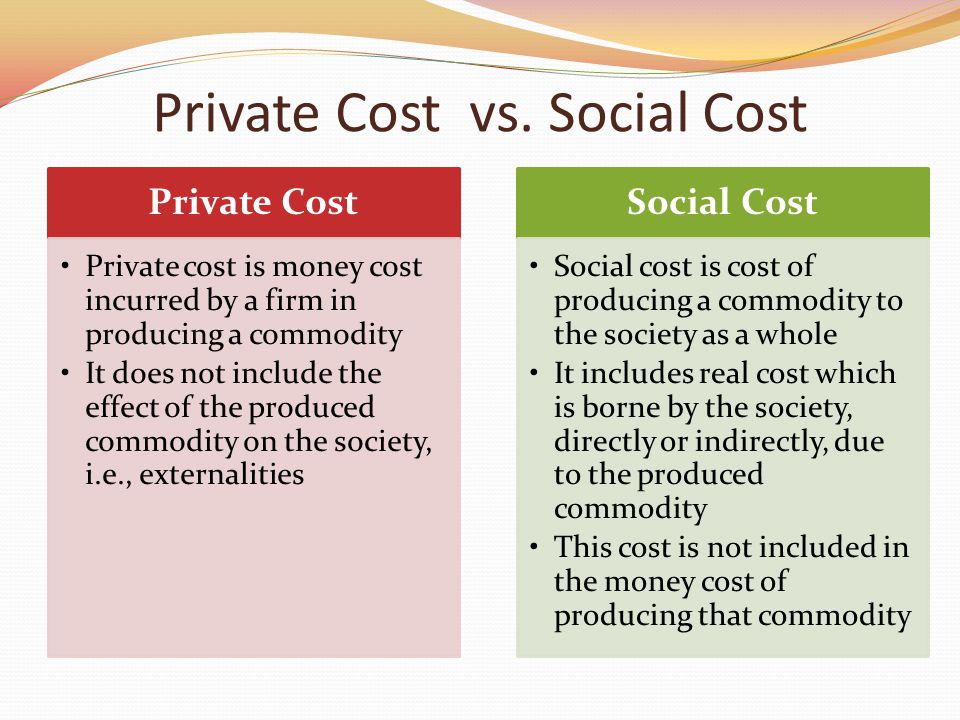
Private costs refer to the costs that are incurred by an individual or a firm in the production and distribution of goods and services. These costs are typically incurred in the process of producing a product or service and are not directly borne by society as a whole. They are an important concept in economics as they play a key role in determining the supply and demand of goods and services in a market.
There are several types of private costs that firms may incur. These include explicit costs, which are costs that are directly incurred in the production process, such as the cost of raw materials, labor, and transportation. Implicit costs, on the other hand, are costs that are not directly incurred in the production process, but are related to the opportunity cost of using a particular resource. For example, if a firm decides to use its own capital to finance a project, the implicit cost is the opportunity cost of not using that capital to invest in another venture.
Private costs are an important factor in the supply of goods and services in a market. When firms incur high private costs, they are less likely to produce a particular good or service, which can lead to a decrease in supply. On the other hand, when private costs are low, firms are more likely to produce a particular good or service, leading to an increase in supply. The relationship between private costs and supply is known as the supply curve.
Private costs also play a role in the demand for goods and services. When the price of a good or service increases, the demand for that good or service may decrease. This is because consumers are willing to pay a lower price for the good or service, which leads to a decrease in demand. On the other hand, when the price of a good or service decreases, the demand for that good or service may increase. This is because consumers are willing to pay a higher price for the good or service, which leads to an increase in demand. The relationship between price and demand is known as the demand curve.
In summary, private costs are an important concept in economics as they influence the supply and demand of goods and services in a market. They are incurred by firms in the production and distribution of goods and services and can take the form of explicit costs, such as the cost of raw materials, or implicit costs, such as the opportunity cost of using a particular resource. Understanding private costs is crucial for firms to make informed decisions about production and for policymakers to make informed decisions about economic policy.
Private cost
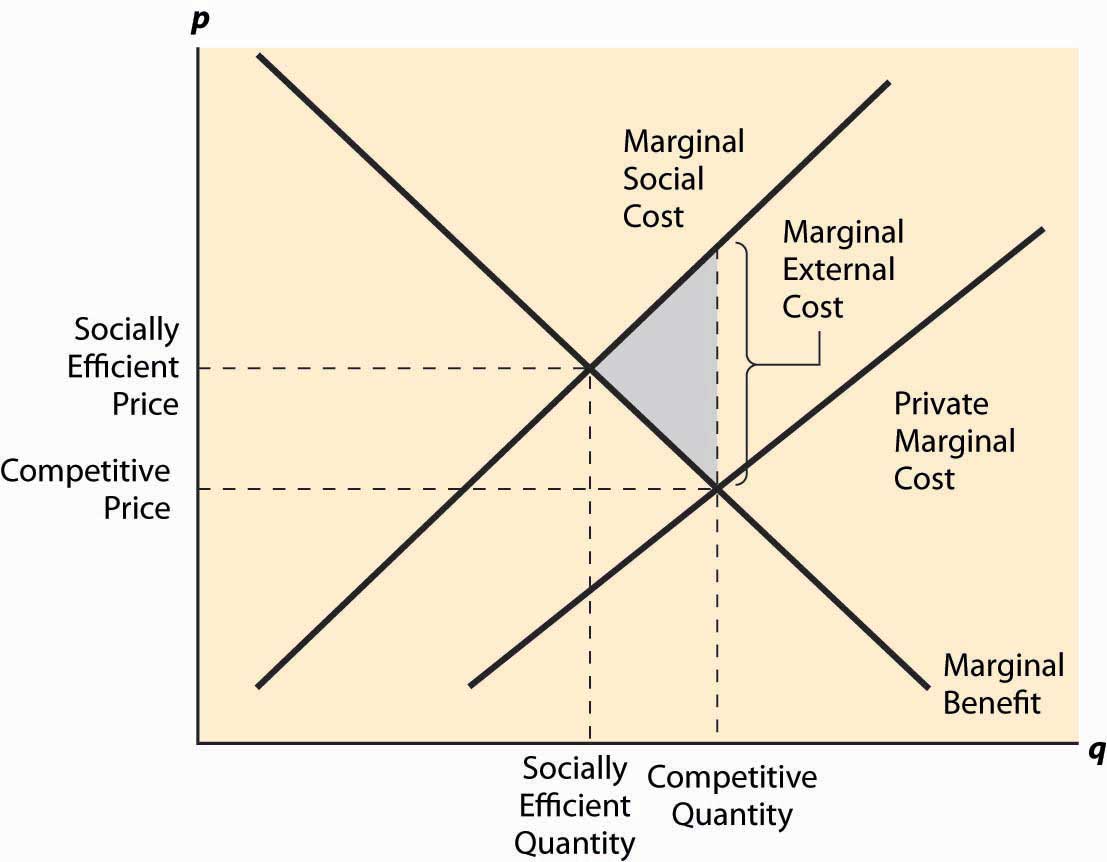
If the value of the social net product or resources is less in any one use than in any other, the national dividend can be increased by transferring resources to more fruitful modes of production. What are examples of social costs? The departures from behavior patterns based on narrowly materialistic utility functions seem to be almost universal only when personal externality relationships exist. In his own formulation, Pigou used the product terminology almost exclusively, although he referred to both types of divergence. As we shall see, the relevance of objectively measurable costs is limited even in this model, but the errors are of a different order of magnitude from those that arise when the externalities refer to an interpersonal interaction or to an interfirm interaction where utility functions are employed. There are many policy efforts undertaken to prevent smoking and encourage cessation. In all such cases, social marginal benefits exceed the private marginal benefits, and the private costs exceed the social costs.
3 Types of Costs and their Benefits in Economics

