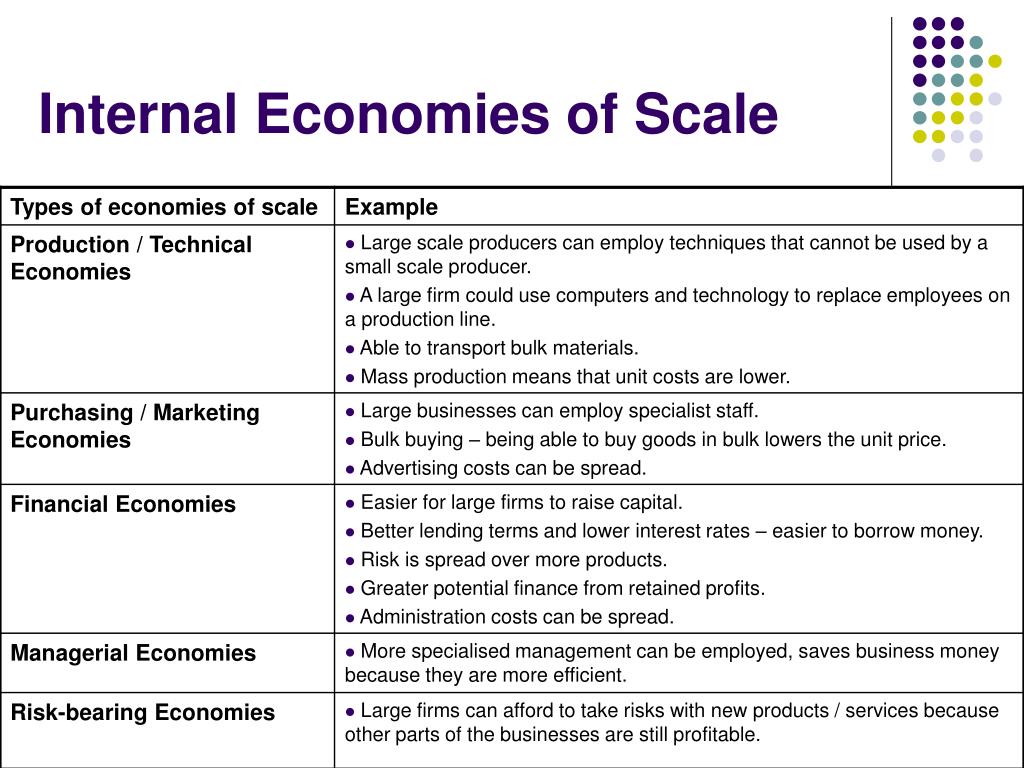
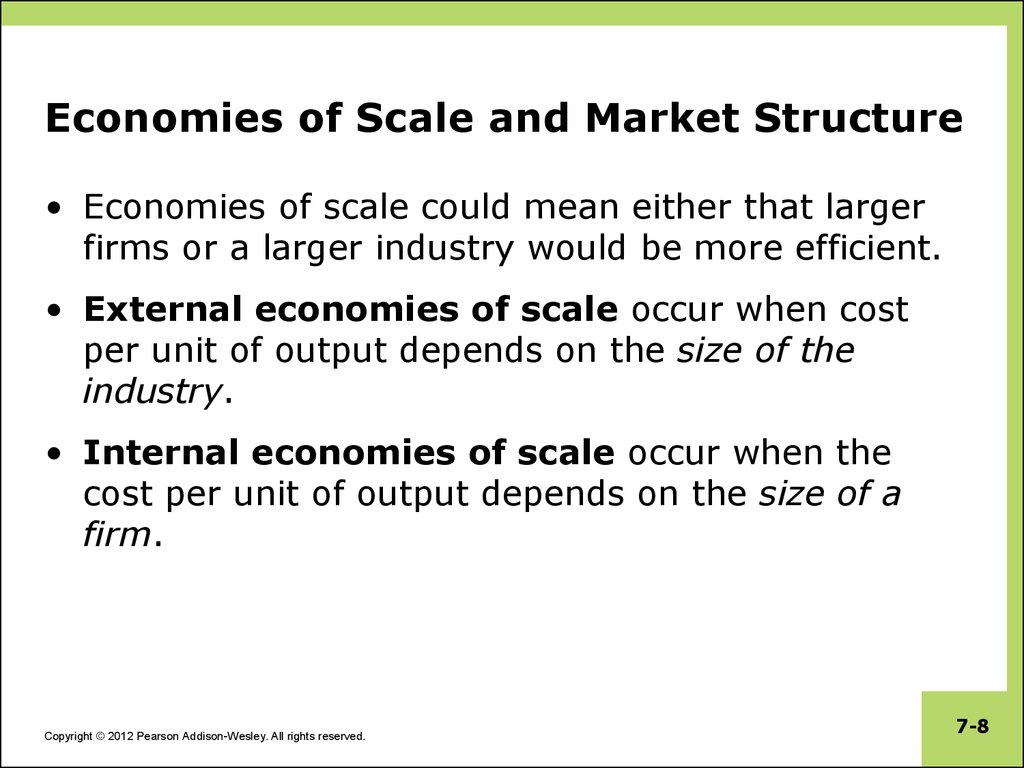
Internal economies refer to the economic activities and processes that take place within a single firm or organization. These can include the production and distribution of goods and services, the management of financial resources, and the allocation of resources to different projects or departments. Internal economies can have a significant impact on the overall efficiency and profitability of a firm, as they determine how effectively the firm is able to utilize its resources to meet the needs and demands of its customers.
There are several factors that can influence the efficiency and effectiveness of a firm's internal economy. These include the organization's management structure, the allocation of resources, and the use of technology and other tools to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
One important aspect of internal economies is the production process, which refers to the way in which a firm creates and delivers its goods or services to customers. This process involves a number of different activities, including research and development, sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, distribution, and marketing. The efficiency of the production process can be improved through the use of technology, such as automation and computerized systems, as well as through the adoption of lean manufacturing techniques, which focus on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Another important aspect of internal economies is the management of financial resources, which includes activities such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting. These activities help a firm to allocate its resources effectively and make informed decisions about how to invest in growth and expansion.
Internal economies can also be affected by external factors, such as economic conditions, competitive pressures, and regulatory changes. For example, a firm that operates in a highly competitive market may need to focus on efficiency and cost-cutting in order to remain competitive, while a firm operating in a stable market may have more flexibility to invest in growth and innovation.
Overall, internal economies play a crucial role in the success of any organization. By managing resources effectively and optimizing the production and distribution of goods and services, firms can increase their efficiency and profitability, and better meet the needs and demands of their customers.