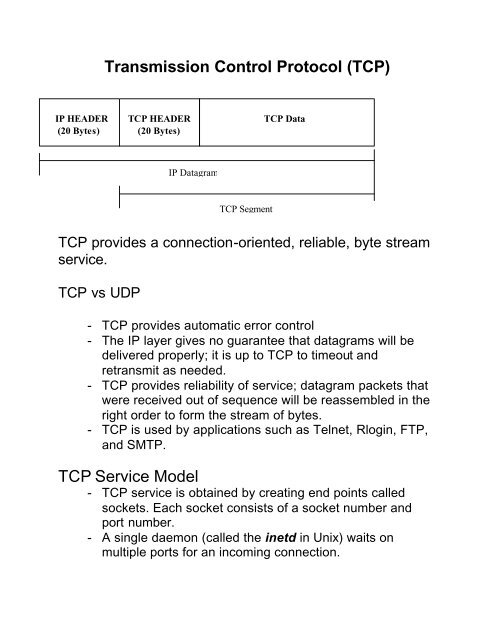
The TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) service model is a core aspect of the internet and its ability to transmit data between devices. It is a networking protocol that is used to establish and maintain connections between devices on a network, allowing them to exchange data in a reliable and efficient manner.
At the heart of the TCP service model is the concept of a "connection." When two devices want to communicate with each other over the internet, they must first establish a connection using the TCP protocol. This involves a series of exchanges between the devices, known as the "handshake." During the handshake, the devices agree on the details of the connection, such as the sequence numbers and window sizes that will be used to transmit data.
Once the connection is established, the devices can begin exchanging data. The TCP protocol ensures that the data is transmitted in an orderly and reliable manner, using sequence numbers and acknowledgement messages to ensure that all of the data is received correctly. If any data is lost or corrupted during transmission, the TCP protocol can detect the problem and request that the data be retransmitted.
One of the key benefits of the TCP service model is that it allows devices to communicate with each other even if they are located on different networks or operating systems. This is because the TCP protocol is implemented at the transport layer of the internet protocol suite, which is a set of standards that define how data is transmitted over the internet. This means that devices using different types of software and hardware can still communicate with each other, as long as they both support the TCP protocol.
The TCP service model is also designed to be scalable, meaning that it can handle a large number of connections simultaneously. This is made possible by the use of "ports," which are virtual channels that allow multiple connections to be established over the same physical network connection. This allows the TCP protocol to support a wide range of applications and services, from simple file transfers to complex multimedia streams.
Overall, the TCP service model is a critical component of the internet and its ability to transmit data reliably and efficiently between devices. It is a robust and scalable protocol that has enabled the growth and development of the internet as we know it today.
TCP
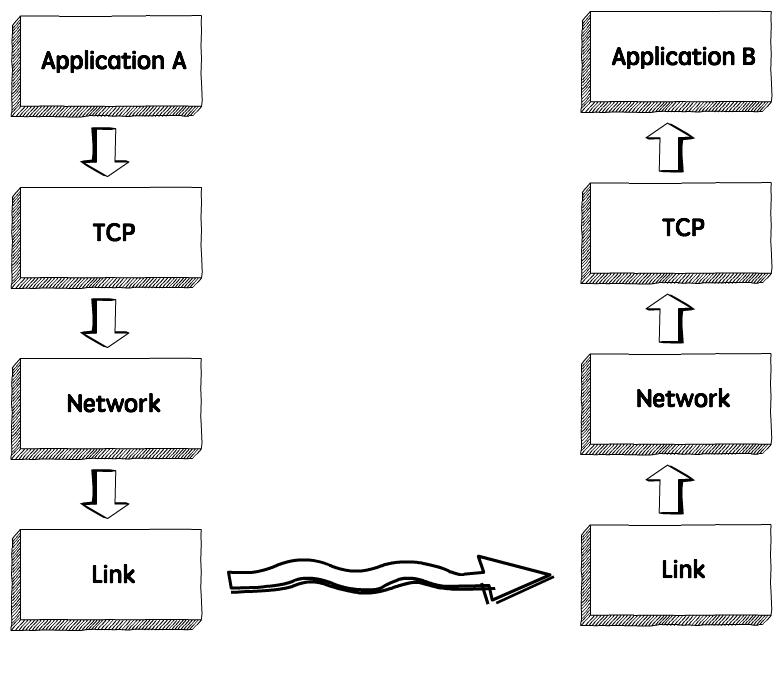
All zeros in the host field of an address specify the entire network. Flow control prevents the receiver from overloading Orderliness Data is delivered to the application in order Congestion control Control network congestion Byte stream: Provide a reliable byte stream between two applications Reliable transmission: TCP uses four mechanisms to ensure reliable transmission, in other words, to ensure that data has been transmitted correctly. The receiver sends an acknowledgement with a window size of 0, telling the sender to wait. It contains four layers, unlike seven layers in the OSI model. The application layer only generates the data in a format that is TCP-ready, while it is the transport layer that ensures all TCP rules are followed during the data transmission.
