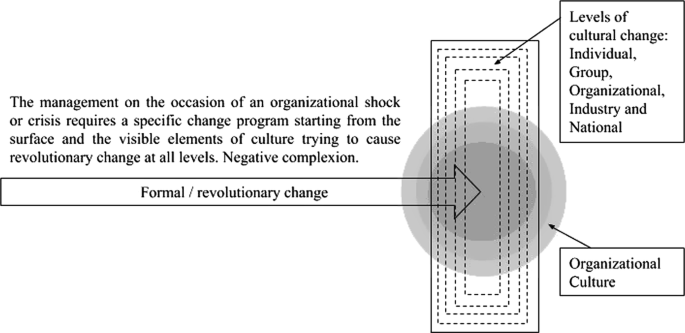
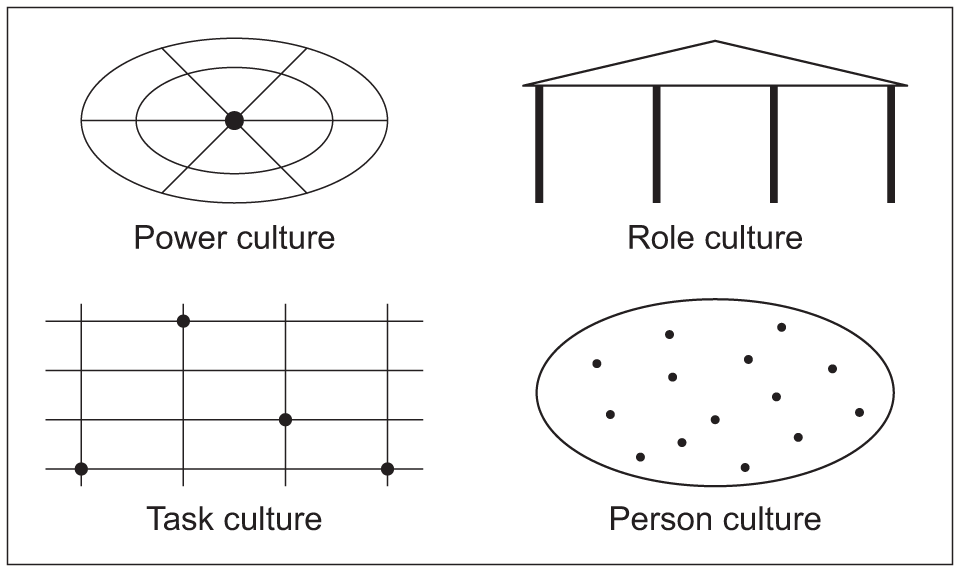
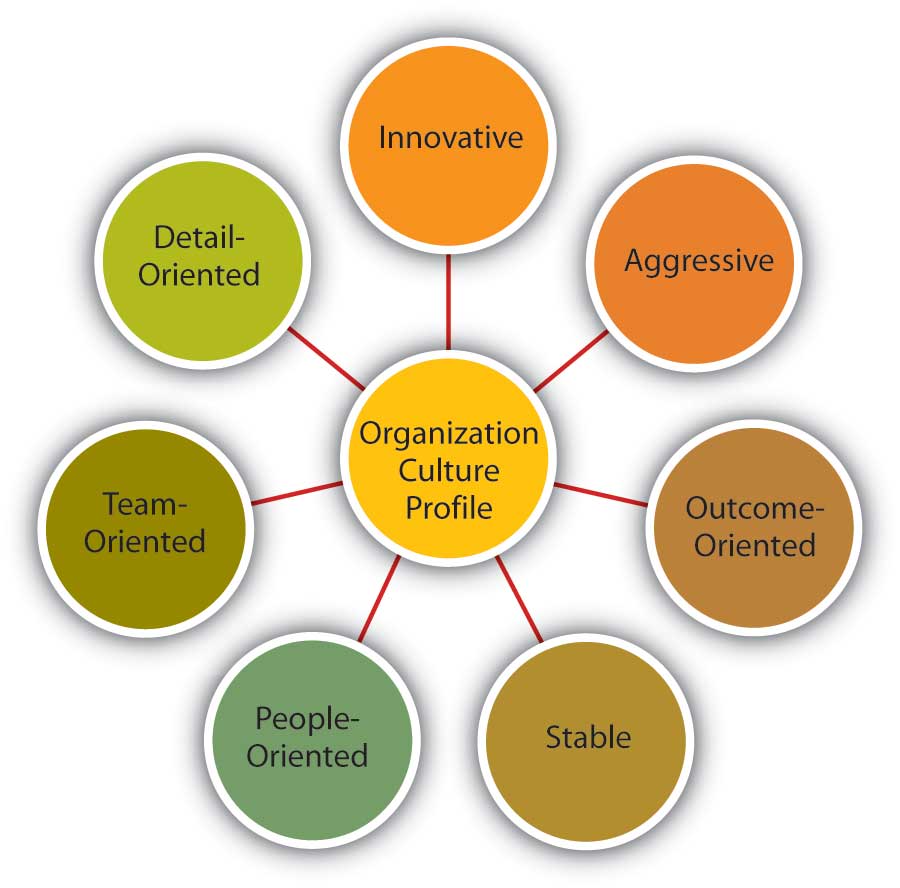
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and practices that shape the way a company operates and the behaviors of its employees. It is an important aspect of any organization as it can greatly impact the effectiveness and success of the organization. There are different levels of organizational culture, each of which can influence the overall culture of the organization.
