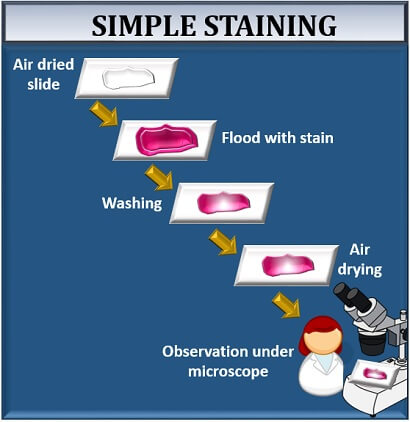
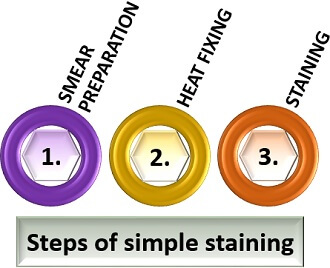
Simple staining is a technique used in microbiology to visualize and differentiate between different types of bacteria. This is accomplished by applying a single stain to the bacterial cells, which can then be observed under a microscope to determine the size, shape, and arrangement of the cells.
There are several different types of stains that can be used for simple staining, including crystal violet, methylene blue, and safranin. These stains are typically applied to a microscope slide containing a sample of the bacterial culture, and then washed off using a decolorizing agent such as ethanol or acetone. The cells that retain the stain appear as a different color under the microscope, allowing researchers to identify and differentiate between different types of bacteria.
One of the main advantages of simple staining is that it is relatively quick and easy to perform, making it a useful tool for identifying and classifying bacterial cultures. It is also relatively inexpensive and can be performed using standard laboratory equipment, such as a microscope and microscope slides.
However, simple staining has some limitations. It is not very specific and cannot distinguish between different types of bacteria with similar morphologies, such as different species within the same genus. In addition, it does not provide any information about the biochemical or metabolic properties of the bacteria. For more detailed analysis, more complex techniques such as gram staining or biochemical testing may be required.
Overall, simple staining is a useful tool for visualizing and differentiating between different types of bacteria, and is an important technique in the field of microbiology. It is frequently used as a first step in the identification and classification of bacterial cultures, and can provide valuable information about the size, shape, and arrangement of bacterial cells.
9: Simple Stain

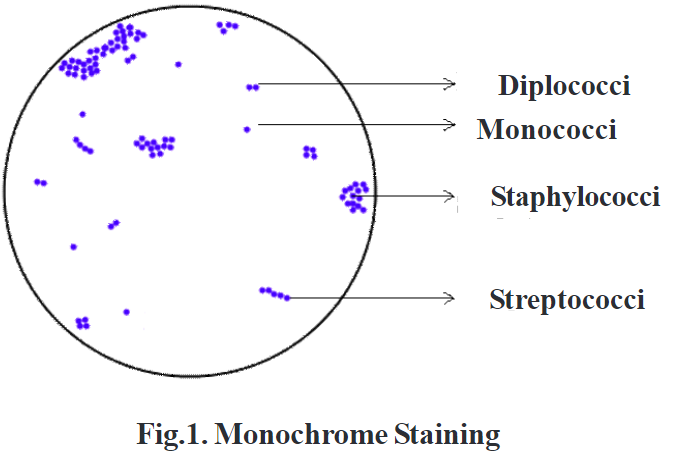
Positively charged cationic dyes such as methylene blue, crystal violet, safranin, etc bind with negatively charged cellular constituents such as nucleic acids and acidic polysaccharides and the cell surface of bacteria. Uses Diagnostic microbiology laboratory generally does not perform simple staining methods. The difference is more obvious with an electron microscope see images below or using other types of light microscopes. Simple Stains Simple stains can be defined as the basic dyes, which are the alcoholic or aqueous solutions diluted up to 1-2%. What is Simple Staining? They are used to stain nucleic acids and cytoplasm. The term simple staining sometimes interchangeable with the terms like direct, positive or monochrome staining.
What Is Simple Staining Of Bacteria Its Principle, And Procedure?