TCP service model
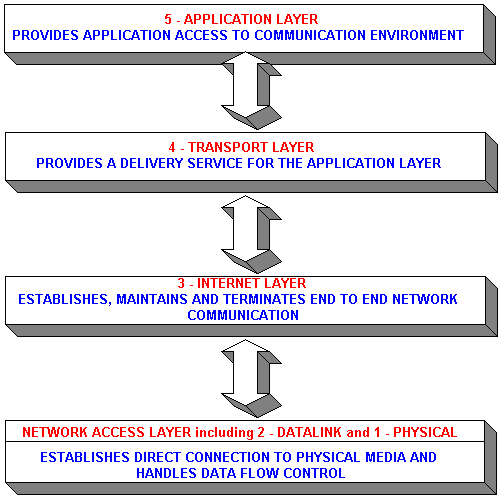
TCP software decides how big segments should be. It is created by the Advanced Research Project Agency Network ARPANET. Some of the protocols present in this layer are: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, TFTP, Telnet, SSH, SMTP, SNMP, NTP, DNS, DHCP, NFS, X Window, LPD. UDP does not include a congestion-control mechanism, so the sending side of UDP can pump data into the layer below the network layer at any rate it pleases. If, on the other hand, the timer goes off before the acknowledgement comes in, and the segment is retransmitted. It does not matter what route is taken, the packet is delivered irrespectively.
What is TCP/IP Model? Layers in TCP IP Model
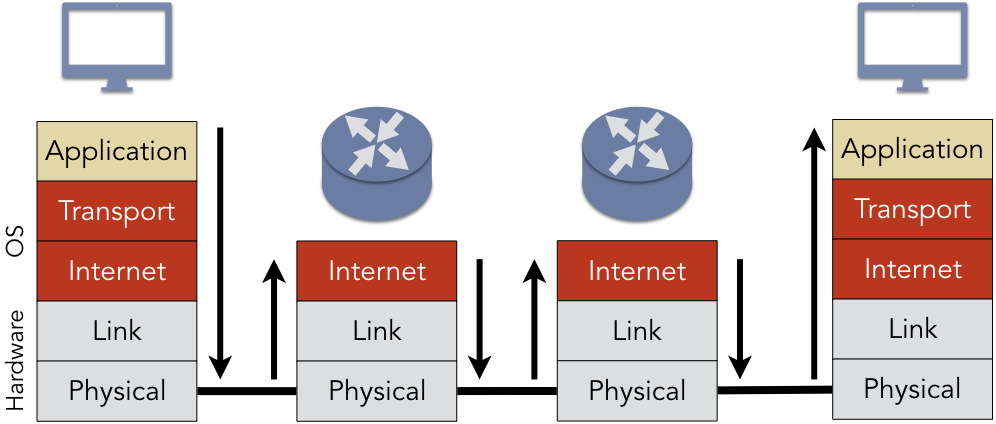
The application layer maintains a smooth connection between the application and user for data exchange and offers various features as remote handling of the system, e-mail services, etc. In general, if you get a segment with the RST bit on, you have problem on your hands. See More: Top 10 Best Practices for Network Monitoring in 2022 To make the most of transmission control protocols in 2022, organizations can follow these best practices: TCP Best Practices 1. The acknowledgement number is of 32 bits size. A third timer that some implementations use is the keep alive timer.
