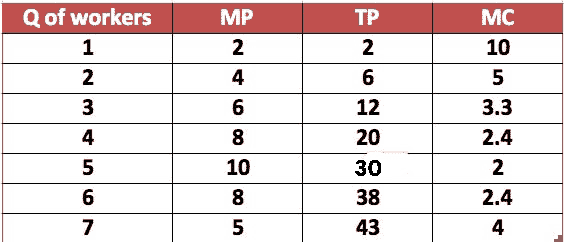
the marginal cost of production increases as the production level increases
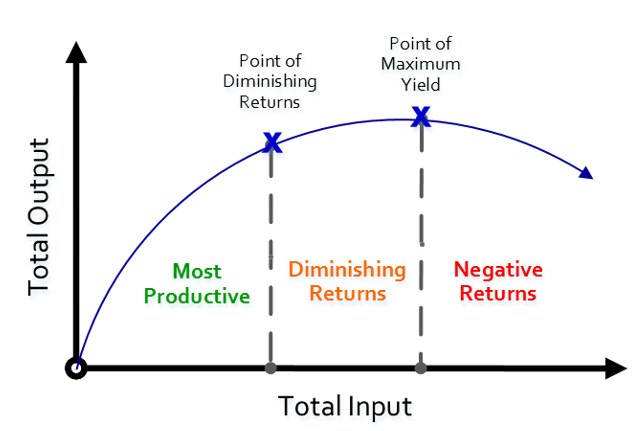
The law of diminishing returns is a principle in economics that states that as the quantity of a particular input increases, while all other inputs are held constant, the marginal output of that input will eventually decrease. This phenomenon can be observed in the production process of goods and services, where the marginal cost of production – the cost of producing one additional unit of output – tends to increase as the production level increases.
There are several reasons why the marginal cost of production increases as the production level increases. One reason is the increasing difficulty of finding and hiring additional workers as the production level increases. As a company expands its production, it may need to hire more workers to keep up with demand. However, as the number of available workers decreases, the cost of hiring additional workers increases. This is due to the fact that the remaining pool of workers may have specialized skills or may be in high demand, leading to higher wages and benefits being offered in order to attract them.
Another reason why the marginal cost of production increases as the production level increases is the increasing difficulty of finding and acquiring additional raw materials and resources. As a company increases its production, it may need to purchase more raw materials and resources in order to meet the increased demand. However, as the demand for these resources increases, the cost of acquiring them may also increase due to the laws of supply and demand.
In addition, as the production level increases, the cost of maintaining and repairing machinery and equipment may also increase. As machines are used more frequently, they are more likely to break down or need maintenance, which can add to the overall cost of production.
Overall, the law of diminishing returns explains why the marginal cost of production increases as the production level increases. As a company increases its production, it may face challenges in finding and hiring additional workers, acquiring raw materials and resources, and maintaining and repairing machinery and equipment. These challenges can lead to an increase in the marginal cost of production as the company strives to meet the increased demand for its goods and services.
The law of diminishing returns helps to explain why:
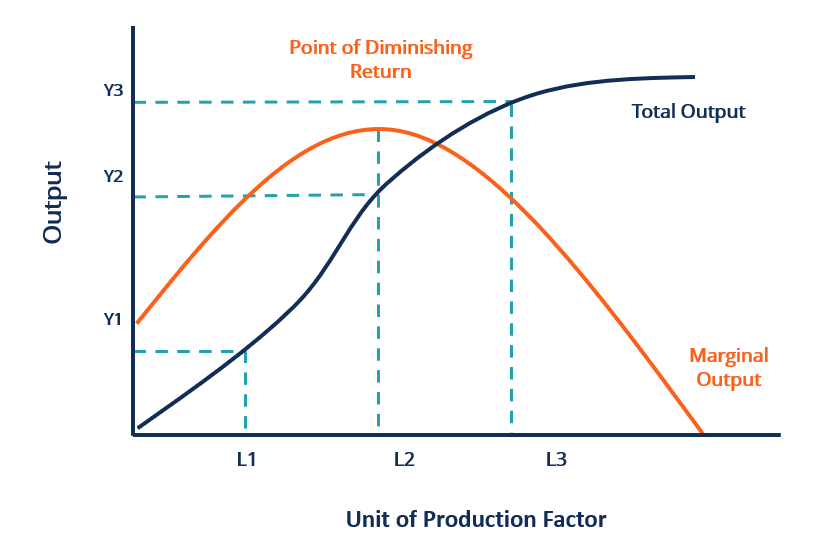
The marginal returns will increase instead of decreasing in the beginning. How does the law of diminishing returns work in the short run? After a certain point, that factor becomes less productive; therefore, there will eventually be a decreasing marginal return and average product. What is the law of diminishing returns quizlet? If every year more, and still more, units of labour and capital are put into it, the successive return per unit does not increase, but actually decreases. The law of diminishing returns applies because certain factors of production are kept fixed. This includes entrepreneurial ability, forgone interest, forgone labor income, etc. If cultivation is extended to inferior lands, the returns per acre must diminish.
Does law of diminishing returns apply in the short run or long run?

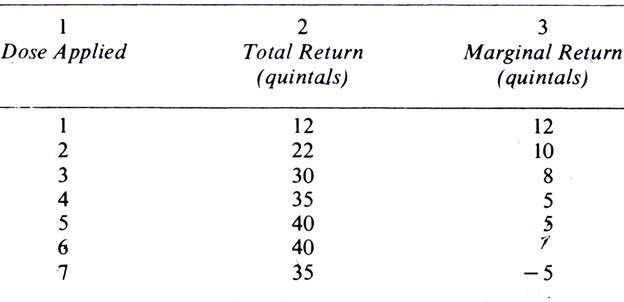
At the 5th dose, the marginal return is stationary, at the 6th it is zero, and at the 7th it is negative. The long-run ATC curve is U-shaped. In case of factor employment, the concept of Marginal Revenue Productivity MRP is used. One is law of increasing returns in stage I and law of diminishing returns in stage II. To calculate the diminishing marginal return of product production, obtain values for the production cost per unit of production. In the beginning, the return may increase but after a point it will diminish. The marginal cost MC of a product is the ratio of cost of a worker and extra quantity that he produces.
Please explain why the law of diminishing returns applies only in the short
It means that the law applies generally, but may not apply always the following exceptions may be noted: ADVERTISEMENTS: a New land, just brought under cultivation, will go on improving with the application of labour and capital. Marginal product MP is the units that can be produced by introducing an additional unit of labor. Very Small quantity leads to a less output, but large quantities can also lead to a less output. We can say that the total return increases but at a diminishing rate. ADVERTISEMENTS: It is so either because the new land is inferior otherwise it would have been cultivated first , or because it is farther away, and the cost of transport increases the cost of production. But economists now give the law a much wider application.
GEOG 1101 Chapter 2 Flashcards

This is because the crowding of inputs eventually leads to a negative impact on the output. This will mean diminishing returns. In the short run, by definition, the scale of the plant cannot change: The firm cannot bring in more machinery or move to a larger building. If long-run ATC drops quickly to its minimum cost which then extends over a long range of output, the industry will likely be composed of both large and small firms. In this case also, the marginal return will go up at first instead of going down. When different laws of returns are found to operate at different times, the figure will be as given below Fig. For example, when the first dose of Rs.