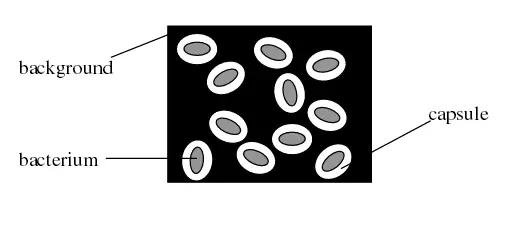
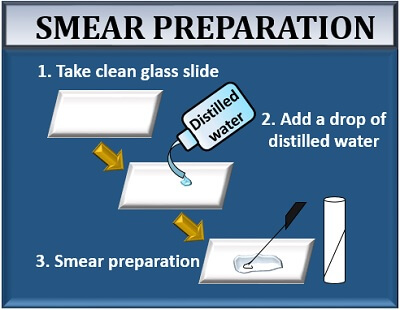
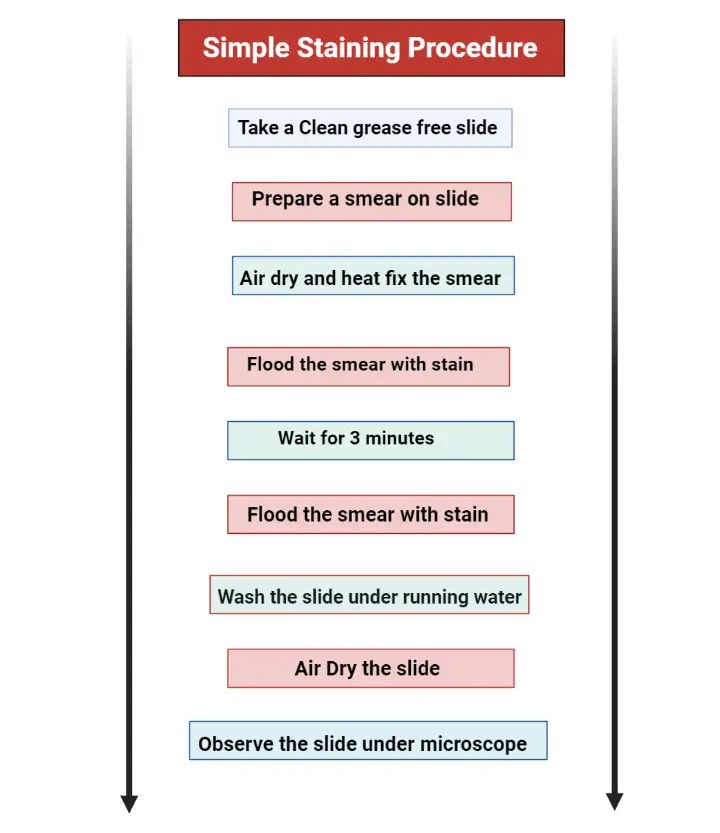
The gram-positive bacteria retain the primary stain even after washing the slide with alcohol. Use a second slide to place a large drop of water on top, and then use your inoculating loop to obtain the amount of water needed for the smear. True to its name, the simple stain is a very simple staining procedure involving only one stain. After bacteria have been applied to a microscope slide, the smear is dried thoroughly before fixation. Some stains commonly used for simple staining include crystal violet, safranin, and methylene blue. Any basic dye, such as methylene blue, safranin, or crystal violet, can be used to color the bacterial cells.
16: Simple Stain

Done correctly, this will attach cells to the microscope slide and kill the cells. As the simple stains are positively charged, they usually termed as positive or cationic dyes. The results of simple staining are based on the type of basic stain that has been used. Why is it important that your smear be thin? Viewing is best where there is a single layer of cells on the slide. Simple Staining Most types of cells do not have much natural pigment and are therefore difficult to see under the light microscope unless they are stained. This basically involves three steps----transferring a liquid suspension of the bacterium on the slide, drying the smear, and then heating slightly to firmly attach the smear to the slide. The most commonly used basic stains are methylene blue, crystal violet, and carbol fuchsin.
What is Simple Staining? Definition, Principle, Procedure & Video
Do not overheat the slide as it will distort the bacterial cells. The basic dye gets attracted to the negatively charged genetic material of the microbial cytoplasm. Staining of Bacteria It is the last and the most crucial step, in which one can identify the morphological characteristics of the bacteria through microscopic examination, once the cells get stained. Reflect on your results. They stains the microbial cell, not the background. Avoid contact, inhalation, or ingestion of dye.