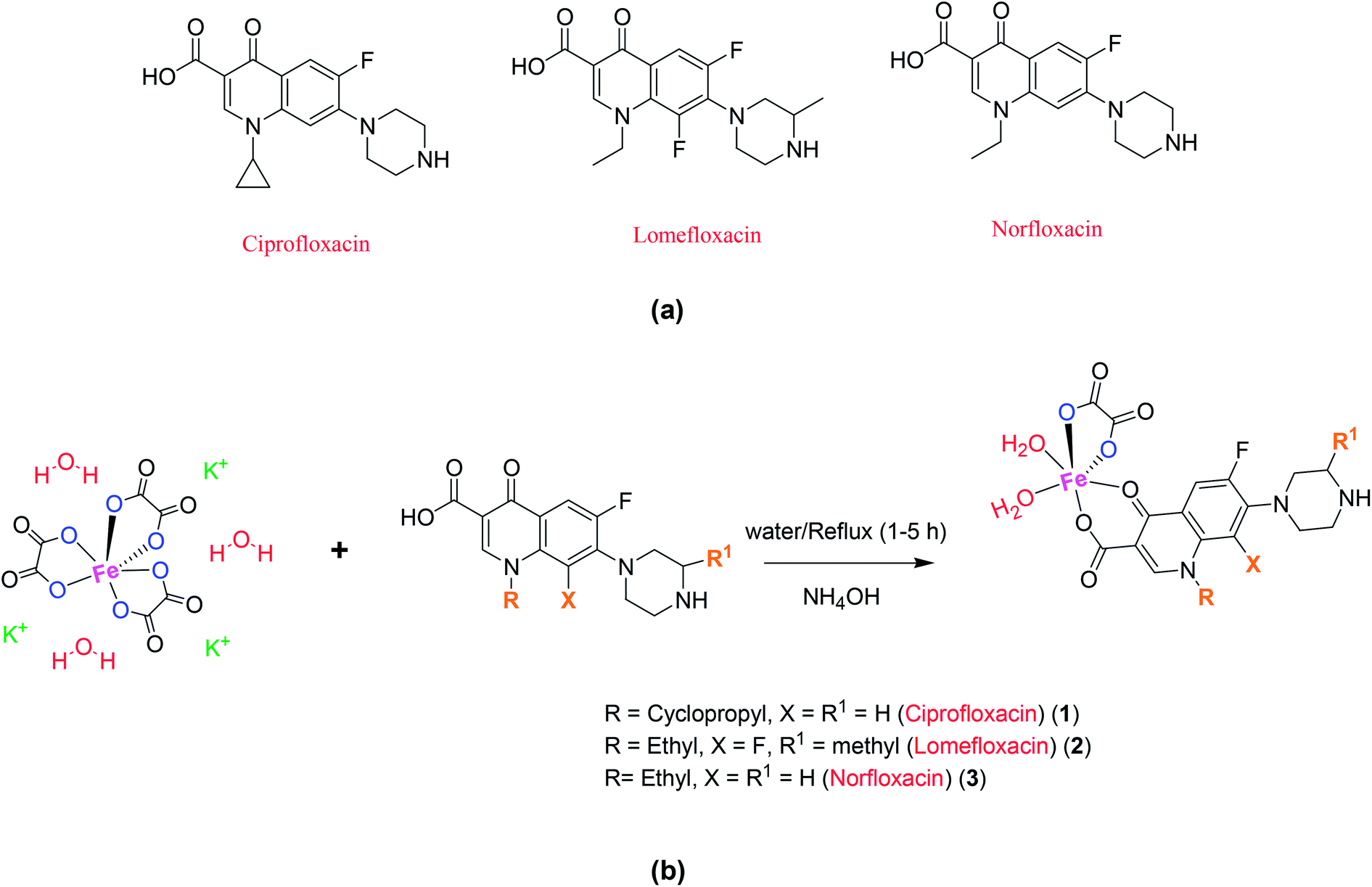
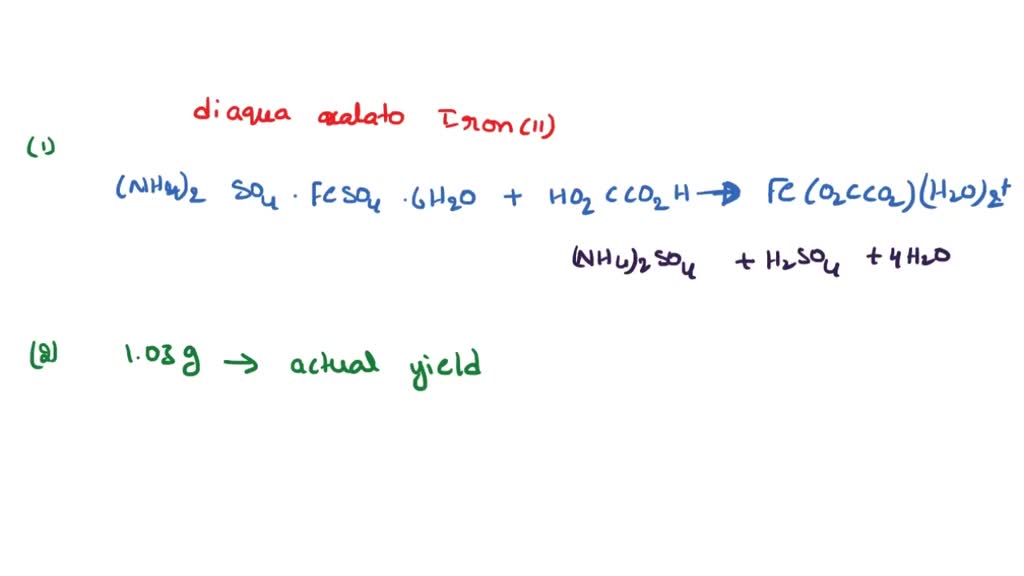
Potassium trisoxalatoferrate(III), also known as potassium ferric oxalate, is a chemical compound with the formula K3[Fe(C2O4)3]. It is a dark purple or red-brown solid that is soluble in water and is commonly used as a laboratory reagent and a disinfectant.
The preparation of potassium trisoxalatoferrate(III) involves several steps. First, ferric oxide (Fe2O3) is reduced to ferric iron (Fe3+) using a reducing agent such as hydrogen gas (H2) or sodium borohydride (NaBH4). The resulting ferric iron is then dissolved in a solution of oxalic acid (H2C2O4) to form a ferric oxalate complex.
Next, potassium hydroxide (KOH) is added to the ferric oxalate complex, causing the formation of potassium ferric oxalate (K3[Fe(C2O4)3]). The resulting solution is then filtered to remove any excess oxalic acid and impurities.
The purified potassium ferric oxalate solution can then be dried and crystallized to obtain the final product, potassium trisoxalatoferrate(III). This can be done by evaporating the solution to a small volume, and then cooling it slowly to allow the crystals to form. The crystals can then be filtered and washed to remove any remaining impurities.
It is important to carefully control the conditions during the preparation of potassium trisoxalatoferrate(III) to ensure the purity of the final product. Impurities can affect the properties and effectiveness of the compound, and it is important to use high-quality reagents and maintain a clean and controlled environment during the synthesis process.
In conclusion, the preparation of potassium trisoxalatoferrate(III) involves the reduction of ferric oxide to ferric iron, the formation of a ferric oxalate complex, and the crystallization of the purified potassium ferric oxalate solution. Careful control of the synthesis conditions is important to obtain a pure and effective final product.