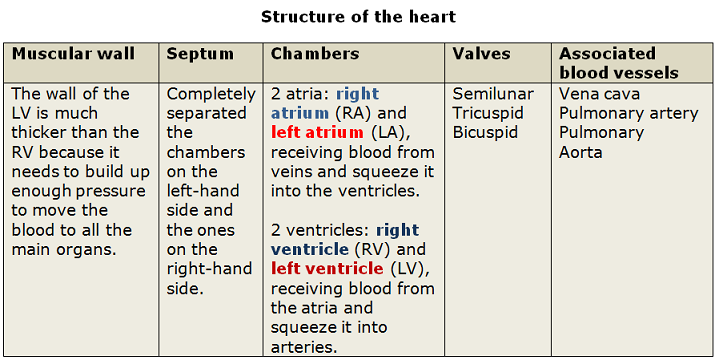
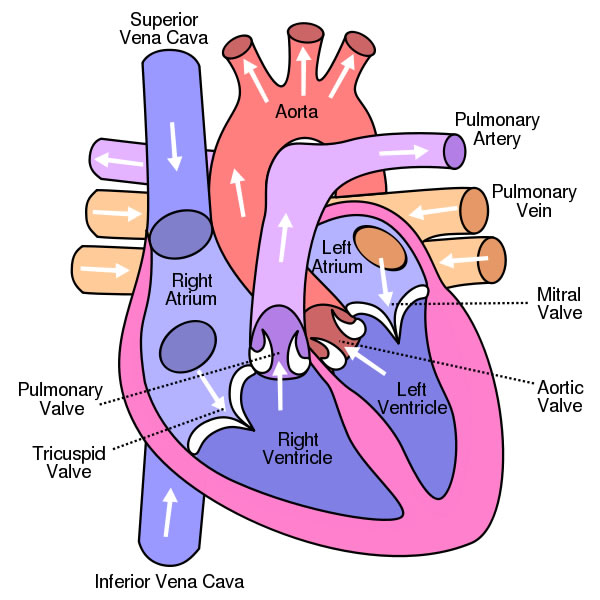
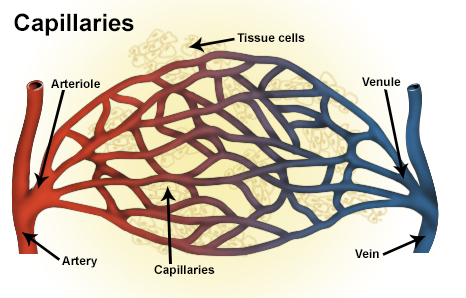
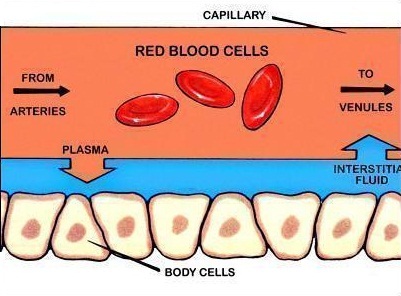
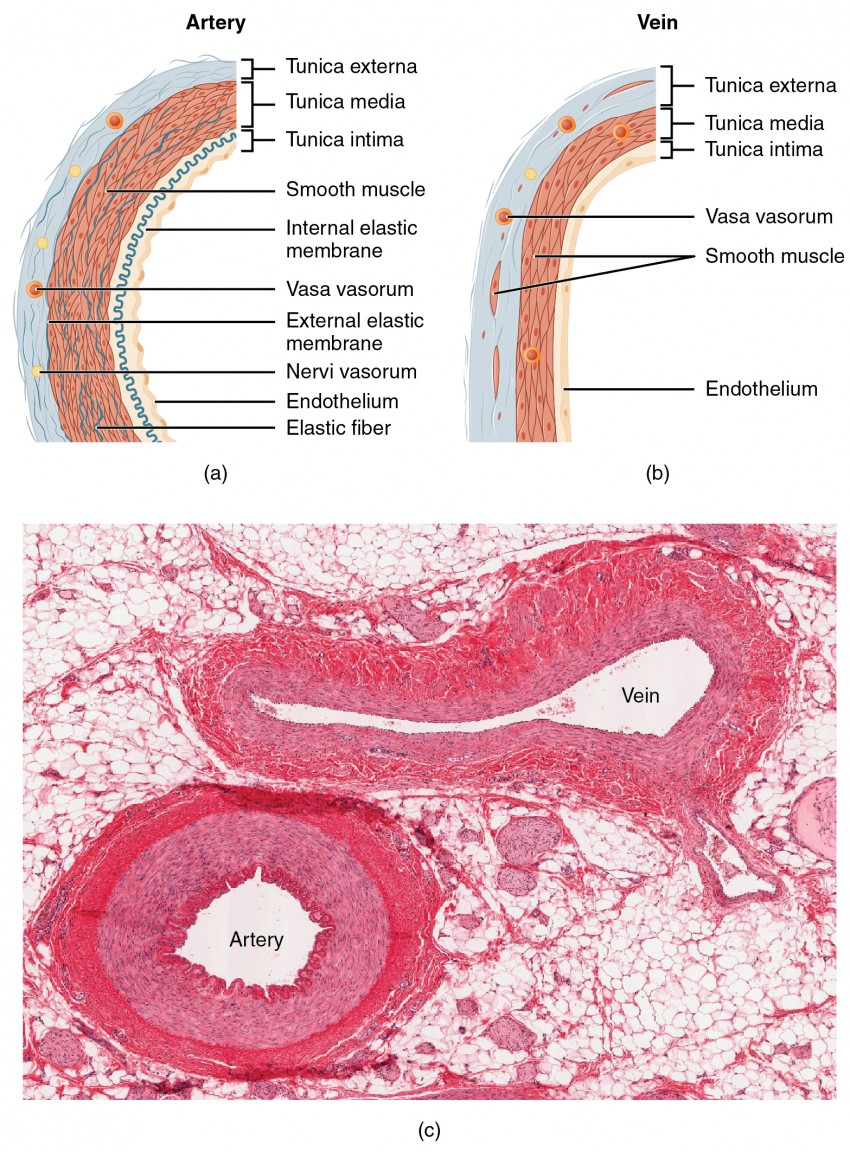
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and towards the body's tissues. They are an essential part of the circulatory system, which is responsible for distributing nutrients and oxygen to the body's cells and removing waste products.
The structure of arteries is designed to withstand the high pressure of the blood being pumped through them by the heart. The walls of arteries are composed of three layers: the innermost layer, called the tunica intima, is made up of a single layer of endothelial cells that line the vessel; the tunica media, or middle layer, is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers; and the outer layer, called the tunica externa, is made up of connective tissue.
The elastic fibers in the tunica media allow arteries to stretch and contract as the heart pumps blood through them. This helps to regulate blood flow and maintain a consistent blood pressure. The smooth muscle in the tunica media also plays a role in regulating blood flow by constricting or dilating the artery in response to various physiological signals.
In addition to their structural role, arteries also have a number of important functions. One of the most crucial is to deliver oxygenated blood to the body's tissues. Oxygen is essential for the body's cells to function properly, and it is carried by red blood cells, which are pumped through the arteries by the heart.
Arteries also help to regulate blood pressure by constricting or dilating in response to various stimuli. This is important because too high or too low of a blood pressure can be harmful to the body. High blood pressure, for example, can damage the walls of the arteries and lead to serious health problems such as heart disease and stroke.
In summary, the structure and function of arteries is essential for maintaining proper blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body's tissues. The elastic fibers and smooth muscle in the arterial walls allow for the regulation of blood pressure, while the endothelial cells lining the innermost layer help to prevent blood clotting and promote healthy blood flow. Overall, the proper functioning of the arteries is vital for the overall health and well-being of the body.