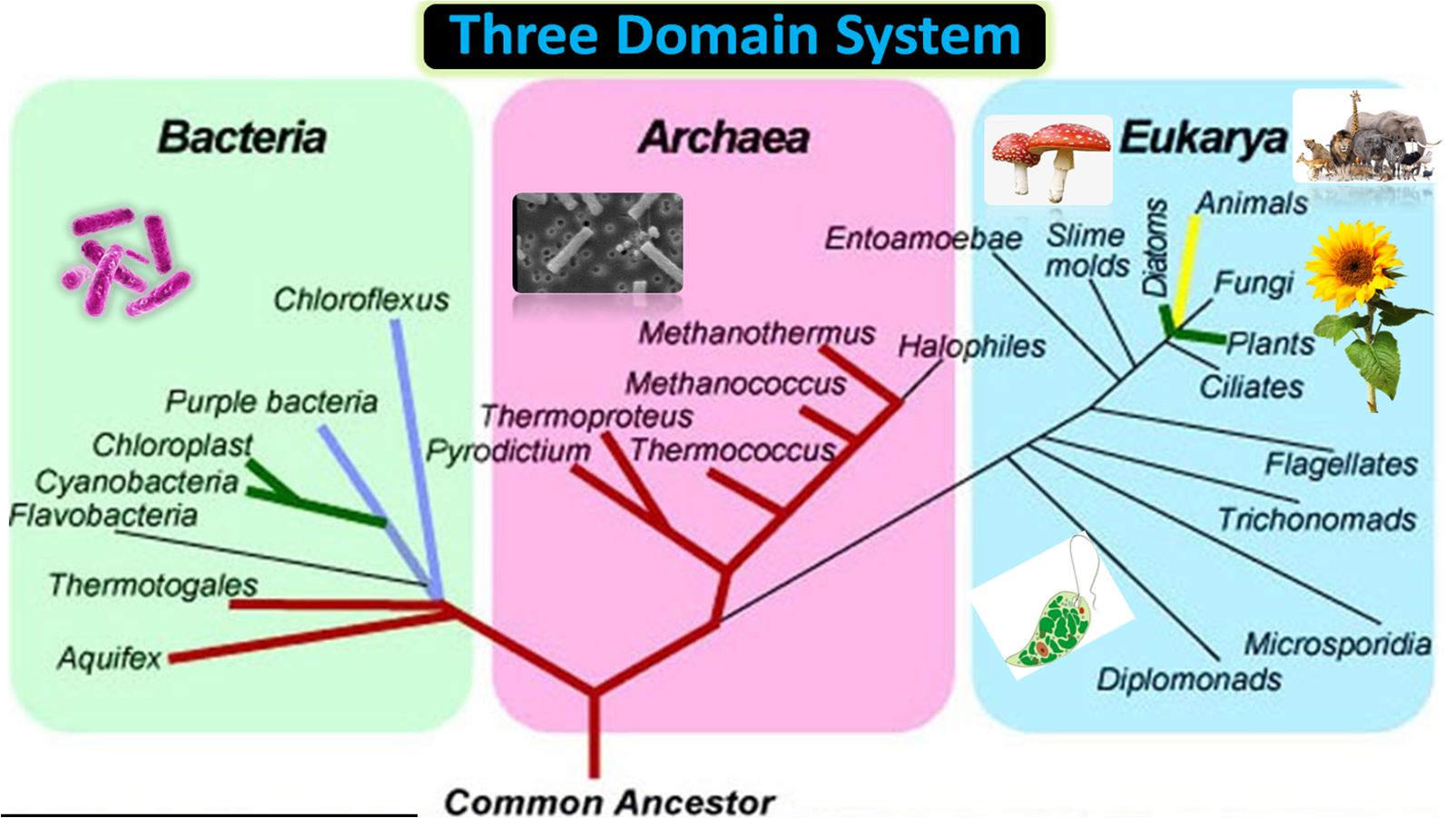
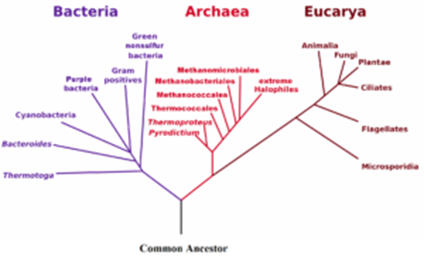
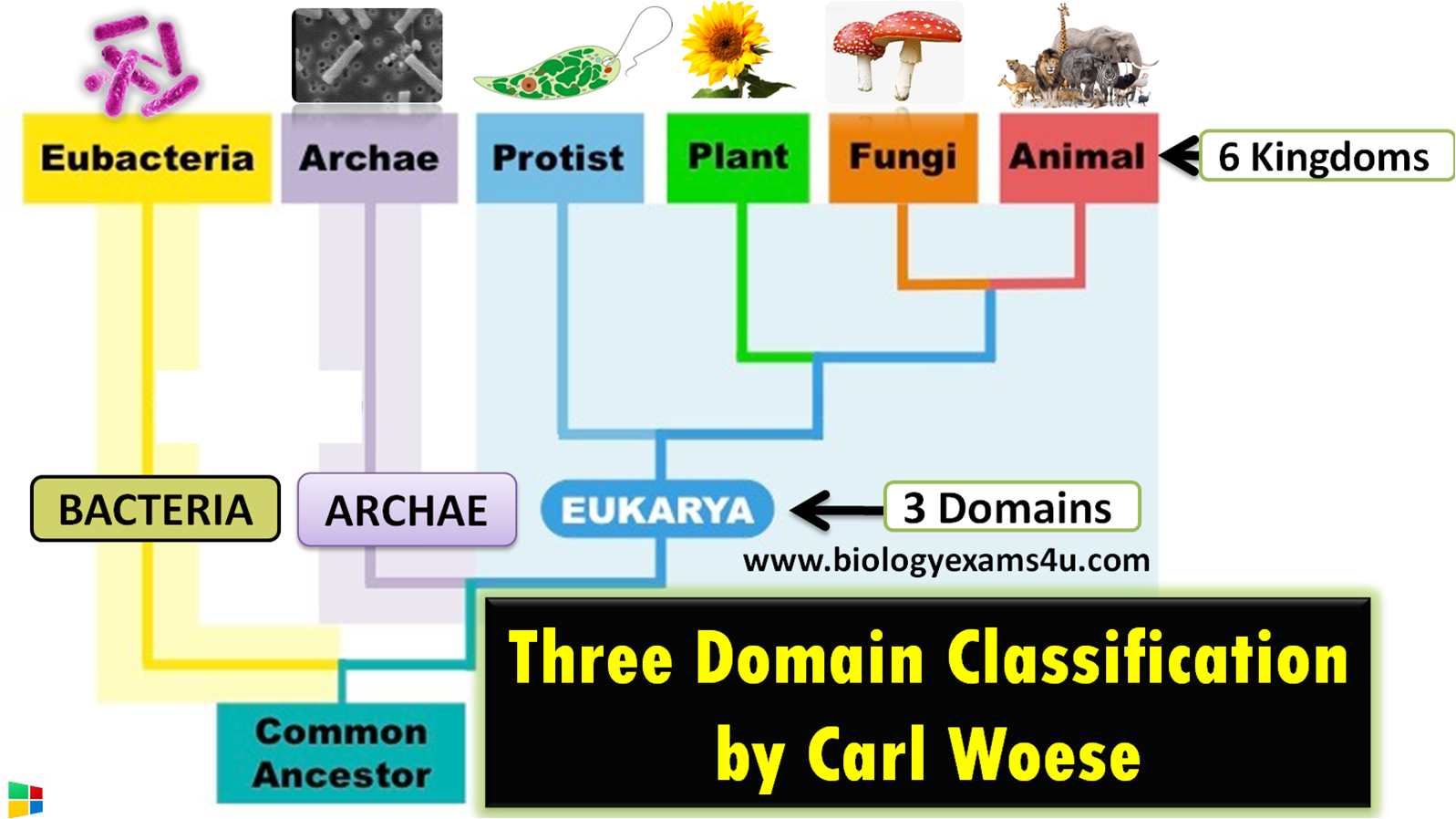
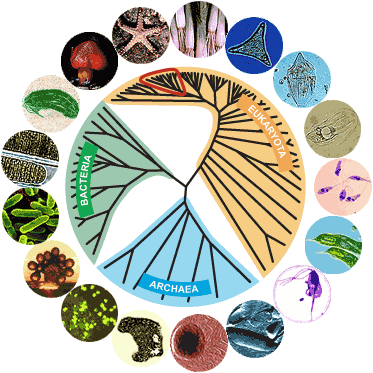
Living organisms are classified into three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. These domains are based on differences in their cellular and molecular characteristics, and they represent the major branches of the tree of life.
