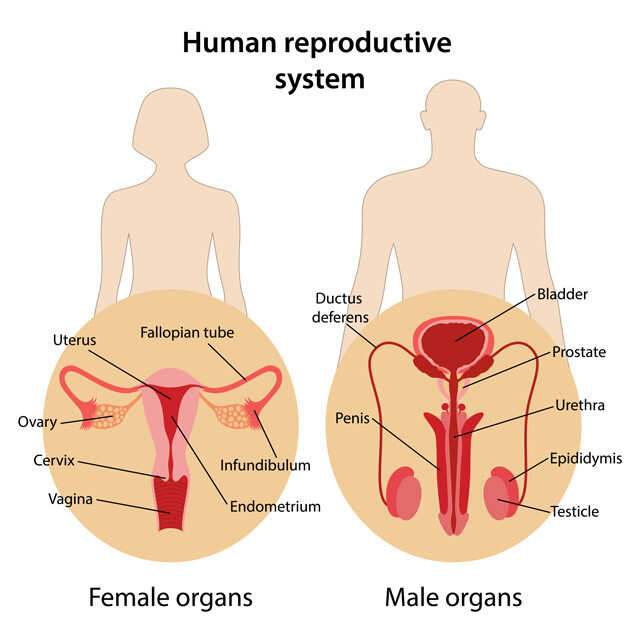
The human reproductive system is a complex network of organs and hormones that work together to produce and transport gametes, the reproductive cells that are responsible for passing on genetic information from one generation to the next. This system is essential for the continuation of the human species, as it allows for the production of offspring and the genetic diversity that is necessary for the survival and evolution of any population.
There are several key parts of the human reproductive system, each with its own specific functions. These parts can be divided into two main categories: the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system.
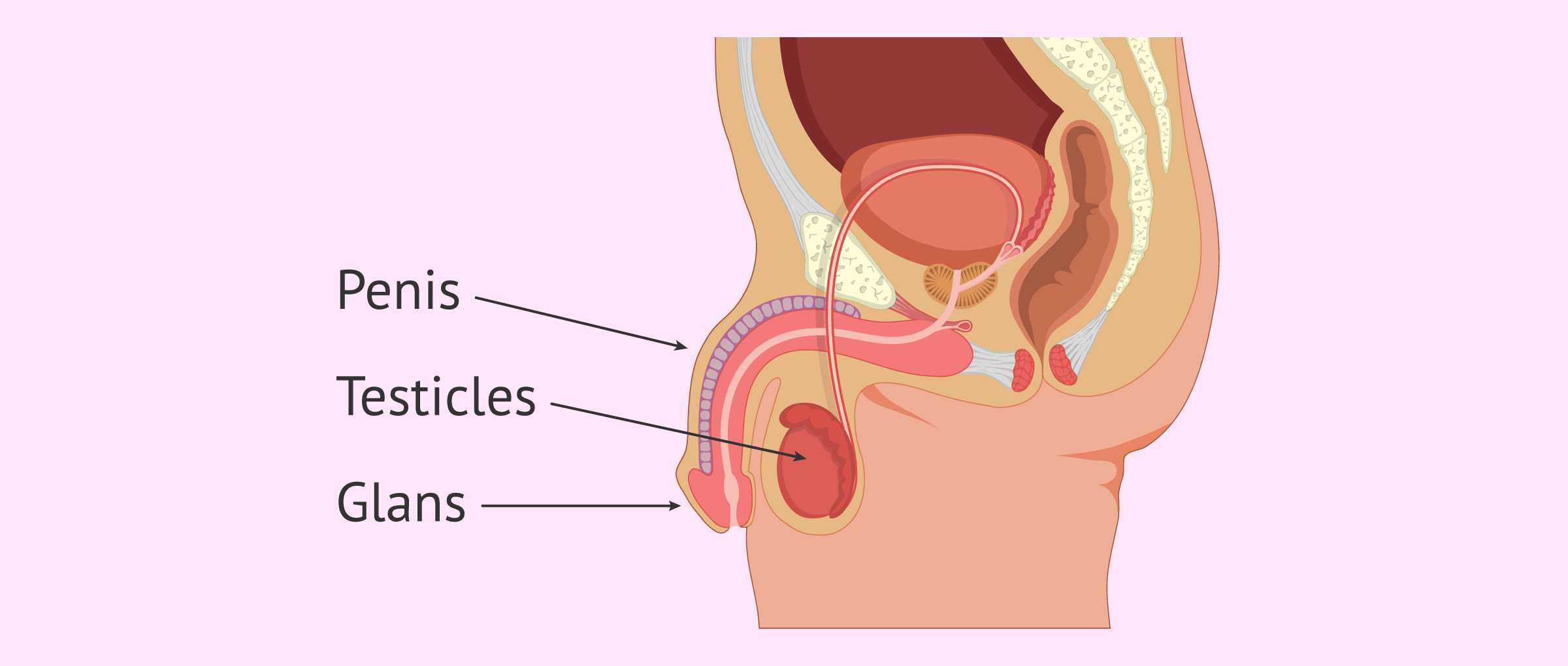
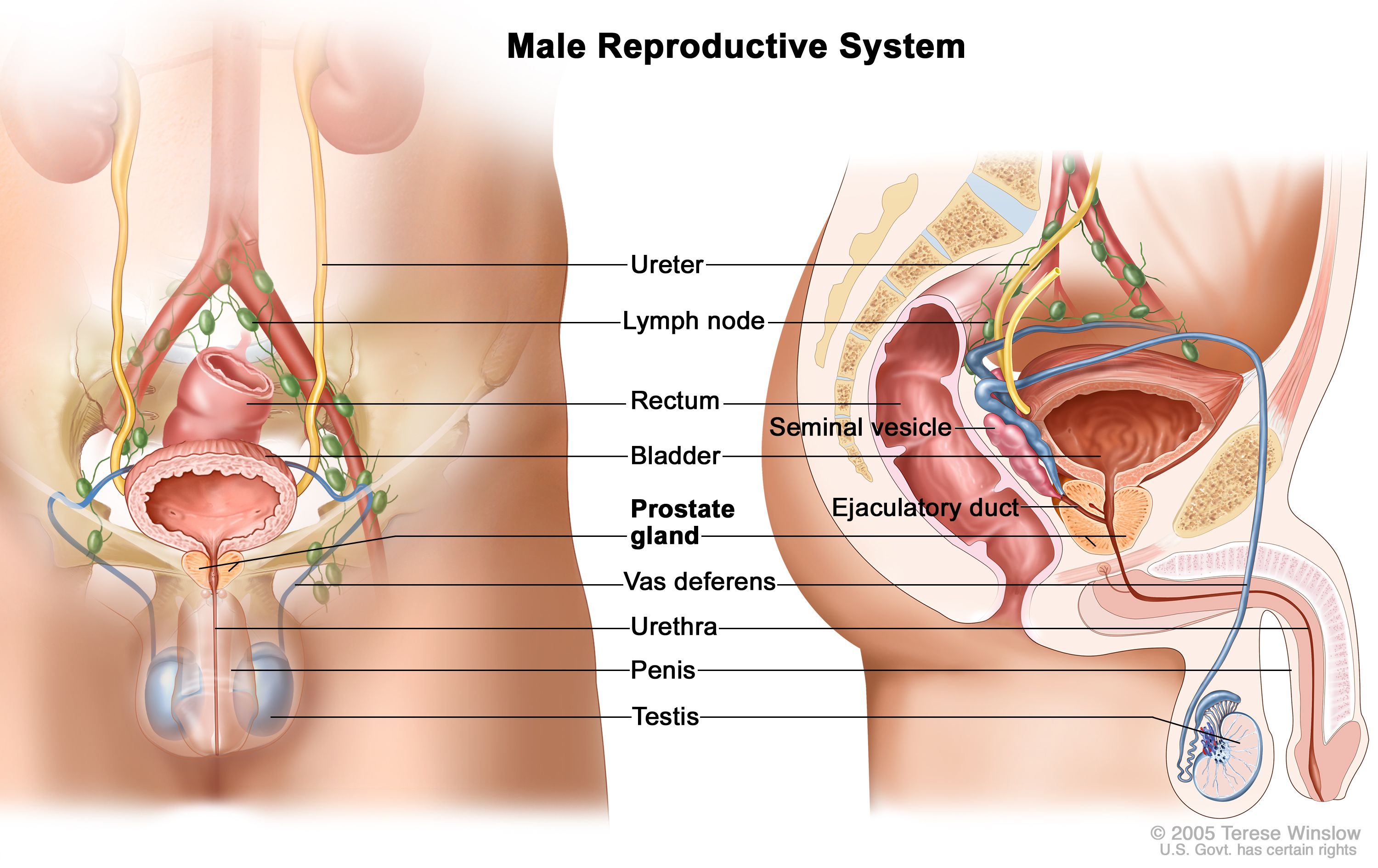
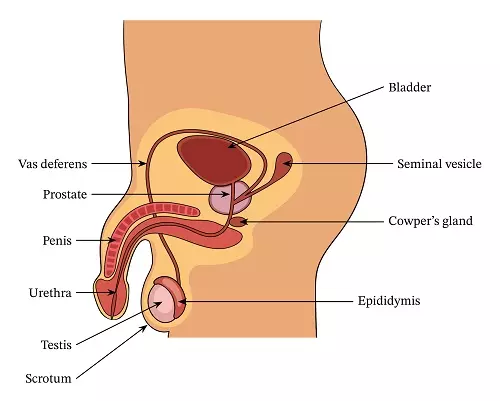
The male reproductive system consists of the testes, the penis, the prostate gland, and several other glands and ducts. The testes are a pair of oval-shaped organs that are located in the scrotum, a sac of skin that hangs outside of the body. The testes are responsible for producing and storing sperm, the male gametes that are essential for fertilization. The sperm are produced in a process called spermatogenesis, which occurs within the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
