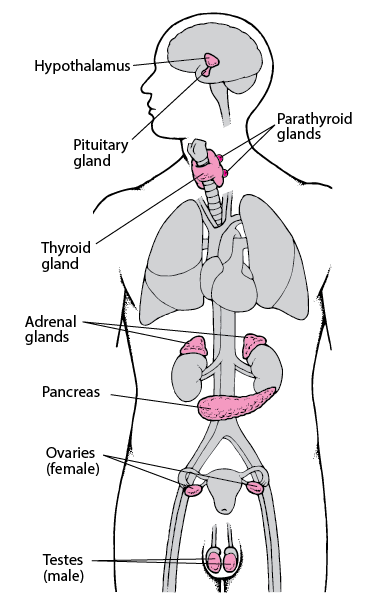
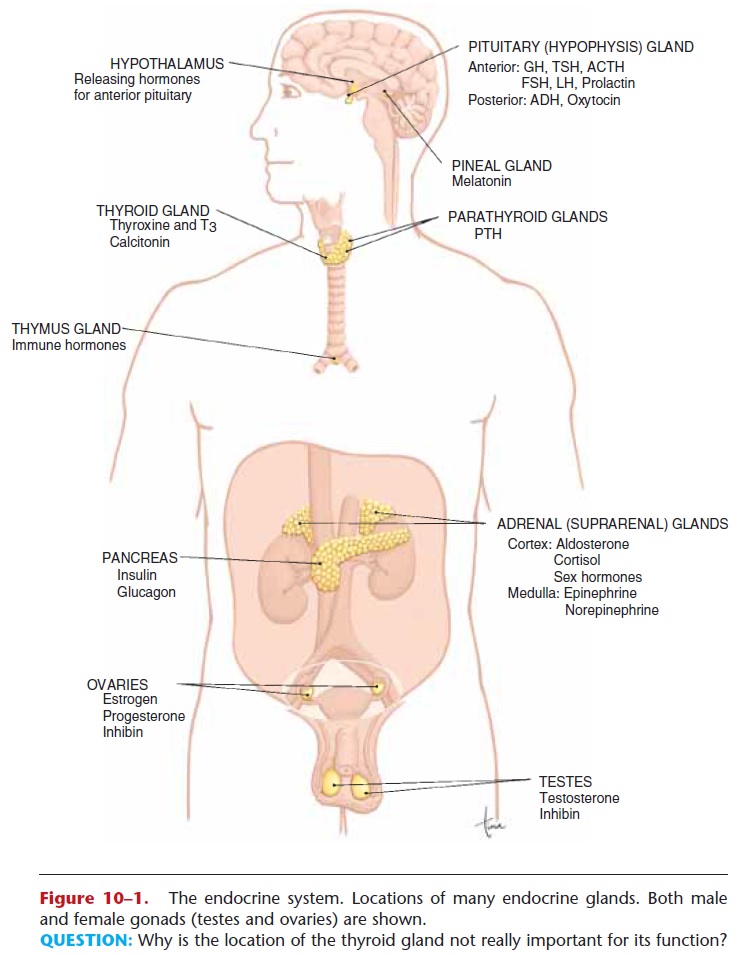
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and hormones that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. These glands produce hormones that regulate various physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, and sexual development. The endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands, as well as the pancreas, ovaries, and testes.
