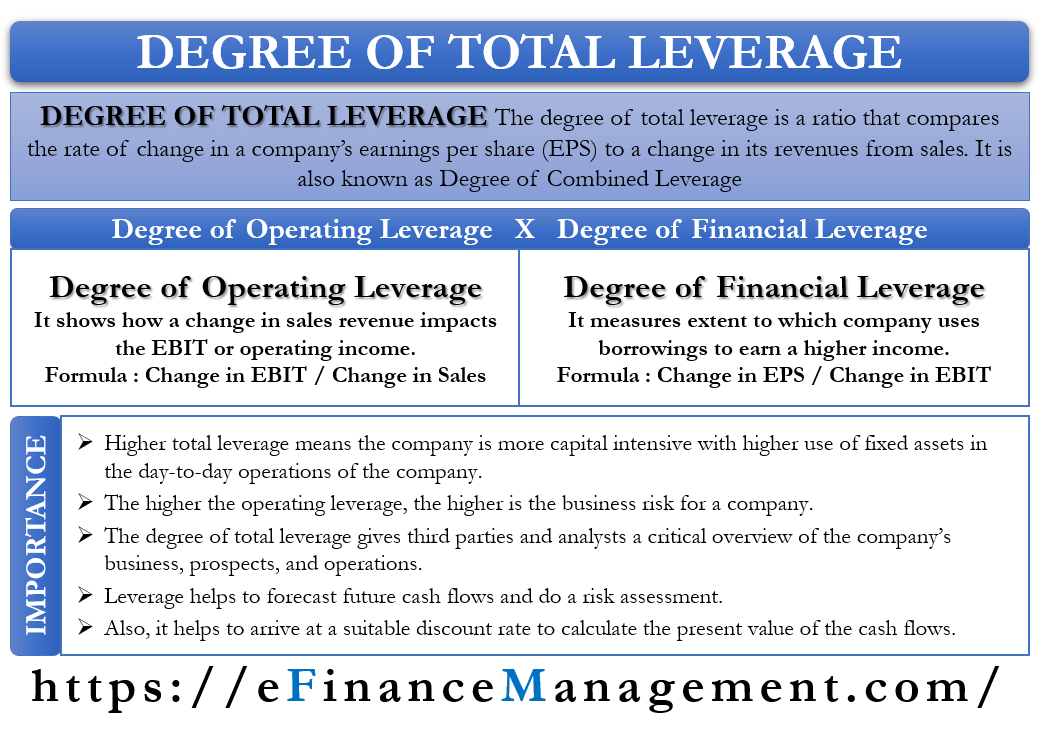
The degree of combined leverage, also known as the financial leverage ratio, is a measure of the level of financial leverage in a company, which refers to the use of borrowed funds to finance the company's operations and investments. The degree of combined leverage is calculated by dividing the total contribution margin by the contribution margin per unit of the degree of leverage. The higher the degree of combined leverage, the greater the financial risk for the company, as it indicates that the company is relying heavily on borrowed funds to finance its operations and investments.
There are several factors that can affect the degree of combined leverage for a company. These include the amount of debt the company has taken on, the interest rate on that debt, and the level of fixed costs relative to the level of variable costs. For example, if a company has a high level of fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, and a low level of variable costs, such as the cost of raw materials, the degree of combined leverage will be higher. This is because the company will have a higher contribution margin per unit of the degree of leverage, which means that it will be more financially leveraged.
There are both benefits and risks associated with the degree of combined leverage. On the positive side, financial leverage can help a company increase its return on equity, as the use of borrowed funds can amplify the returns on the company's investments. This can be especially useful for companies that have a high level of uncertainty or risk, as the use of financial leverage can help to reduce the overall risk of the company's operations.
However, there are also significant risks associated with financial leverage. If a company takes on too much debt and becomes over-leveraged, it can be exposed to significant financial risk if it is unable to meet its debt obligations. This can lead to bankruptcy or other financial problems, which can have serious consequences for the company and its shareholders.
In conclusion, the degree of combined leverage is an important measure of the financial leverage of a company and can have significant implications for the company's financial risk and return on equity. It is important for companies to carefully consider their level of financial leverage and to ensure that it is appropriate for their level of risk and return expectations.