Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division that are essential for the growth and reproduction of living organisms. While they have some similarities, they also have many important differences.
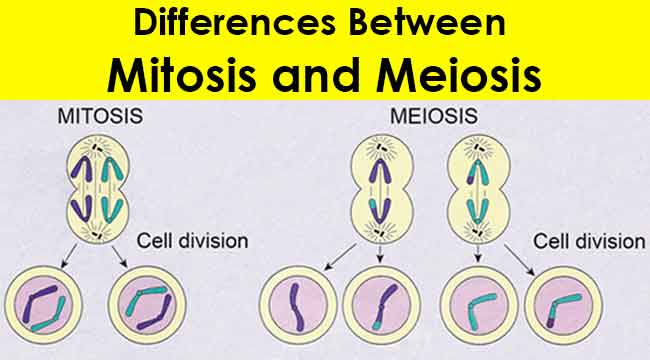
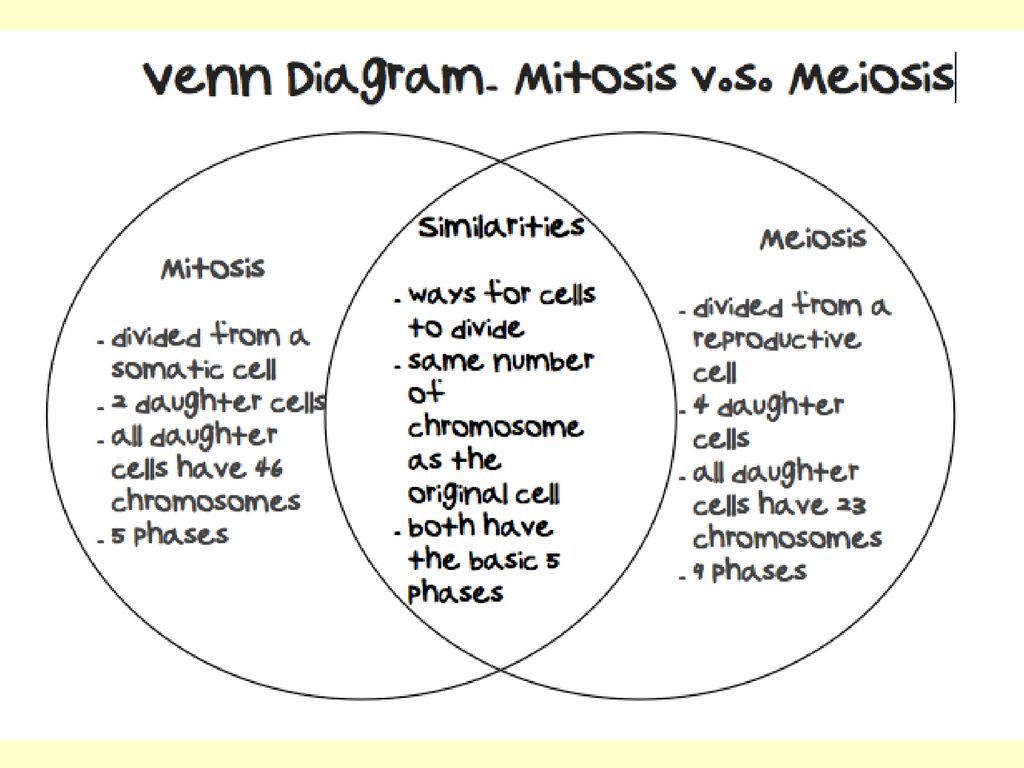
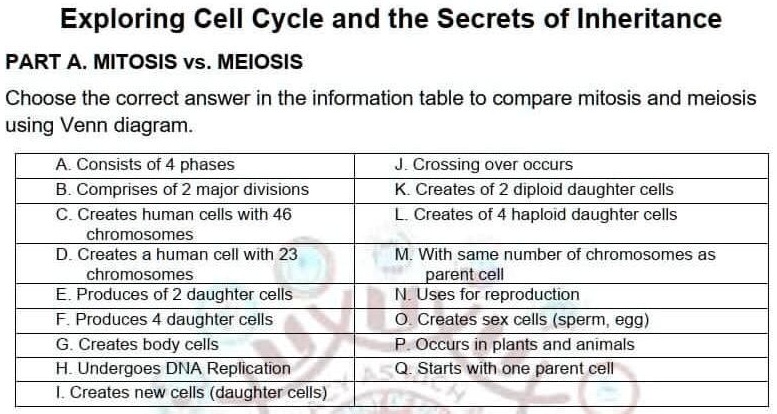
One of the main differences between mitosis and meiosis is the purpose they serve. Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This is important for the growth and repair of tissues in the body. On the other hand, meiosis is the process by which a single cell divides into four non-identical daughter cells, called gametes. These gametes are used for sexual reproduction and the creation of new individuals.
Another major difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of divisions that occur. Mitosis involves only one division, while meiosis involves two divisions. The first division of meiosis, called meiosis I, separates homologous chromosomes, while the second division, called meiosis II, separates sister chromatids.
In terms of the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells, there is also a significant difference between mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis, the daughter cells receive the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. In meiosis, the daughter cells receive only half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This reduction in chromosome number is important for sexual reproduction, as it allows for the mixing of genetic material from two different individuals.
Another difference between mitosis and meiosis is the type of cells that undergo these processes. Mitosis occurs in most types of cells in the body, including somatic cells (body cells). Meiosis, on the other hand, occurs exclusively in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and produces gametes (sperm and eggs).
In summary, mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division that are essential for the growth and reproduction of living organisms. However, they have different purposes, involve different numbers of divisions and produce different types of daughter cells. Mitosis is important for the growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction and the creation of new individuals.