The Archaea domain consists of single-celled microorganisms that are adapted to extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high salt concentrations, and low pH. They are thought to be the oldest group of organisms on Earth, and they are found in a variety of habitats, including hot springs, deep-sea vents, and the digestive tracts of animals. Archaea have unique cell walls and a distinct type of ribosome, which is the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis. They also have unique metabolic pathways that allow them to use unusual sources of energy, such as sulfur and methane.
The Bacteria domain is made up of single-celled microorganisms that are found almost everywhere on Earth. They are the most diverse group of organisms, and they play important roles in a variety of ecological processes, such as decomposition and nitrogen fixation. Bacteria have a simple cellular structure and a flexible metabolism that allows them to survive in a wide range of conditions. They can be classified based on their shape (e.g., spherical, rod-shaped, spiral), their mode of reproduction (e.g., binary fission, conjugation), and their ability to cause disease (e.g., pathogenic, opportunistic).
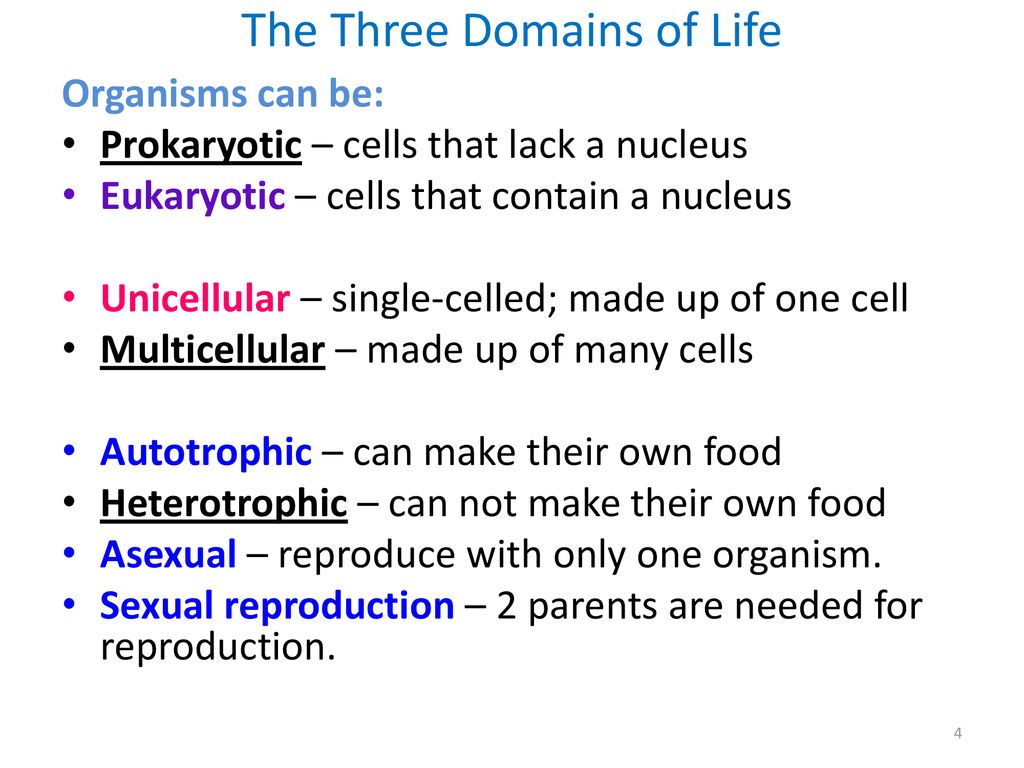
The Eukarya domain consists of all multicellular organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists. These organisms have complex cells with a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They also have a wide range of cellular and molecular characteristics that allow them to perform specialized functions, such as photosynthesis in plants and muscle contraction in animals. Eukarya are found in almost every habitat on Earth and play important roles in the global ecosystem.
In conclusion, the three domains of living organisms represent the major branches of the tree of life and are characterized by differences in their cellular and molecular characteristics. Understanding these differences is important for understanding the evolution and diversity of life on Earth.