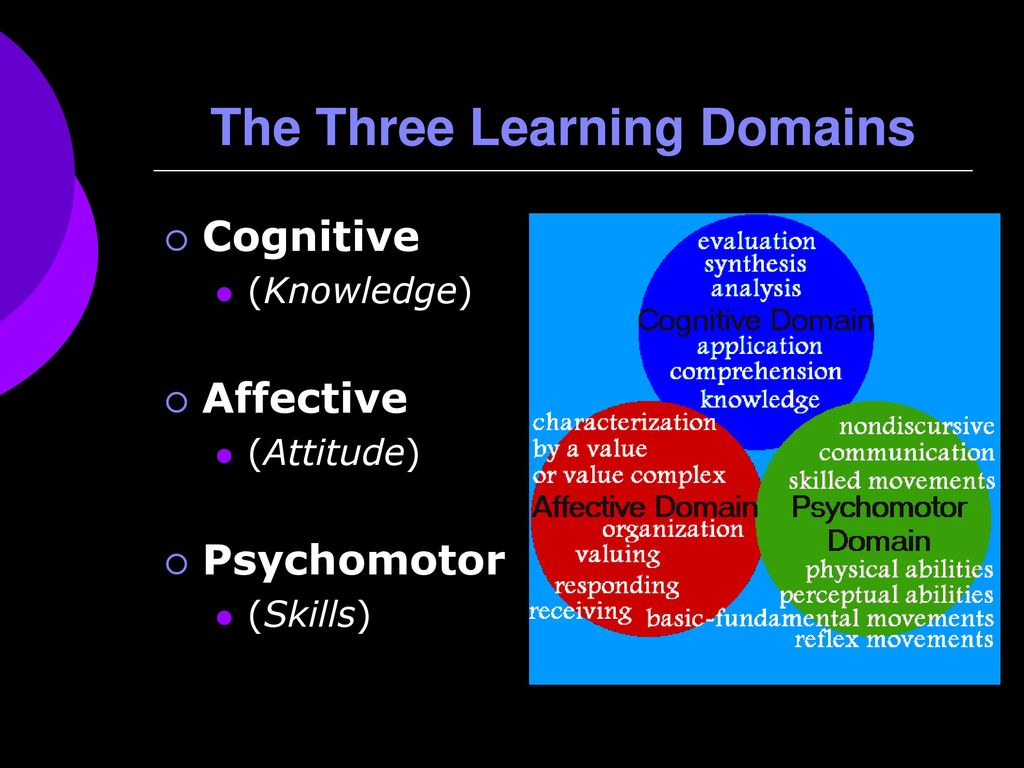
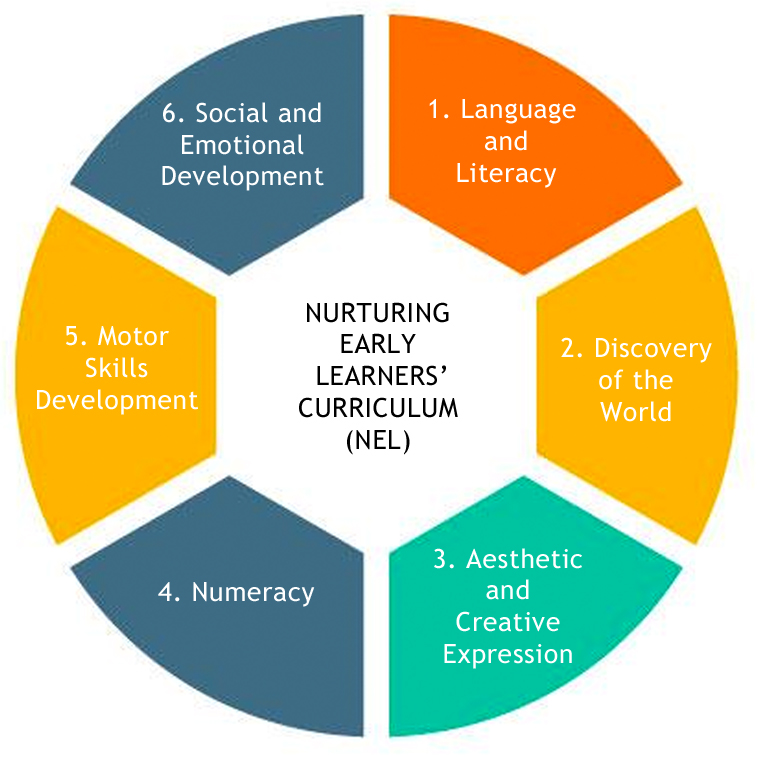
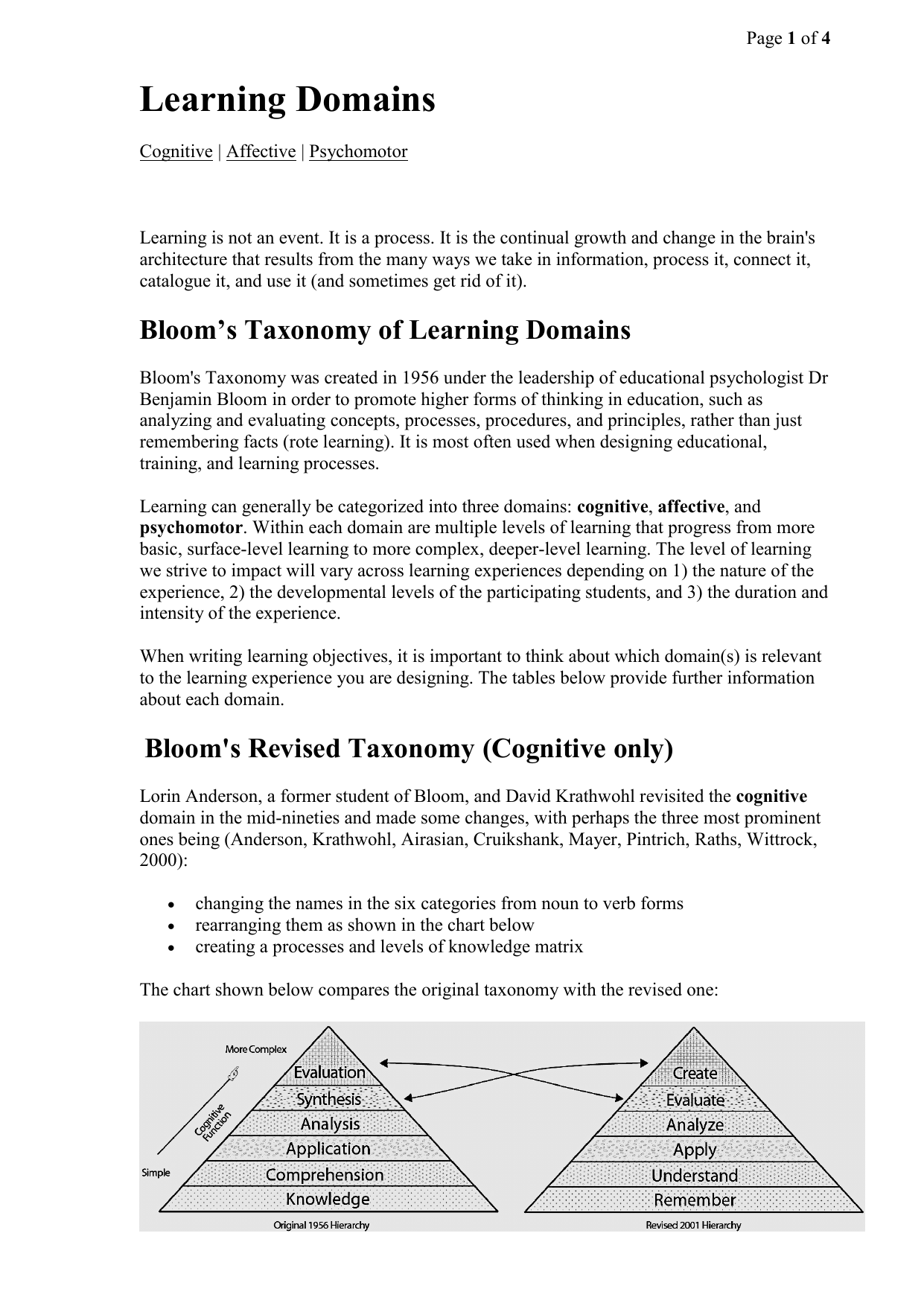
The domains of learning are the various areas or categories in which a person can acquire knowledge and skills. These domains are often referred to as the "Three Rs" – reading, writing, and arithmetic – but there are actually five main domains of learning: cognitive, physical, emotional, social, and aesthetic.
The cognitive domain refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring and understanding information. This includes things like memory, problem-solving, and critical thinking. The physical domain involves the development of physical skills and abilities, such as fine and gross motor skills.
The emotional domain refers to the development of a person's emotional intelligence, or their ability to recognize and manage their own emotions, as well as those of others. This includes things like self-awareness, self-regulation, and empathy.
The social domain involves the development of social skills and the ability to interact effectively with others. This includes things like communication, teamwork, and conflict resolution.
The aesthetic domain refers to the development of a person's appreciation and understanding of the arts, such as music, dance, and visual arts. This includes things like creativity, expression, and the ability to interpret and evaluate works of art.
Each of these domains is important for overall personal and academic development. For example, a well-rounded education should include opportunities for students to develop their cognitive skills through rigorous academic coursework, their physical skills through physical education and sports, their emotional intelligence through social-emotional learning, their social skills through group projects and team sports, and their aesthetic appreciation through exposure to the arts.
Furthermore, these domains are not mutually exclusive – they often overlap and intersect with one another. For example, developing physical skills can also improve cognitive skills, such as coordination and spatial awareness. Similarly, developing emotional intelligence can improve social skills, as it helps a person better understand and respond to the emotions of others.
In conclusion, the domains of learning are the various areas in which a person can acquire knowledge and skills. These include the cognitive, physical, emotional, social, and aesthetic domains, and each is important for overall personal and academic development. By providing a well-rounded education that includes opportunities for development in all of these domains, we can help individuals become well-rounded, capable, and confident learners.