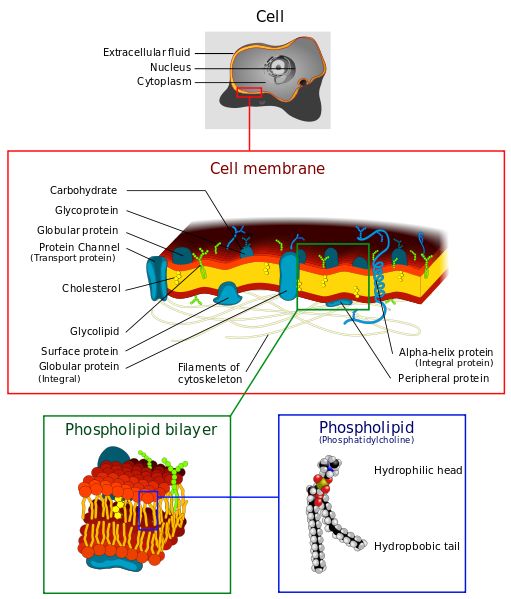
Cell transport mechanisms refer to the various ways in which substances can enter and exit cells. These mechanisms are essential for maintaining homeostasis, allowing cells to take in nutrients, expel waste, and communicate with their environment. In the cell transport and permeability lab, students may explore several different types of transport mechanisms and how they can be affected by various factors.
One type of cell transport mechanism is diffusion, which is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process occurs spontaneously and does not require any input of energy. In the lab, students may observe diffusion by placing a dye in a container of water and watching as it spreads out evenly throughout the water.
Another type of cell transport mechanism is facilitated diffusion, which also involves the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, but it requires the assistance of a protein called a carrier molecule. Carrier molecules bind to the particles being transported and help them pass through the cell membrane. In the lab, students may observe facilitated diffusion by adding a substance, such as glucose, to a container of water and measuring its concentration on either side of a membrane that has carrier molecules specific for glucose.
A third type of cell transport mechanism is active transport, which involves the movement of particles against their concentration gradient and requires the input of energy. This type of transport is typically used to move ions and other small molecules that cannot cross the cell membrane by diffusion or facilitated diffusion. In the lab, students may observe active transport by measuring the movement of ions across a membrane in the presence and absence of energy sources such as ATP.
Finally, cells can also transport substances through bulk transport, which involves the movement of large molecules or particles through the cell membrane via endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis involves the uptake of substances into the cell, while exocytosis involves the release of substances from the cell. In the lab, students may observe bulk transport by adding a large particle, such as a bead, to a solution and observing its movement across the cell membrane.
In addition to exploring these different types of cell transport mechanisms, students in the cell transport and permeability lab may also examine the concept of permeability, which refers to the ability of a membrane to allow substances to pass through it. Factors that can affect membrane permeability include the size and charge of the substances being transported, as well as the presence of specific transport proteins. In the lab, students may test the permeability of a membrane to various substances under different conditions to see how these factors influence transport.
Overall, the cell transport and permeability lab is a valuable opportunity for students to learn about the mechanisms by which cells communicate with their environment and maintain homeostasis. By exploring diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and bulk transport, as well as the concept of permeability, students can gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes that occur within cells.