Blood clotting, also known as coagulation, is a crucial process that occurs in the body to prevent excessive bleeding and promote healing. When a blood vessel is injured, the body activates a series of complex reactions that lead to the formation of a blood clot. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity of the vascular system and ensuring that the body has sufficient blood volume to function properly.
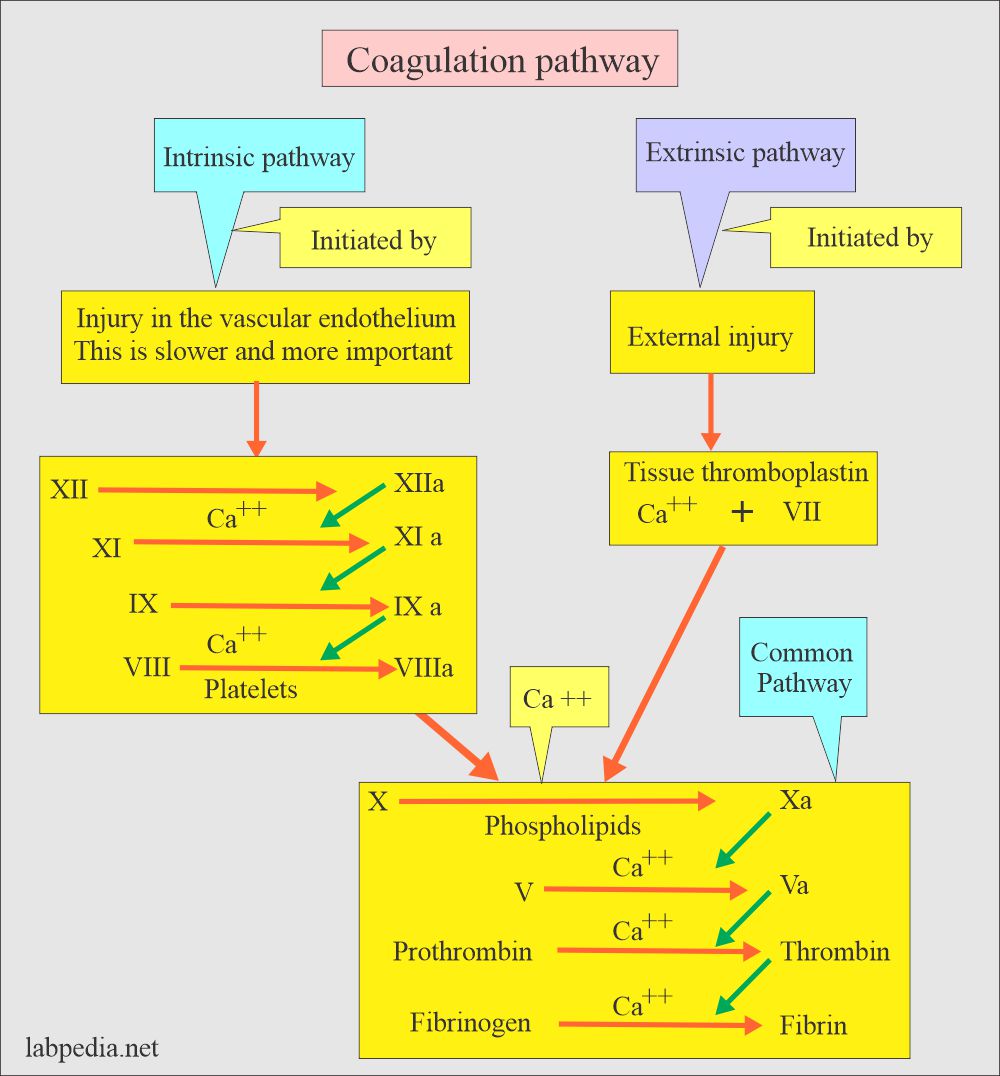
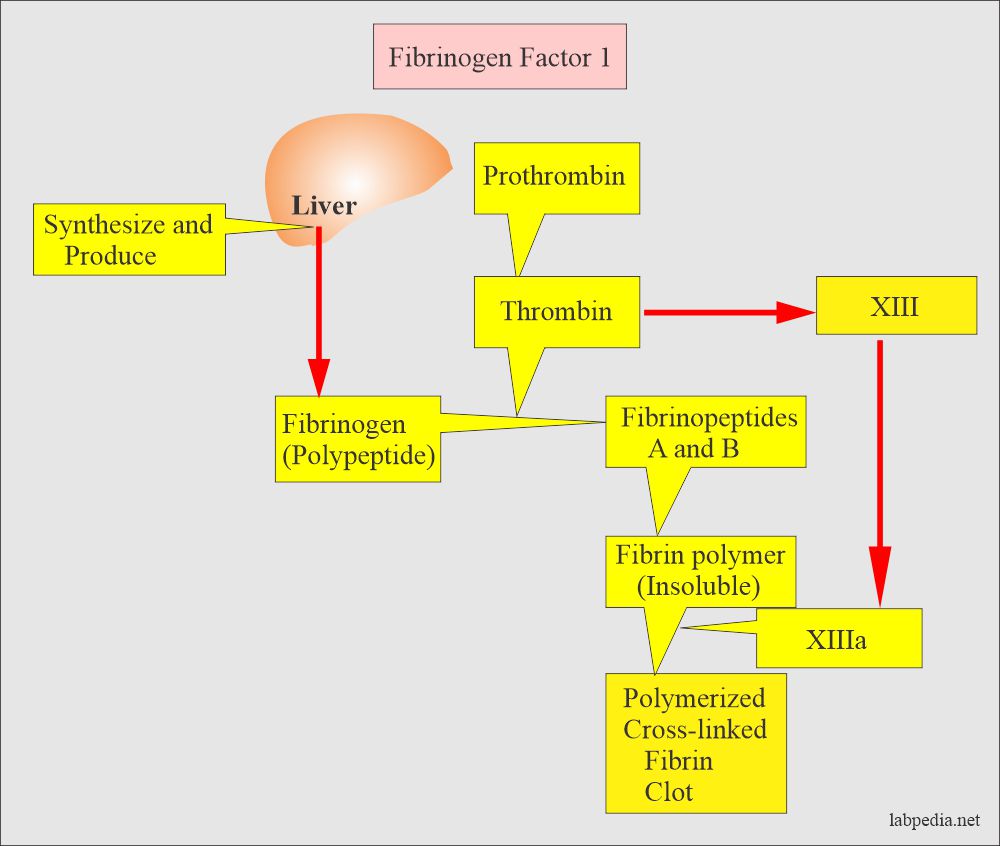
There are several different factors that are responsible for blood clotting, including proteins called clotting