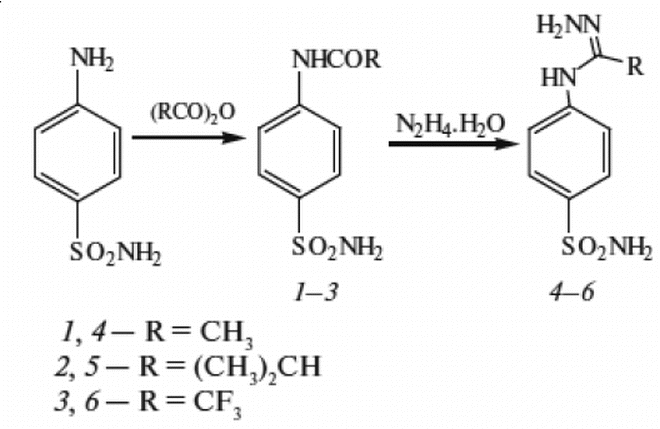
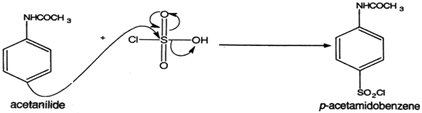
Sulfanilamide is a white, crystalline compound that is used as an antibiotic and as a raw material in the production of other pharmaceuticals. It is also known as 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide or 4-aminobenzenesulphonamide.
The melting point of pure sulfanilamide is around 303-305°C. However, the melting point of impure sulfanilamide may be different due to the presence of impurities. Impurities can be introduced into the compound during its synthesis or during its handling and storage.
The melting point of a compound is a measure of its purity. When a compound is pure, its molecules are all arranged in an orderly, repeating pattern. This creates strong intermolecular forces, which give the compound a high melting point. When a compound is impure, the presence of impurities disrupts the repeating pattern of the molecules, resulting in weaker intermolecular forces and a lower melting point.
There are several ways to determine the melting point of a compound, including using a melting point apparatus. To use this instrument, a small amount of the compound is placed in a capillary tube, which is then inserted into the apparatus. The temperature is then slowly increased until the compound melts. The melting point is recorded as the temperature at which the compound transitions from a solid to a liquid.
It is important to accurately determine the melting point of a compound, as it can be used to identify and distinguish different compounds. For example, if the melting point of a sample of sulfanilamide is significantly lower than the known melting point of pure sulfanilamide, it is likely that the sample is impure. In the case of sulfanilamide, the presence of impurities can affect its effectiveness as an antibiotic and may also affect its safety profile.
In conclusion, the melting point of impure sulfanilamide may differ from the melting point of pure sulfanilamide due to the presence of impurities. The melting point is an important physical property that can be used to determine the purity and identity of a compound. It is important to accurately determine the melting point of a compound, especially in the pharmaceutical industry, to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the final product.