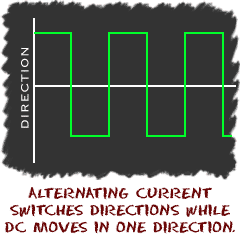
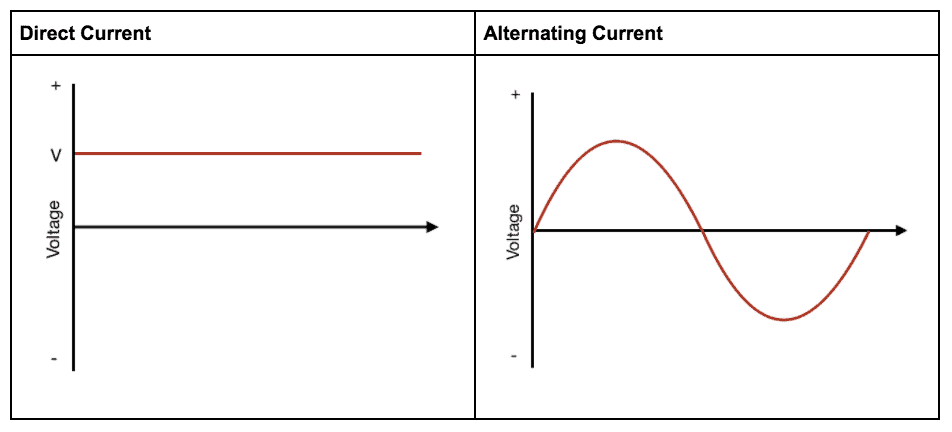
AC current, or alternating current, is a type of electrical current that periodically changes direction. This is in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. AC current is the type of electrical current that is commonly used in homes and businesses, as it is easier to transmit over long distances without losing power.
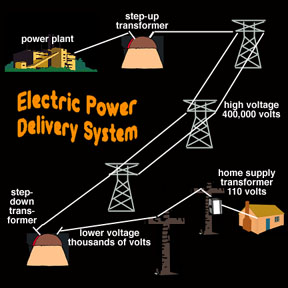
There are several examples of AC current in everyday life. One common example is the use of AC current in the power grid. When electricity is generated at a power plant, it is typically generated as AC current. This current is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses, where it is used to power a wide range of appliances and devices.
Another example of AC current is the use of AC motors in appliances and machinery. Many types of appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and fans, use AC motors to operate. These motors work by using the changing direction of the AC current to rotate a shaft, which powers the appliance or machinery.
AC current is also used in the operation of electric vehicles. Many electric vehicles use AC motors to power the wheels, and these motors are powered by AC current from the vehicle's battery.
In addition to these everyday examples, AC current is also used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. For example, AC current is often used to power large industrial machines, such as lathes and welding equipment. It is also used in the operation of elevators, as well as in the lighting systems of commercial buildings and public spaces.
Overall, AC current is a versatile and widely used form of electricity that plays a vital role in many aspects of modern life. From powering our homes and appliances to enabling the operation of electric vehicles and industrial machinery, AC current is a vital part of our world.