Cells are the basic unit of life, and they are composed of a variety of different organelles, each with its own specific function. In this essay, we will explore the different cell organelles and their functions in detail.
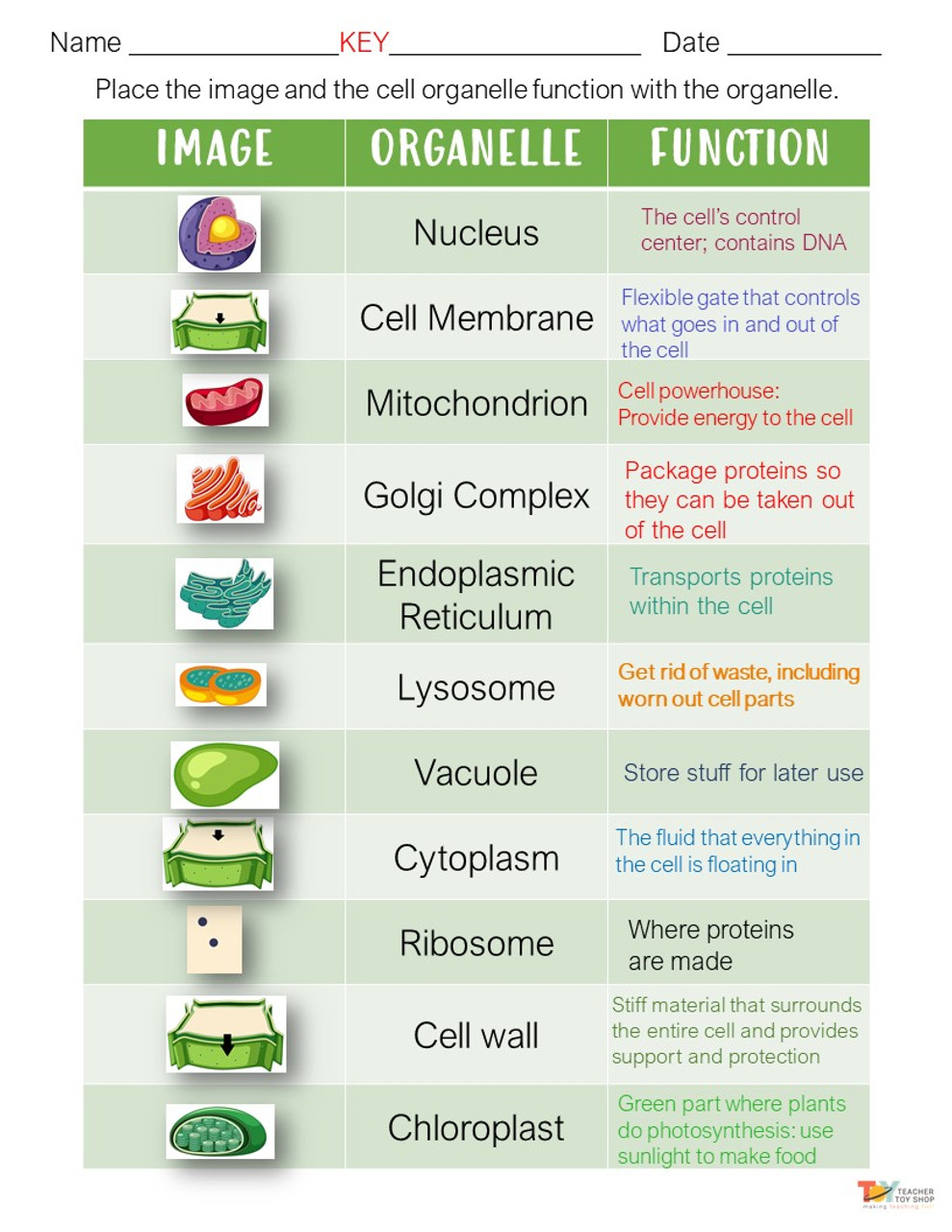
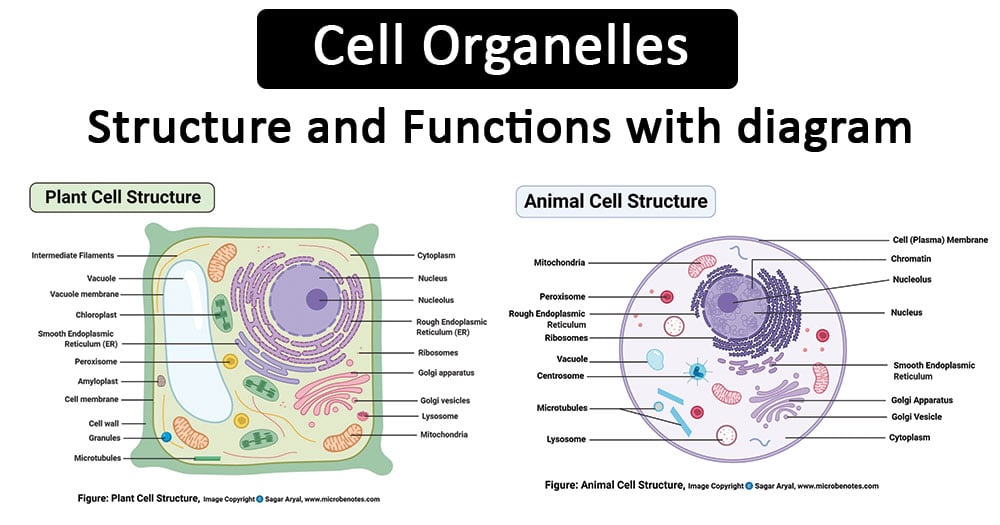
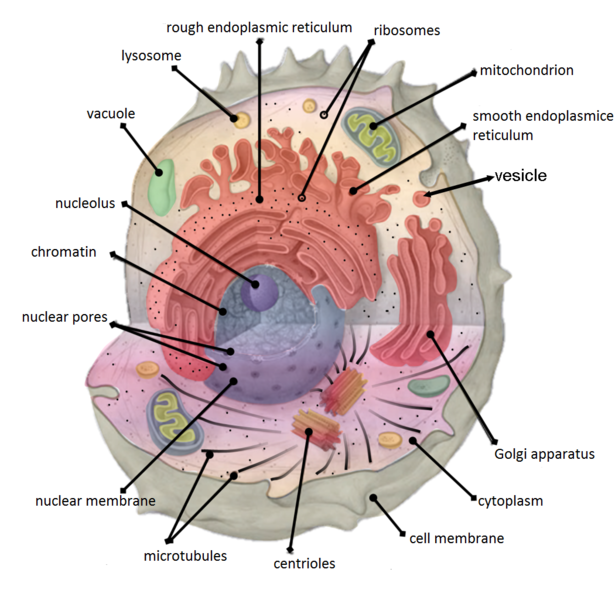
The first organelle we will discuss is the cell membrane, which surrounds and encloses the cell. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer and serves as a barrier, separating the inside of the cell from the external environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it allows certain substances to pass through while preventing others from entering the cell. It also plays a role in cell communication and signaling.
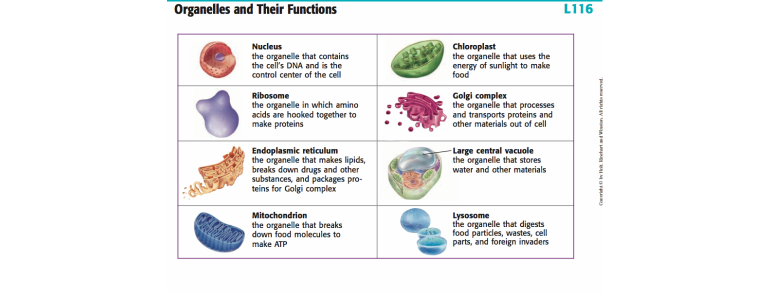
Next, we have the nucleus, which is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell's DNA, which carries the genetic information that determines the cell's characteristics and functions. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell by the nuclear envelope, which is made up of two layers of phospholipid bilayers. The nucleus also contains small, spherical structures called nucleoli, which are involved in the synthesis of ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is another important organelle in cells. There are two types of ER: the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The SER is involved in the synthesis of lipids, while the RER is involved in the synthesis and modification of proteins. The RER is called "rough" because it has ribosomes attached to its surface, which are involved in protein synthesis. The ER is also connected to the Golgi apparatus, which is responsible for sorting, modifying, and transporting proteins and lipids.