factors, platelets, and other cells in the blood. Clotting factors are proteins that are produced by the liver and released into the bloodstream. They play a key role in the coagulation process by activating other proteins and enzymes that are needed for blood clot formation.
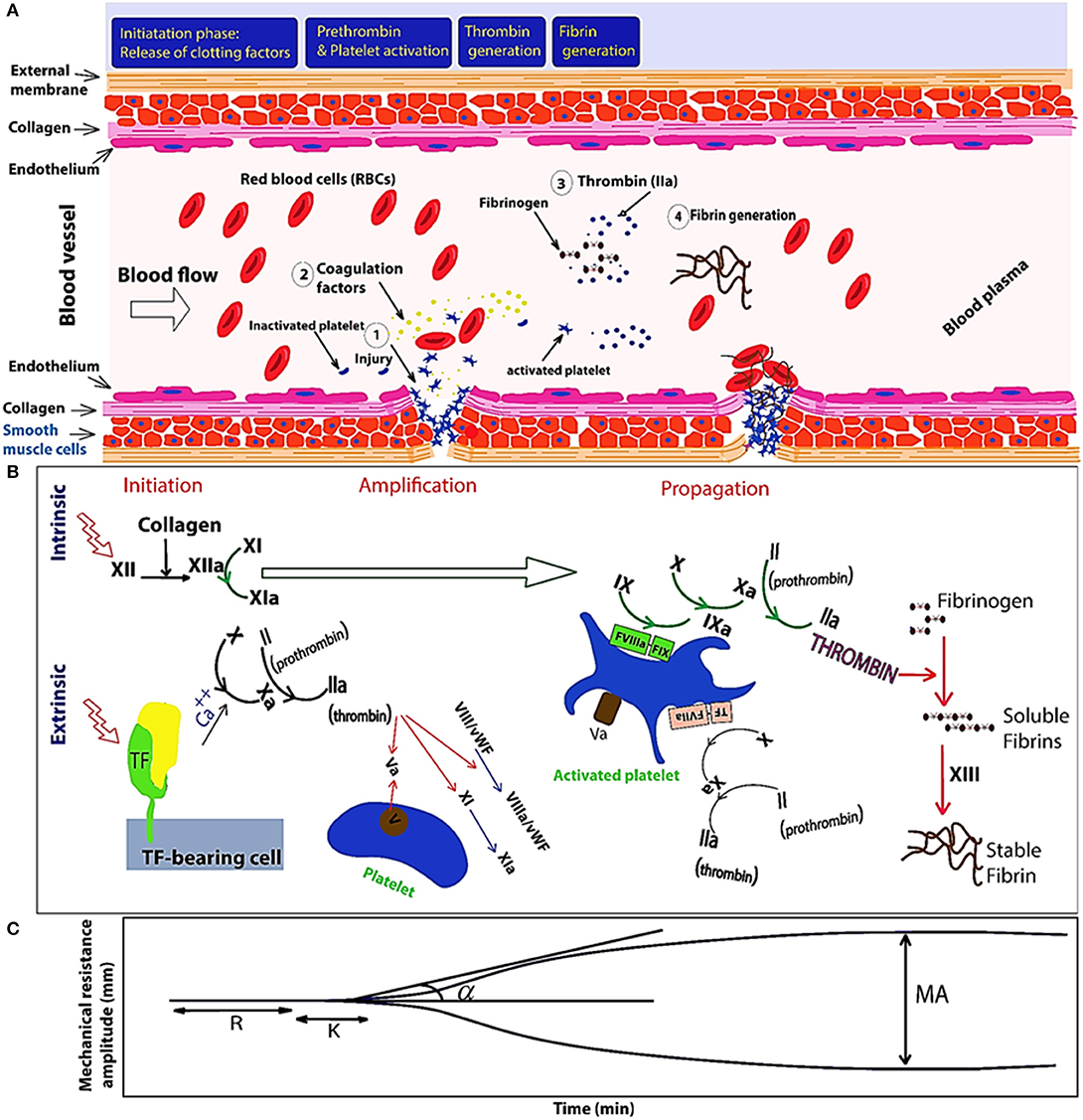
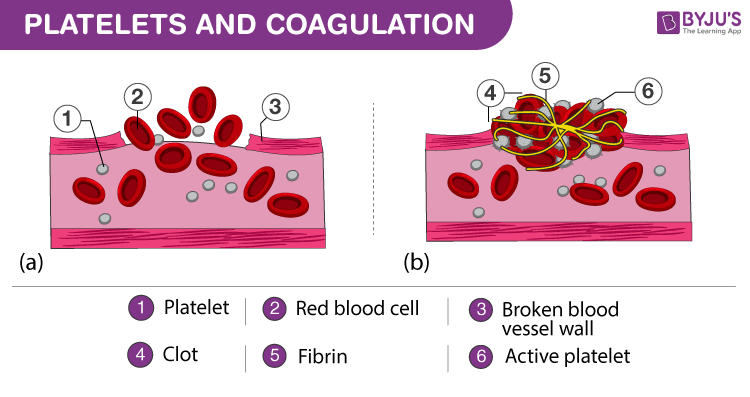
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are small, disk-shaped cells that are found in the blood. They are important for blood clotting because they contain granules that contain clotting factors and other proteins that are needed for clot formation. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets are activated and stick to the damaged area, forming a platelet plug. This plug helps to stop the bleeding and provides a foundation for the formation of a more permanent blood clot.
Other cells in the blood, such as white blood cells and red blood cells, also play a role in the coagulation process. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, help to remove bacteria and other foreign substances from the bloodstream. Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, carry oxygen to the body's tissues and help to maintain blood volume.