TCP/IP Model vs. OSI Model
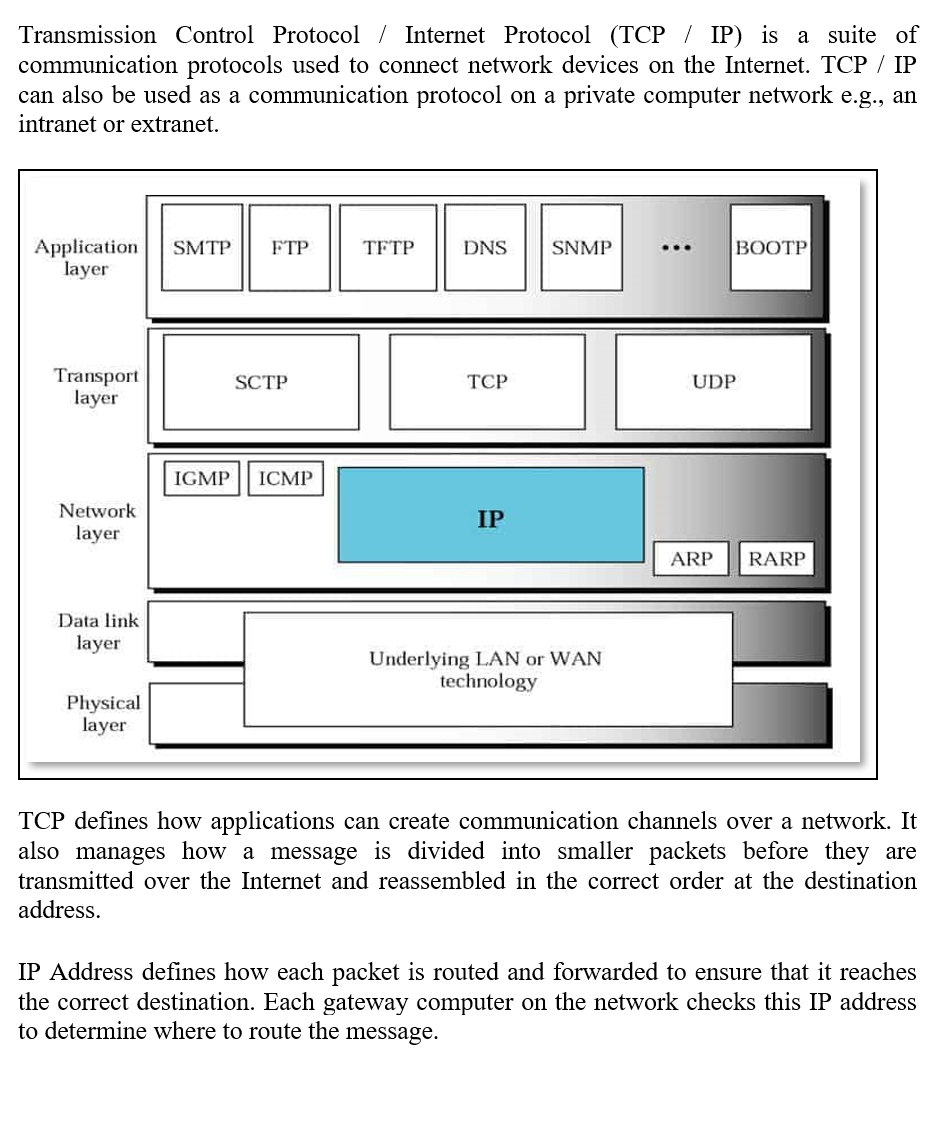
For example, assume that a network has been assigned a Class A address and all the nodes on the network use a Class A address. The protocol was initially termed the department of defense DOD networking model because TCP and other internet protocols were mainly used for military use cases and research. The PSH bit indicates pushed data. When a receiver receives out of order packets, it sends duplicate acknowledgements to the sender so that the sender can retransmit the packet, which is presumed to be lost. The subnet mask that specifies 16 bits of subnetting for Class A address 34. It makes us aware of the error but does not tell us about the error. Wetherall, Computer Networks, 5th ed.
TCP/IP Model: An Overview of How the Internet Works
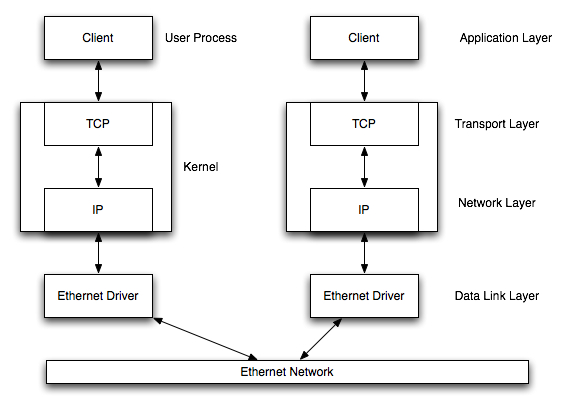
In the two decades since their invention, the heterogeneity of networks has expanded further with the deployment of Ethernet, Token Ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface FDDI , X. Generally the MTU is 1,500 bytes the Ethernet payload size , so 1,500 bytes is often the upper bound on the segment size. The server listens for incoming connections by executing the LISTEN and ACCEPT primitives To establish a connection, the client executes a CONNECT primitive with the IP address and port number of the server, and the maximum segment size it will accept. Without standardization, communication would go haywire, and fast internet service relies on efficiency. UDP provides an unreliable data transfer service—that is, when a process sends a message into a UDP socket, UDP provides no guarantee that the message will ever reach the receiving process.