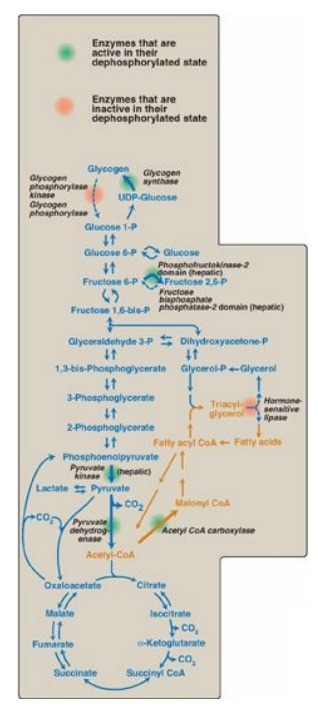
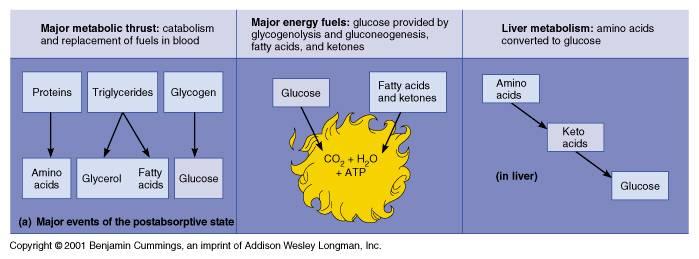
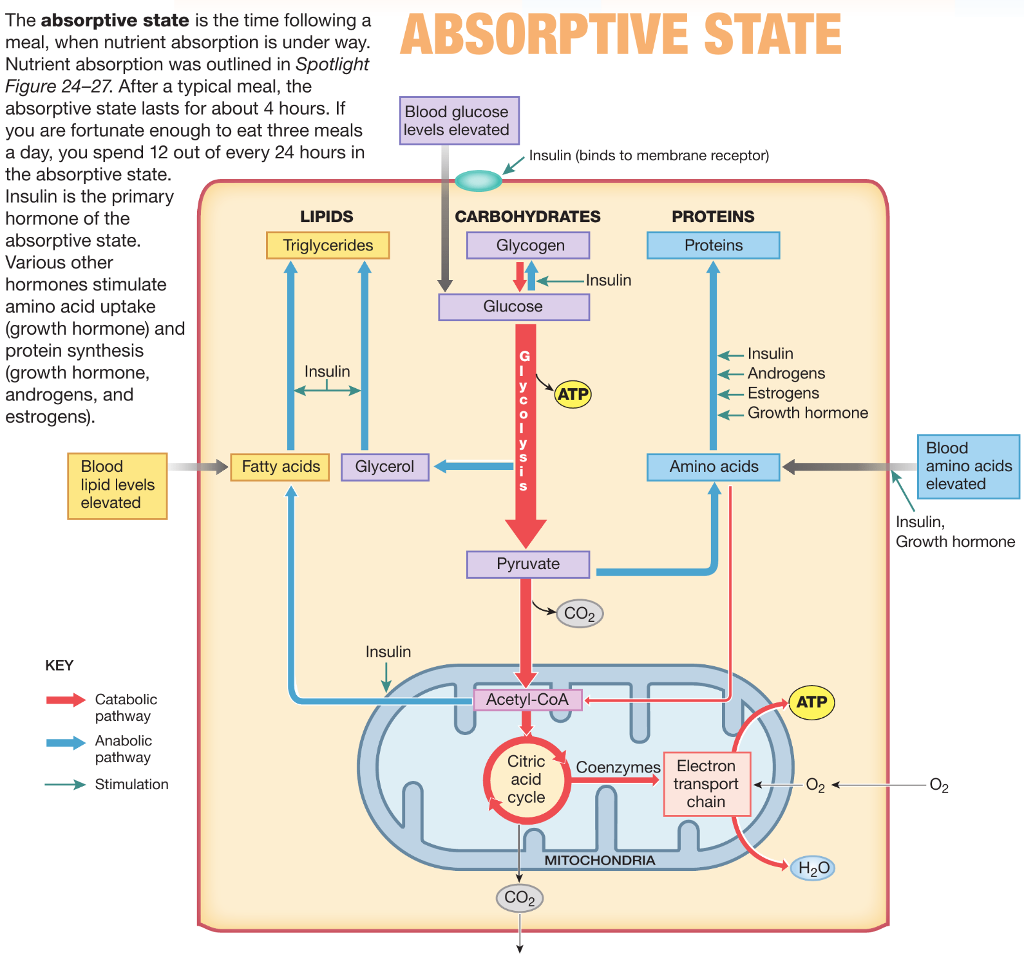
The absorptive state, also known as the absorptive capacity, is a concept in business and economics that refers to an organization's ability to effectively acquire, assimilate, and utilize new knowledge and information. This includes the ability to learn from experience, adapt to new technologies and markets, and integrate new ideas and practices into the organization's operations.
The absorptive state is important because it plays a crucial role in an organization's ability to innovate and remain competitive in a rapidly changing business environment. Organizations with a high absorptive state are better able to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, and are more likely to succeed in the long run.
There are several factors that can impact an organization's absorptive state. One important factor is the organization's culture and leadership. Organizations with a culture that values learning and encourages experimentation and innovation are more likely to have a high absorptive state. Similarly, leaders who foster a culture of continuous learning and encourage employees to challenge the status quo are more likely to create an environment that is conducive to the development of an organization's absorptive state.
Another factor that can impact an organization's absorptive state is the availability of resources. Organizations that have access to a diverse range of resources, including financial resources, human resources, and technological resources, are more likely to have a high absorptive state. This is because these resources provide the necessary support and infrastructure for the organization to effectively acquire, assimilate, and utilize new knowledge and information.
In addition to culture and resources, the absorptive state can also be impacted by external factors, such as the organization's industry and the level of competition within that industry. Organizations operating in highly competitive industries may have a higher absorptive state due to the pressure to continuously innovate and adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
In conclusion, the absorptive state is a crucial concept in business and economics that refers to an organization's ability to effectively acquire, assimilate, and utilize new knowledge and information. It plays a vital role in an organization's ability to innovate and remain competitive, and is influenced by factors such as culture, resources, and industry conditions. By understanding and actively working to improve their absorptive state, organizations can better navigate a rapidly changing business environment and position themselves for long-term success.