Another organelle that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis is the ribosome. Ribosomes are made up of RNA and protein and are responsible for translating the genetic code stored in DNA into proteins. They can be found either attached to the RER or floating freely in the cytosol (the fluid inside the cell).
The mitochondria are the "powerhouses" of the cell, responsible for generating the cell's energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). They are made up of two membranes and contain their own DNA and ribosomes. The inner membrane of the mitochondria is folded into cristae, which increase the surface area and allow for more efficient energy production.
Another organelle found in cells is the lysosome, which contains enzymes that break down waste products and cellular debris. They are formed from the Golgi apparatus and contain enzymes that can break down carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Finally, we have the vacuole, which is a large, fluid-filled organelle found in plant cells. Vacuoles play a variety of roles, including storing water and other substances, maintaining the cell's shape, and helping to rid the cell of waste products.
In conclusion, cells are made up of a variety of different organelles, each with its own specific function. The cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the external environment, the nucleus contains the cell's DNA and controls the cell's functions, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are involved in protein synthesis and transport, the ribosomes are responsible for translating DNA into proteins, the mitochondria produce the cell's energy, the lysosomes break down waste products and cellular debris, and the vacuoles found in plant cells play a variety of roles. Together, these organelles work together to allow cells to carry out their various functions and maintain homeost