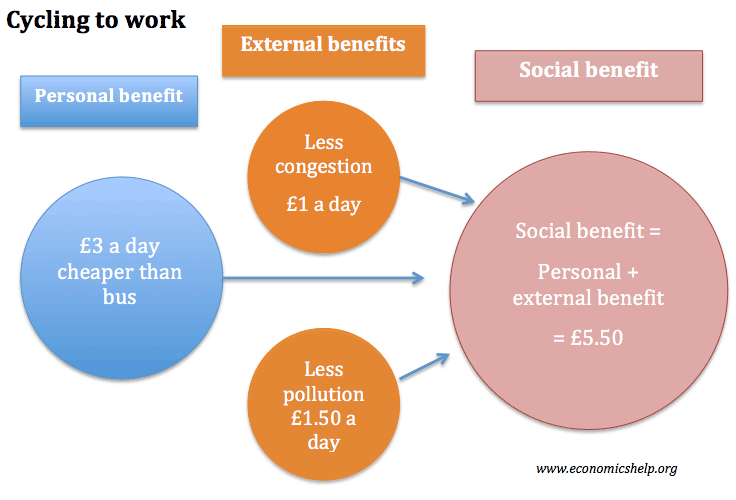
External cost — definition An external cost is the cost incurred by an individual, firm or community as a result of an economic transaction which they are not directly involved in. These issues help explain why most reject that smoking is a pure private activity, even if tax rates could cover the external costs. They are available to everybody whether a person pays for them or not. What is social benefit in project management? For example, if you take time off work to a training scheme. A higher inflation rate leads to a higher nominal interest rate which, in turn, leads to lower real balances. The firms that are engaged in logging, in the forests, are only taking into account private costs and benefits.
Types of Costs

This suggests that, for such cases, the corrective devices implied by the Pigovian analysis should not generate conflicts with standard allocative norms provided, of course, that all of the other conditions required for their applicability are met. Economic benefits are benefits that can be quantified in terms of money generated, such as net income, revenues, etc. If the benefits received by them by undertaking the journey exceed the costs — for example the cost of petrol and wear and tear on the vehicles, they will make the journey. In noncompetitive structures, by contrast, the attempt to levy corrective taxes on an externality-generating firm may do more harm than good. These are called internalized costs, since the firm or party that uses these resources pays for them.
IGCSE PRIVATE & SOCIAL COSTS AND BENEFITS
For example, the cost of providing justice does not increase when one additional person seeks justice from the court. In this research, we found that the less liquid a company, the higher its cost of debt. For a firm, all the actual costs incurred, both implicit depreciation, interest, insurance, etc. Pollution is a negative externality. The Price of Smoking. For example, if you smoke, some people may suffer from passive smoking. A number of governments, including Singapore and the UK, have introduced road pricing schemes.
What is Private Cost? definition and meaning

Marshall and Pigou developed the externality notion within the context of interfirm models, implicitly assuming competitive structures. This is the socially optimum level of output. Each person must simply adjust to the degree of air cleanliness that exists in his environment. We analyse these external economies and diseconomies. As an earlier discussion has shown, however, there is no logical support for this presumption in the general case. What is social service expenditure? In the case of a logging company, private costs will include, for example, the cost of transporting the wood and the cost of labour.