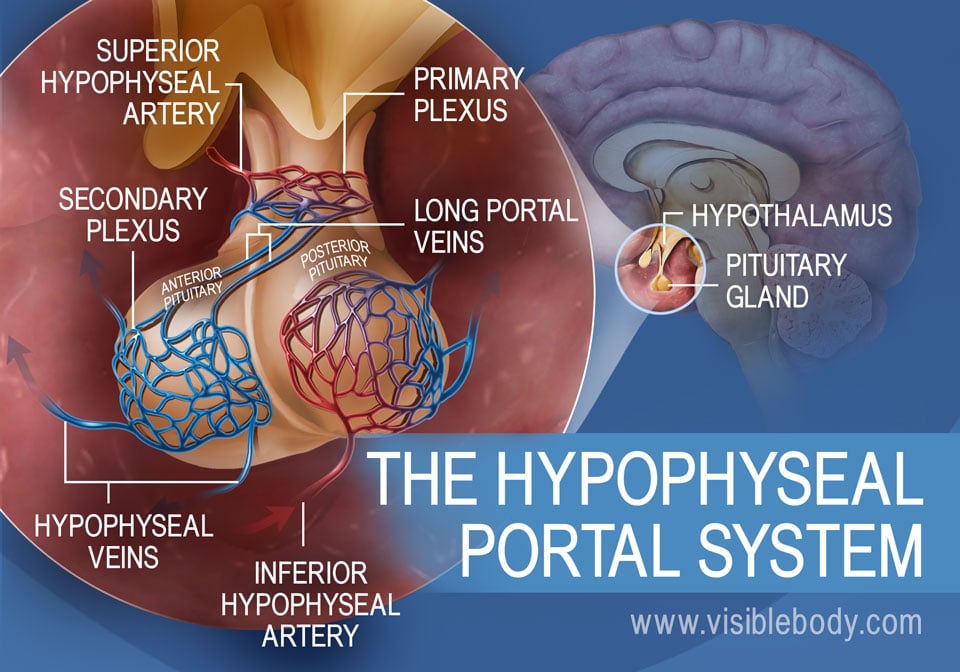
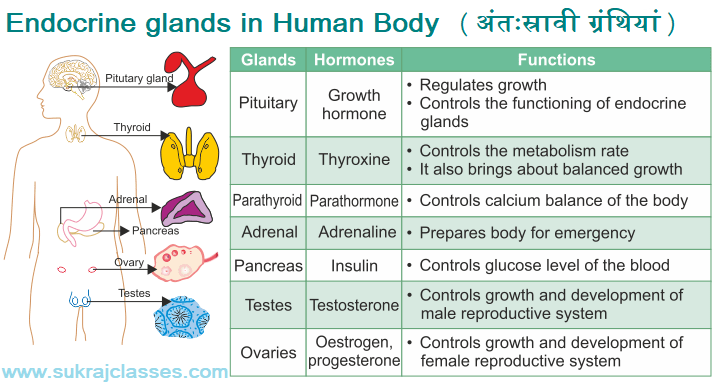
The pituitary gland, also known as the "master gland," is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for producing a variety of hormones that regulate many of the body's functions. The anterior pituitary gland produces hormones that stimulate the thyroid gland, regulate growth, and control the production of milk in the breasts. The posterior pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate the body's water balance, such as vasopressin and oxytocin.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck and produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolism, including thyroid hormone and calcitonin. Thyroid hormone plays a key role in maintaining the body's energy levels and body temperature, while calcitonin helps regulate the body's calcium levels.
The parathyroid glands, located near the thyroid gland, produce parathyroid hormone, which helps regulate the body's calcium levels. This hormone works in conjunction with calcitonin to maintain the balance of calcium in the body.
The adrenal glands, located above the kidneys, produce hormones that help the body respond to stress. The outer portion of the adrenal gland, called the adrenal cortex, produces hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone, which help regulate metabolism and the body's electrolyte balance. The inner portion of the adrenal gland, called the adrenal medulla, produces hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine, which help the body respond to stress and increase heart rate and blood pressure.
The pineal gland, located in the brain, produces the hormone melatonin, which helps regulate the body's sleep-wake cycle.
The pancreas, located in the abdomen, produces hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which help regulate the body's blood sugar levels. Insulin helps lower blood sugar levels, while glucagon raises them.
The ovaries, located in the female reproductive system, produce hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and help control the development of female secondary sex characteristics.
The testes, located in the male reproductive system, produce the hormone testosterone, which plays a key role in the development of male secondary sex characteristics and the regulation of the male reproductive system.
In conclusion, the endocrine glands play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body by producing hormones that regulate various physiological processes. Dysfunction of the endocrine system can lead to a range of health issues, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances.