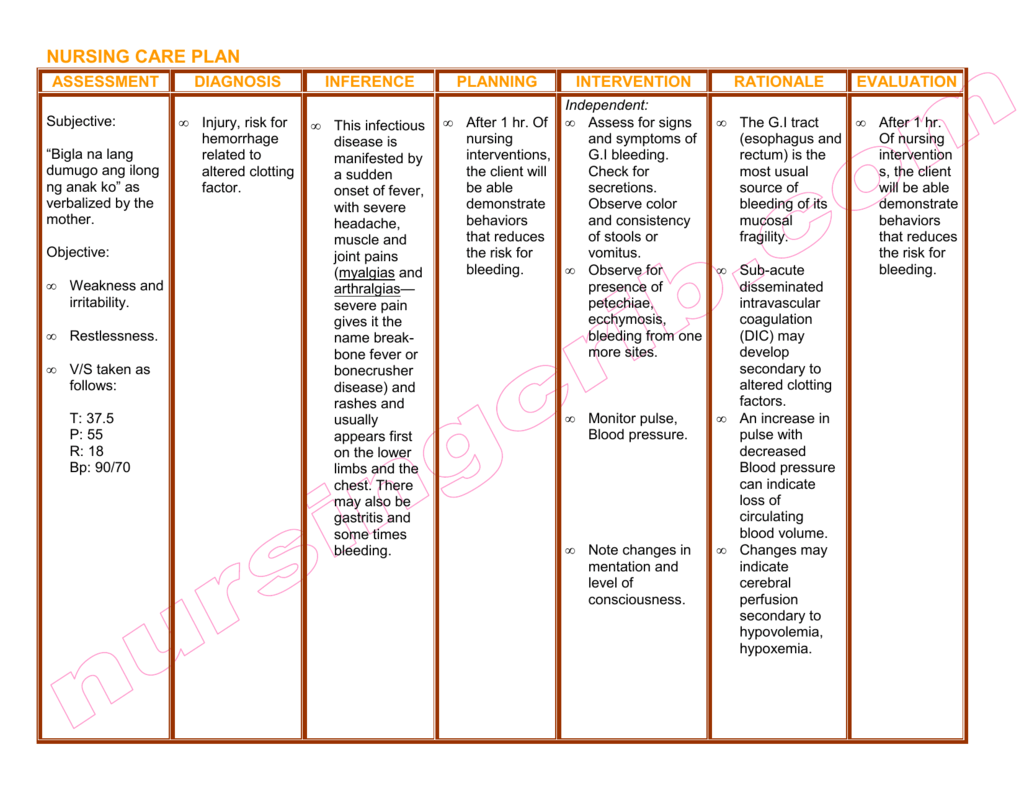
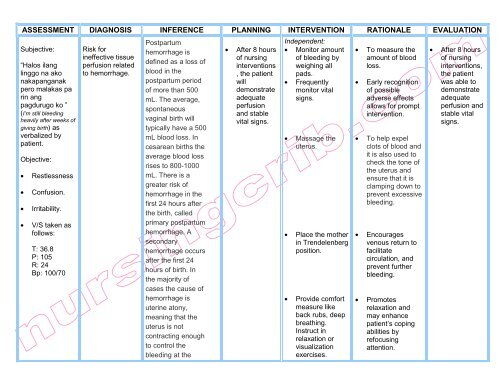
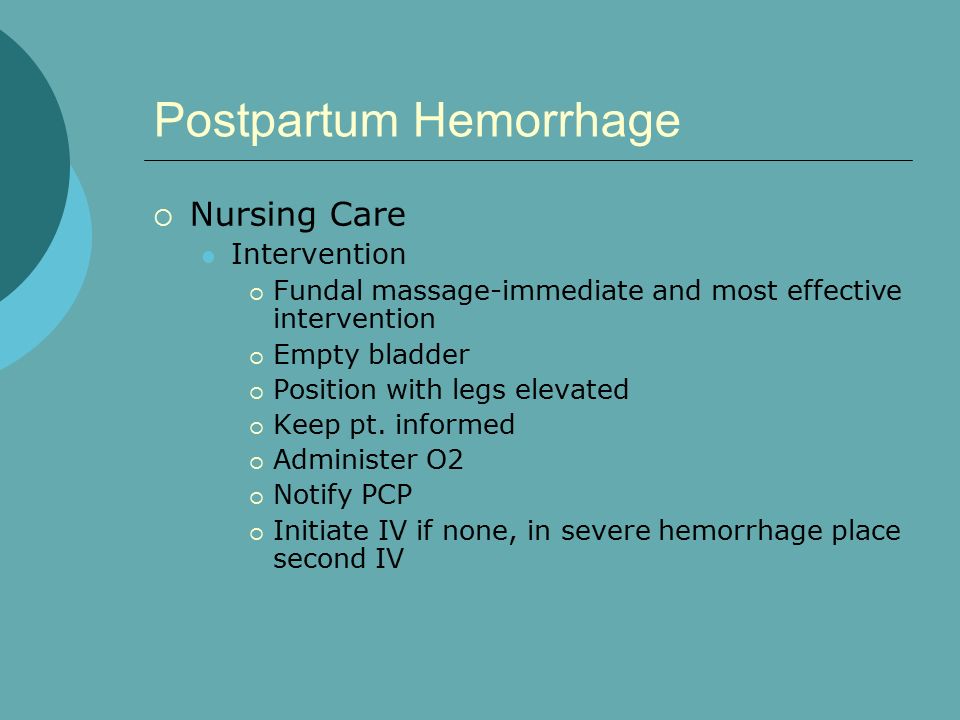
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a serious complication that can occur after childbirth and is defined as any bleeding that exceeds 500 mL after vaginal delivery or 1000 mL after cesarean delivery. It is a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality, and it is important that healthcare providers have a clear nursing care plan in place to manage and treat PPH effectively.
The first step in managing PPH is to identify the risk factors and initiate appropriate interventions. Risk factors for PPH include prolonged labor, uterine atony, uterine rupture, placental abnormalities, and cesarean delivery. To prevent PPH, it is important to monitor the mother's vital signs and uterine contractions during labor, and to encourage the mother to push effectively during the second stage of labor. If PPH does occur, it is important to identify the cause and initiate appropriate interventions, such as uterine massage, oxytocin administration, and manual removal of the placenta.
Once PPH has been identified and treated, the next step in the nursing care plan is to monitor the mother for any ongoing bleeding and to implement measures to control the bleeding. This may include the use of uterotonics, such as oxytocin or methylergonovine, to contract the uterus and stop the bleeding. Other interventions may include the use of uterine compression sutures or the placement of a balloon tamponade to apply pressure to the uterine artery and stop the bleeding.
It is also important to monitor the mother's vital signs and fluid balance closely, as PPH can lead to fluid and blood loss, which can result in hypovolemic shock. It may be necessary to administer fluids and blood transfusions to maintain the mother's blood pressure and prevent organ damage.
In addition to medical interventions, it is important for the nursing care plan to include measures to support the mother's emotional and physical well-being. This may include providing emotional support and education about PPH and its treatment, as well as helping the mother to manage any physical discomfort or pain.
In summary, the nursing care plan for postpartum hemorrhage should include identification and treatment of the cause of the bleeding, measures to control the bleeding, monitoring of vital signs and fluid balance, and support for the mother's emotional and physical well-being. By implementing this care plan, healthcare providers can effectively manage and treat PPH, improving the outcomes for mothers and their newborns.