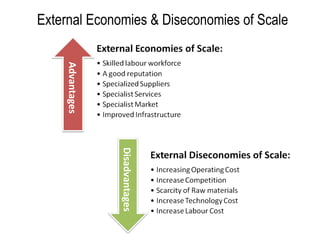
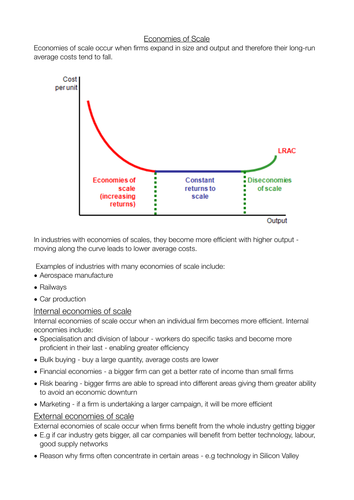
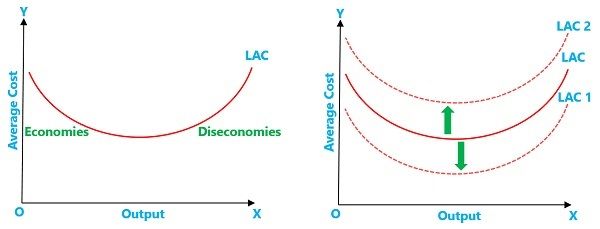
Internal economies refer to the economic activities that take place within a firm or organization. These activities are focused on the production and distribution of goods and services to meet the needs of the organization and its stakeholders. Internal economies can be contrasted with external economies, which refer to economic activities that take place outside of a firm or organization.
There are several types of internal economies that can be identified. One type is the technical economy, which refers to the production of goods and services within an organization. This includes the use of raw materials, labor, and capital to produce finished goods or services. Technical economies can be further divided into two categories: production economies and service economies. Production economies involve the production of tangible goods, while service economies involve the production of intangible services.
Another type of internal economy is the organizational economy, which refers to the management and administration of the organization. This includes the planning and coordination of activities, the allocation of resources, and the decision-making processes that guide the organization's operations. The organizational economy is concerned with the efficiency and effectiveness of the internal operations of the organization.
Internal economies also include the distribution economy, which refers to the distribution of goods and services within the organization. This includes the transportation, storage, and distribution of finished goods, as well as the marketing and promotion of these goods and services. The distribution economy is concerned with ensuring that the organization's products and services reach their intended customers in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Internal economies can also include the financial economy, which refers to the financial management and control of the organization. This includes the collection and allocation of financial resources, as well as the management of financial risks and liabilities. The financial economy is concerned with ensuring the financial stability and sustainability of the organization.
Internal economies are an important aspect of organizational management and can have a significant impact on the overall performance and success of the organization. By optimizing the internal economies of an organization, firms can increase their efficiency and effectiveness, reduce costs, and improve their competitive advantage. Internal economies can also help organizations to adapt to changing market conditions and to respond to the needs and preferences of their stakeholders.
In conclusion, internal economies refer to the economic activities that take place within a firm or organization. These activities are focused on the production and distribution of goods and services to meet the needs of the organization and its stakeholders. Internal economies include the technical, organizational, distribution, and financial economies, and are an important aspect of organizational management. By optimizing the internal economies of an organization, firms can increase their efficiency and effectiveness, reduce costs, and improve their competitive advantage.