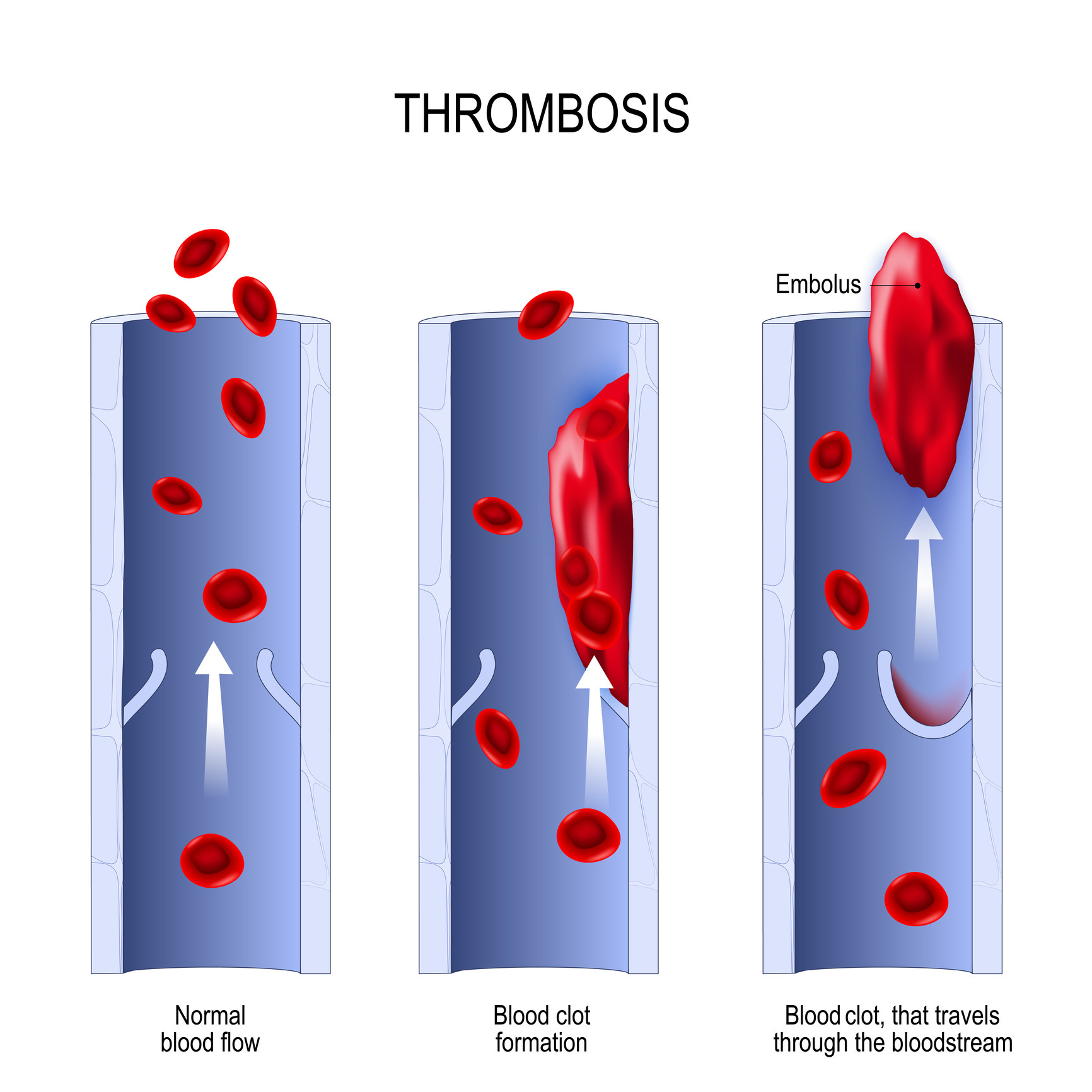
The coagulation process is complex and involves several different steps. When a blood vessel is damaged, the injured area releases a chemical called thrombin, which activates the clotting factors and begins the process of clot formation. The activated clotting factors then work together to form a fibrin mesh, which is a network of fibers that helps to hold the blood clot in place.
In addition to the proteins and cells that are involved in blood clotting, there are also several hormones and enzymes that play a role in the process. For example, hormones such as adrenalin and cortisol help to regulate the coagulation process, while enzymes such as thrombin and plasmin help to break down clots once they have formed.
Overall, blood clotting is a complex and essential process that is responsible for maintaining the integrity of the vascular system and preventing excessive bleeding. It is regulated by a variety of factors, including clotting factors, platelets, and other cells in the blood, as well as hormones and enzymes. Without the ability to form blood clots, the body would be at risk of serious bleeding and injury.