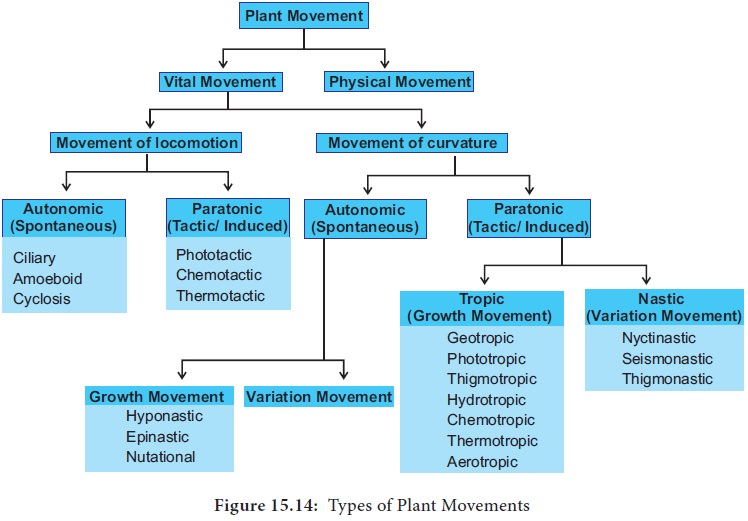
Paratonic movement refers to a type of musical movement or progression in which the notes of a melody or chord progression move by a small interval, such as a half step or whole step, rather than by larger leaps. This type of movement is often found in music that is characterized by a steady, flowing melody or a repetitive, rhythmic pattern, as it creates a sense of continuity and unity within the music.
One of the key features of paratonic movement is that it creates a sense of tension and resolution within the music. By moving in small intervals, the music builds a sense of anticipation and expectation, as the listener waits for the next note to be played. When the next note is finally played, it creates a sense of resolution and release, as the tension is relieved. This tension and resolution can be especially effective in creating an emotional response in the listener, as it mirrors the natural ups and downs of human emotions.
Paratonic movement is also often used to create a sense of continuity and unity within a piece of music. By using small intervals to move between notes, the music is able to flow smoothly and seamlessly, creating a sense of cohesiveness and continuity. This can be especially effective in music that is characterized by a repetitive, rhythmic pattern, as the paratonic movement helps to keep the music moving forward and creates a sense of momentum.
There are a number of different musical styles and genres that make use of paratonic movement, including classical, folk, and popular music. In classical music, paratonic movement is often used to create a sense of continuity and unity within a piece, as well as to create an emotional response in the listener. In folk music, paratonic movement is often used to create a sense of simplicity and authenticity, as it allows the music to be played and sung in a more natural, unpretentious way. In popular music, paratonic movement is often used to create a catchy, memorable melody that sticks in the listener's head.
Overall, paratonic movement is an important musical device that is used to create a sense of continuity, unity, and emotional response in music. Whether it is used in classical, folk, or popular music, it helps to create a sense of flow and momentum within a piece of music, and can be a powerful tool for engaging and connecting with the listener.