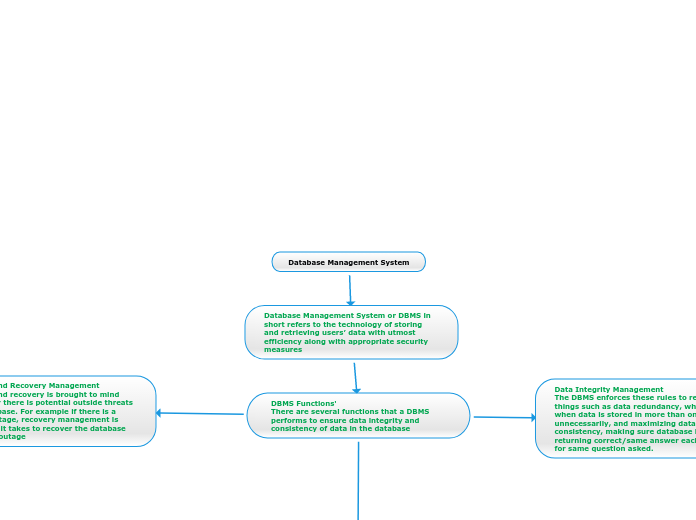
A database management system (DBMS) is a software system that allows users to create, store, and manage a database, which is a collection of data organized in a specific way. DBMSs are used in various industries and applications, including business, government, education, healthcare, and finance.
While DBMSs provide numerous benefits and make it easier for organizations to store, retrieve, and analyze data, they also pose various threats and vulnerabilities. Some of the main threats in DBMSs are discussed below.
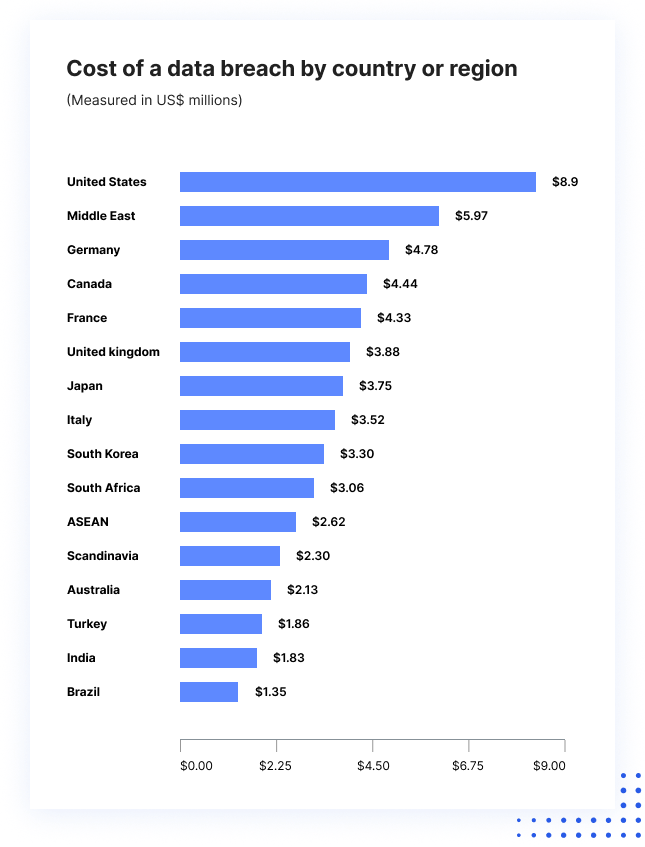
Data breaches: A data breach occurs when unauthorized parties gain access to sensitive data stored in a database. Data breaches can lead to the theft of sensitive information, such as financial data, personal identification data, and confidential business information. Data breaches can be caused by hackers, malware, and other cyber attacks, as well as insider threats, such as employees who access or misuse data without authorization.
SQL injection attacks: SQL injection attacks involve injecting malicious code into a database through a website or application. The injected code can be used to manipulate data, steal sensitive information, or disrupt the operation of the database. SQL injection attacks can be difficult to detect and prevent, and they can have serious consequences for organizations.
Denial of service attacks: A denial of service (DoS) attack is a type of cyber attack that involves flooding a server or network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. DBMSs can be vulnerable to DoS attacks, which can disrupt the operation of the database and prevent users from accessing it.
Insider threats: Insider threats refer to individuals within an organization who have access to the database and may misuse or steal data. Insider threats can include employees, contractors, and third-party vendors. They can be difficult to detect and prevent, as they have legitimate access to the database.
Physical threats: Physical threats to a database include natural disasters, such as fires, earthquakes, and floods, as well as human actions, such as theft, vandalism, and sabotage. These threats can damage or destroy the hardware or infrastructure that hosts the database, leading to data loss or corruption.
To mitigate these threats, organizations should implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption, and regularly update and patch their DBMS software. They should also establish strict access controls and monitor database activity to detect and prevent unauthorized access or activity.
In conclusion, while DBMSs provide many benefits, they also pose various threats, including data breaches, SQL injection attacks, DoS attacks, insider threats, and physical threats. To protect against these threats, organizations should implement robust security measures and establish strict access controls to ensure the integrity and security of their data.
Types of Database security in DBMS

