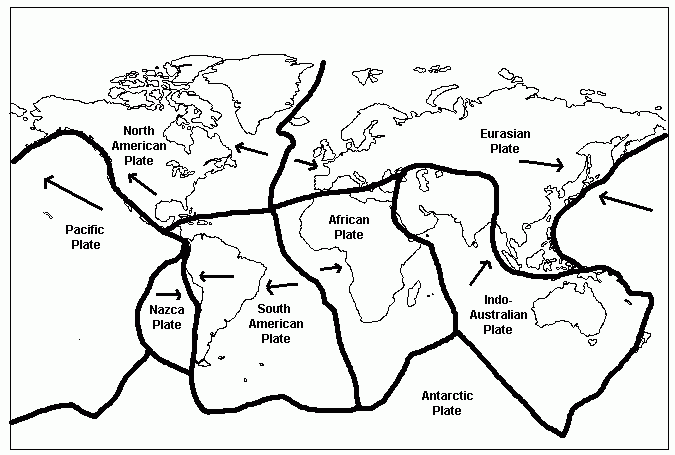
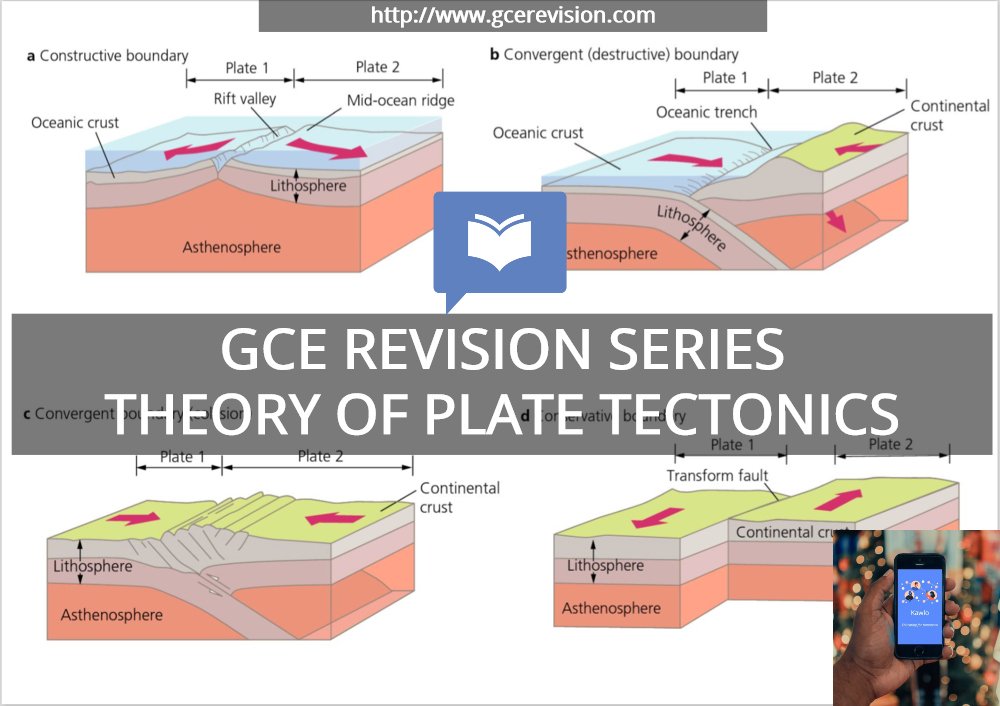
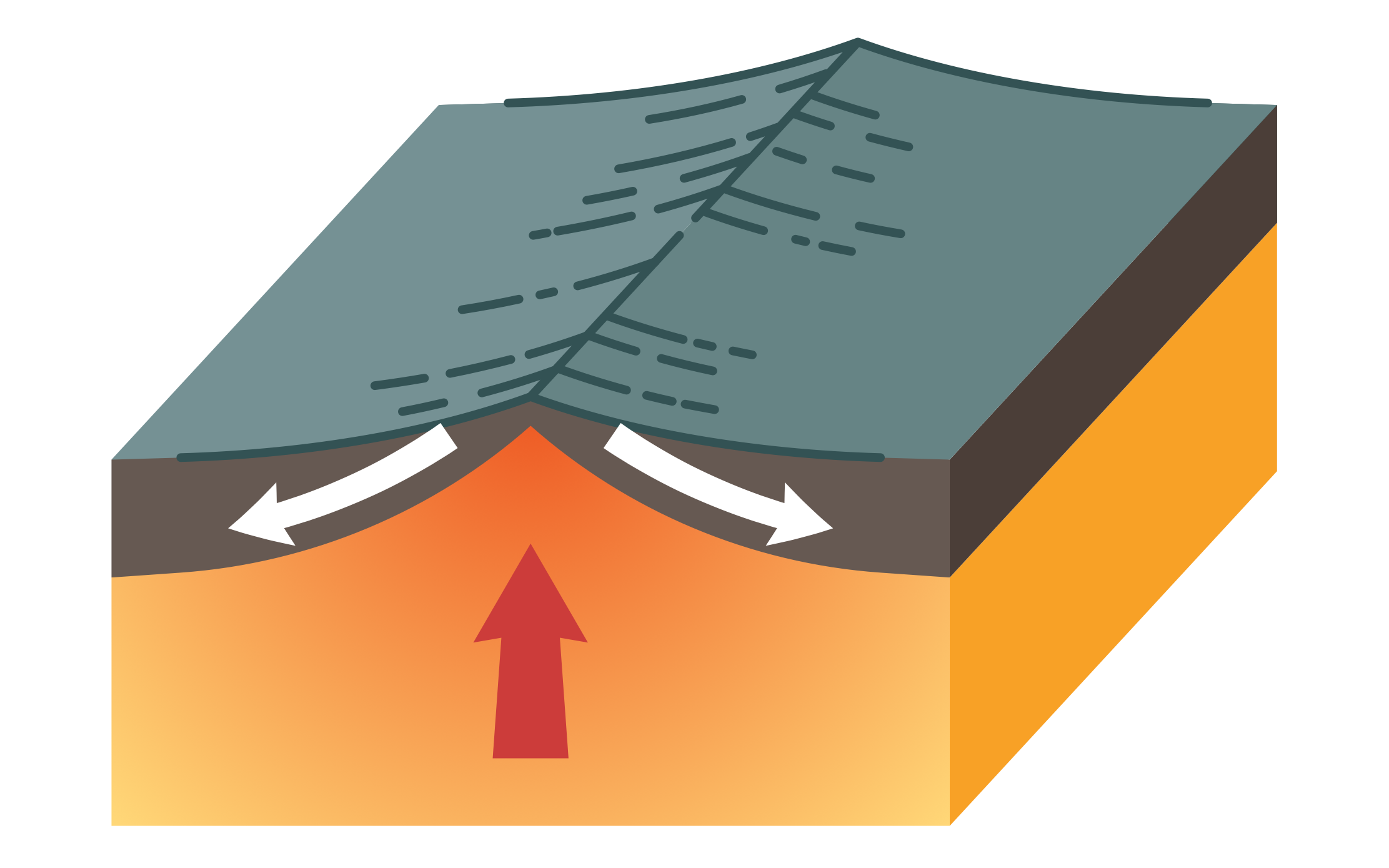
A constructive margin is a geological feature that is formed when two tectonic plates are moving away from each other. This type of margin is characterized by the formation of new crust along the boundary between the two plates, as magma from the mantle rises up to fill the gap created by the separating plates.
Constructive margins are also known as divergent plate boundaries or spreading centers. They can be found in a variety of locations around the world, including along mid-ocean ridges, where the ocean floor is spreading apart and new crust is being formed.
One of the most well-known examples of a constructive margin is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which runs down the center of the Atlantic Ocean. This ridge marks the boundary between the North American and African tectonic plates, and as the plates move apart, magma from the mantle rises up to fill the gap and create new ocean crust.
Constructive margins are an important part of the Earth's tectonic system, as they help to regulate the movement and positioning of the planet's crust. They also play a significant role in the creation and evolution of the planet's landscape, as the movement of the tectonic plates can lead to the formation of mountains, valleys, and other geological features.
In addition to their geological significance, constructive margins can also have practical implications for human activities. For example, the volcanic activity associated with these margins can create geothermal energy sources, and the minerals and other resources found in the newly formed crust can be extracted for economic gain.
Overall, a constructive margin is a dynamic and important feature of the Earth's geology, with both scientific and practical significance. It is the result of the movement of tectonic plates, and plays a key role in shaping the planet's landscape and supporting various human activities.