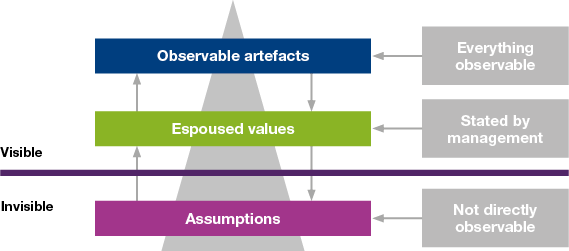
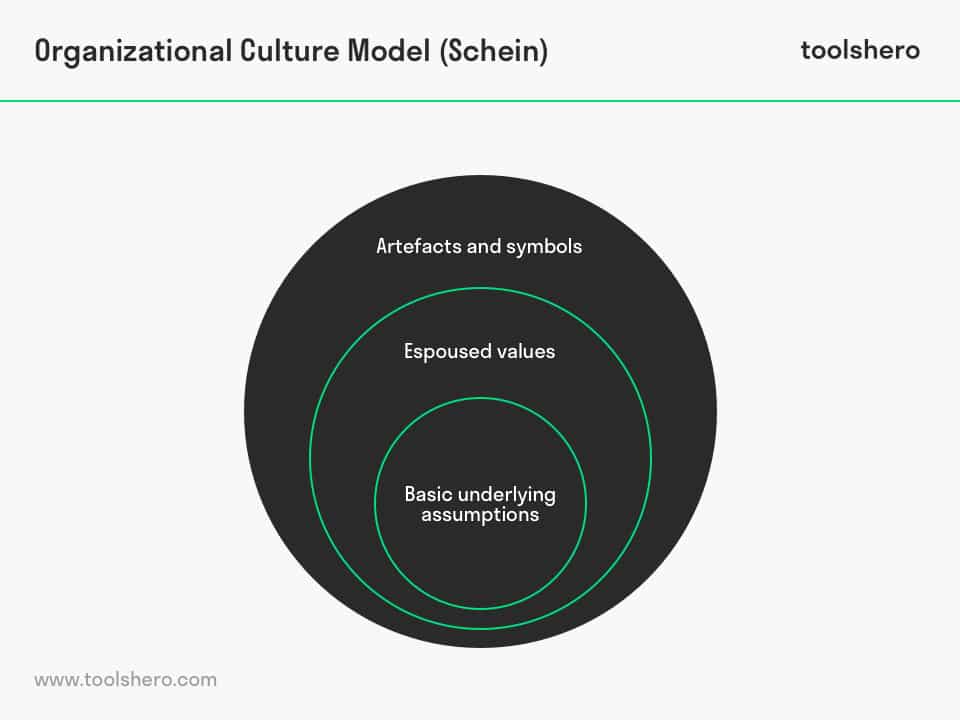
The first level of organizational culture is the surface level, which includes the visible aspects of culture such as dress code, office layout, and language. These visible elements of culture may be influenced by the industry, location, and history of the organization. While these surface-level elements of culture may seem superficial, they can still have a significant impact on the behavior and attitude of employees. For example, a company with a relaxed dress code may have a more casual and informal atmosphere, while a company with a strict dress code may have a more formal and professional atmosphere.
The second level of organizational culture is the espoused values level, which refers to the values and beliefs that the organization formally communicates to its employees and stakeholders. These values may be articulated in the company's mission statement, code of conduct, or other public documents. Espoused values are important because they serve as a guide for the behavior and decision-making of employees. For example, if a company values innovation, employees may be encouraged to take risks and think creatively in order to find new solutions to problems.
The third level of organizational culture is the enacted values level, which refers to the values and beliefs that are actually demonstrated and put into practice by the organization and its employees. This level of culture may differ from the espoused values level because the values that are actually practiced may not always align with the values that are formally communicated. For example, a company may espouse values of honesty and integrity, but if employees see managers engaging in unethical behaviors, they may begin to doubt the sincerity of the company's espoused values.
The fourth and final level of organizational culture is the basic assumptions level, which refers to the deep-seated and often unconscious beliefs and values that shape the way the organization operates. These basic assumptions may be difficult to change because they are often deeply ingrained and may not be fully understood or recognized by the organization. However, they can have a powerful influence on the behavior and attitudes of employees. For example, if an organization has a basic assumption of hierarchy and power dynamics, it may be difficult for employees to challenge authority or speak up with new ideas.
In conclusion, organizational culture is a complex and multifaceted concept that is made up of different levels, each of which can influence the overall culture of the organization. Understanding these different levels can help organizations identify areas for improvement and make changes that can positively impact the culture and success of the organization.