The adult skeleton is made up of various bones and cartilages, which are tissues made up of cells surrounded by a matrix of fibers. Cartilages are found in various parts of the body, including the joints, the respiratory system, and the ear. In this essay, we will focus on the major cartilages of the adult skeleton.
One of the most well-known cartilages in the body is the hyaline cartilage, which is a type of connective tissue found in many parts of the body. It is composed of cells called chondrocytes that are embedded in a matrix made up of collagen and elastin fibers. The hyaline cartilage is smooth and glossy in appearance, and it is found in several areas of the body, including the ends of the long bones, the ribs, the larynx, and the trachea.
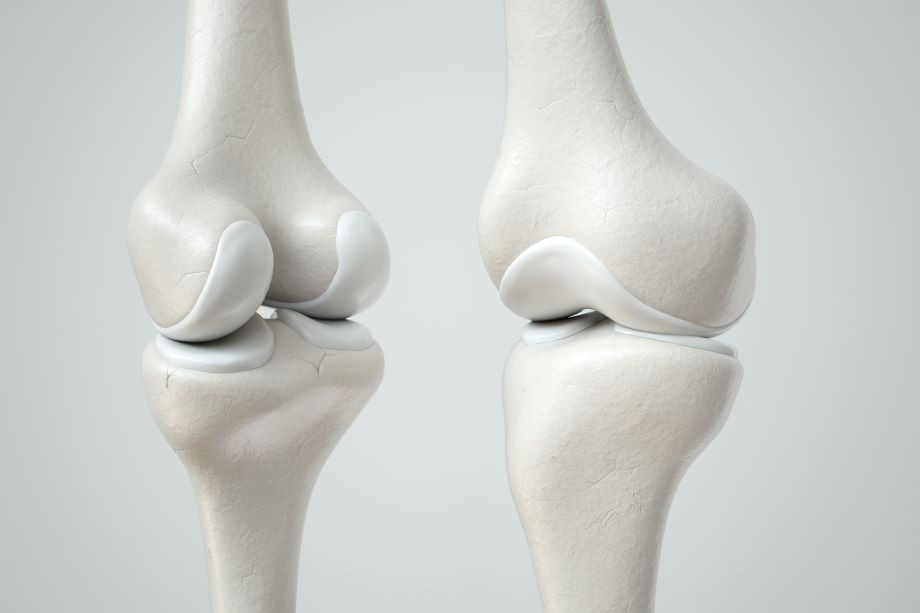
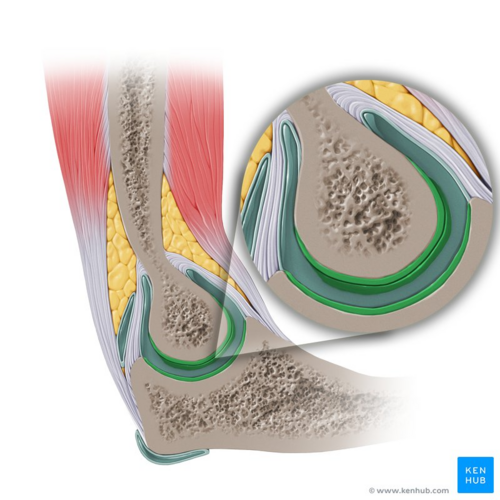
Another important cartilage in the adult skeleton is the fibrocartilage, which is a type of connective tissue that is composed of chondrocytes and a matrix made up of collagen fibers. Fibrocartilage is found in areas of the body that experience a lot of mechanical stress, such as the intervertebral discs, the pubic symphysis, and the menisci of the knee. It is also found in the tendons and ligaments, which are connective tissues that attach bones to each other and help to support and stabilize the joints.
Another major cartilage in the adult skeleton is the elastic cartilage, which is composed of chondrocytes and a matrix made up of elastic fibers. Elastic cartilage is found in several parts of the body, including the external ear, the epiglottis, and the larynx. It is responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of these structures, and it is also able to withstand a great deal of stretching and bending.
In addition to these cartilages, the adult skeleton also contains several other types of connective tissues, including bone, fat, and blood. These tissues play important roles in the structure and function of the skeleton, and they work together to support and protect the body.
In conclusion, the adult skeleton is made up of several major cartilages, including the hyaline cartilage, the fibrocartilage, and the elastic cartilage. These cartilages are found in various parts of the body and play important roles in maintaining the structure and function of the skeleton.

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11130/Thorax_Thumbnail_02.png)