It works on making database secure from any kind of unauthorized or illegal access or threat at any level. ERP security is a broad set of measures designed to protect an ERP system from unauthorized access and ensure the accessibility and integrity of system data. It can also run import utility. Database auditing checks the log files regularly to see who accessed the database, when they accessed it, how long they stayed there, and what they did in the database. Retrieved July 16, 2015, from Weiss, A.
Database Security: Threats and Security issues

These attacks do not harm the system but are only the attempts to learn and make use of information from devices. SQLADM: Allows to monitor and tune SQL statements. Hence, security of confidential data is of essential importance. If the primary and secondary servers are configured in the same area and the primary server fails, the secondary server may fail as well. However, these measures are not enough, and organizations should consider multi-factor authentication MFA solutions that require users to identify themselves with a token or device they own, or via biometric means. Dedicated Test Environment In addition to VCS and sound backups, a dedicated test environment helps ensure successful database deployments.
4 Major Threats to Database Security

Lastly, if homegrown software is suspected of causing database security vulnerabilities, then regular audits and even friendly hacking attempts should be considered. Security measures must be applied to various levels in order to protect the database. This technique is auditing. DBMS Challenges of database security Seeing the vast increase in volume and speed of threats to databases and many information assets, research efforts need to be consider to the following issues such as data quality, intellectual property rights, and database survivability. Depending on the degree of corruption, the database may need to be deleted, recreated, and repopulated with data. Database security depends on it.
DDBMS

There is also the case of abuse of legitimate permissions: users who use their database privileges to make unauthorized use of it—for example, divulging confidential information. Information inference occurs when some data x is read by user which can be further used to get data y. CRM data is also personally identifiable information PII and is subject to data privacy regulations. Since data being one of the most valuable assets to any individual or a firm, security is an essential part of the Database management system which can ever be neglected in any scenario. However, when data moves to the cloud, it is more difficult to control and prevent data loss. Database security and integrity threats are often devastating, and there are many types of database security threats that can affect any type of operation. The database contains vital information of the system.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
An Intrusion Detection System IDS is a system that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is discovered. A database security strategy involves tools, processes, and methodologies to securely configure and maintain security inside a database environment and protect databases from intrusion, misuse, and damage. It performs an observation of passing traffic on the entire subnet and matches the traffic that is passed on the subnets to the collection of known attacks. By controlling the access rights, it may also helps in reducing the risks that might impact the security of the databases. Unfortunately, bypassing the application's utilities can destroy a database. The tool works with any SQL Server version after 2005. There are many techniques by which we can secure the databases and there are many more techniques which need more research in order to develop better techniques.