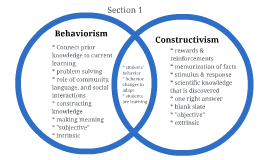
Behaviorism and constructivism are two influential approaches to understanding and explaining human learning and behavior. While they have some similarities, they also have some important differences.
Behaviorism is a psychological perspective that focuses on observable behaviors and the ways in which they can be changed through reinforcement and punishment. According to behaviorists, all behavior is learned through the process of classical or operant conditioning. In classical conditioning, an unconditioned stimulus (such as food) is paired with a conditioned stimulus (such as a bell), and over time, the conditioned stimulus becomes associated with the unconditioned stimulus and elicits the same response. In operant conditioning, behavior is modified through reinforcement or punishment. Positive reinforcement is the addition of a reinforcing stimulus (such as a reward) following a behavior, while negative reinforcement is the removal of an unpleasant stimulus (such as an uncomfortable noise) following a behavior. Punishment, on the other hand, is the presentation of an unpleasant stimulus or the removal of a reinforcing stimulus following a behavior.
Constructivism is a learning theory that emphasizes the role of the learner in constructing their own knowledge and understanding. According to constructivists, learning is an active process in which the learner actively constructs meaning from their experiences and interactions with the world. Constructivism emphasizes the importance of prior knowledge and experiences in shaping how new information is understood and integrated. It also emphasizes the importance of social interaction and collaboration in learning, as learners can construct new knowledge through dialogue and negotiation with others.
One key difference between behaviorism and constructivism is their views on the nature of learning. Behaviorism sees learning as a passive process in which the learner simply responds to stimuli, while constructivism sees learning as an active process in which the learner actively constructs meaning from their experiences. Another difference is their emphasis on the role of the learner in the learning process. Behaviorism emphasizes the role of reinforcement and punishment in shaping behavior, while constructivism emphasizes the role of the learner in constructing their own understanding and meaning.
Despite these differences, both behaviorism and constructivism have had a significant impact on our understanding of human learning and behavior. Behaviorism has had a particularly strong influence on the development of educational practices and has contributed to the understanding of how reinforcement and punishment can be used to shape behavior. Constructivism, on the other hand, has had a major influence on the way we approach teaching and learning, particularly in the fields of education and psychology. It has also contributed to the understanding of how prior knowledge and experiences can shape the way we understand and learn new information.
In conclusion, behaviorism and constructivism are two influential approaches to understanding and explaining human learning and behavior. While they have some differences, they both have made significant contributions to our understanding of how people learn and the factors that influence their behavior.
Learning Theories: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism, and Connectivism — Travis Lee

Unfortunately, this is not the case. They assert that individuals cause behavior and that choice is not an illusion. Educational Researcher, 16 9 , 13-20. Clearly the focus of constructivism is on creating cognitive tools which reflect the wisdom of the culture in which they are used as well as the insights and experiences of individuals. The theory of constructivist learning is vital to understanding how students learn. Contrary to other two theories where prior knowledge was crucial, behaviorism does not depend on the same. Unionists and other educational apologists can cling to Piaget and, with the possible exception of falsely blaming societal ills such as poverty and family breakdown, maintain that everyone is blameless in this genetically determined process of the learner having to construct his own learning at a developmentally appropriate rate.
Constructivism And Behaviorism In Designing Online Learning Programs

The behaviorist school of psychology maintains that all behaviors can be described scientifically without recourse either to internal physiological events or to Constructivism in psychology theorizes about and investigates how human beings create systems for meaningfully understanding their worlds and experiences. Constructivism focuses on the idea that students create knowledge through learning experiences such as inquiry-based or problem-based learning. Assessing constructions and constructing assessments: A dialogue. The major point of reasoning in the behaviorist approach of psychology is the importance of behavior reinforcement. Long- term memory is a limitless cognitive system which can store information permanently Rosser-Majors, 2017. Subsequently, what has been learned, what will be understood and what has been given meaning can be generalized if Furthermore, when learning, there are no single laws, but aspects such as The role of context in constructivism For this current, the the interactive triangle is considered , which refers to the interaction between the characteristics of the learner, the material to be learned and the person or thing that transmits the information. For example, the idea that pink is for girls and blue is for boys is an example of a social construct related to gender and the color of items.
Learning Theories: Constructivism, humanism, behaviorism

This places Dewey in the educational philosophy of pragmatism. Therefore, it is important to provide classroom situations in order for individuals to develop individual learning. What Types of Learning Are Best Explained by This Position? Educational Technology, 31 9 , 28-33. Teachers may use it as such, however. Therefore, it is hard for teachers to play a passive role as suggested by constructivists Pavlović, 2015. Scenario: A high school social study teacher is planning a class on the Vietnam War. Hence, the theory maintains that knowledge varies from one person to another based on his or her experience no one can have the power to define what constitute knowledge.
Constructivism & Behaviorism: Teaching Students with Learning Disabilities
Educational Technology, 31 9 , 38-40. The new knowledge is acquired and developed through a different stage. Moreover, human beings have an inherent quest of wanting to know something new that they think will be of help to them. Therefore, learners are supposed to use the information gained in the learning process to solve new problems in life. According to Piaget children go through four stages of Cognitive development, the sensory stage, the preoperational stage, The concrete operational stage and the formal operational stage. In order to ensure that the knowledge learnt sticks, learners use the same problems that were used by the teacher in their exercises.