The penis is a male external genital organ that is responsible for the transfer of sperm during sexual intercourse. It is made up of three main parts: the shaft, the glans, and the urethra. The shaft is the main part of the penis, and it is covered with skin and muscle. The glans is the sensitive, rounded tip of the penis, and the urethra is a tube that runs through the shaft of the penis and carries both urine and sperm.
The prostate gland is a small, muscular gland located in the pelvis that surrounds the urethra. It produces a fluid that makes up a significant portion of the ejaculate, the fluid that is released during ejaculation.
The female reproductive system consists of the ovaries, the uterus, the fallopian tubes, and the vagina. The ovaries are a pair of almond-shaped organs that are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries produce and release eggs, or ova, during the menstrual cycle. The eggs are released into the fallopian tubes, which are tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg will travel down the fallopian tubes and into the uterus, where it will implant itself in the uterine lining and begin to develop into a fetus.
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a muscular, pear-shaped organ that is located in the pelvis. It is responsible for providing a supportive environment for the developing fetus during pregnancy. The uterus is lined with a thick layer of blood vessels and connective tissue called the endometrium, which is essential for the implantation and nourishment of the fertilized egg.
The vagina is a muscular, elastic tube that connects the uterus to the outside of the body. It is the female external genital organ, and it is responsible for the passage of menstrual blood and for sexual intercourse. The cervix, which is the lower, narrow end of the uterus, extends into the vagina and forms a barrier between the uterus and the outside world.
In summary, the human reproductive system is a complex and vital system that is responsible for the production and transportation of gametes and the support of a developing fetus. It is made up of a variety of organs and hormones that work together to ensure the continuation of the human species.

(280).jpg)