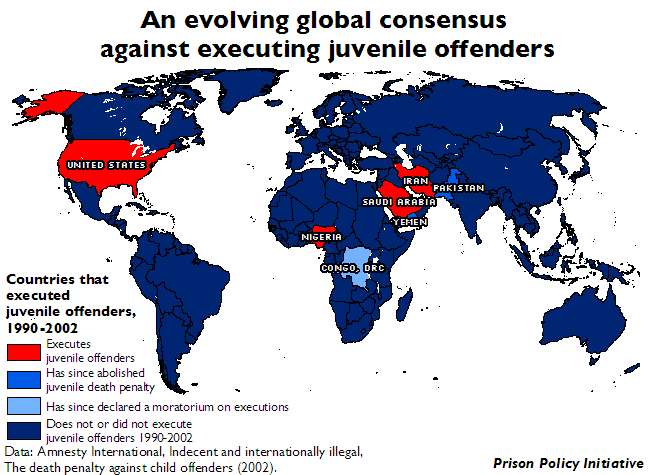
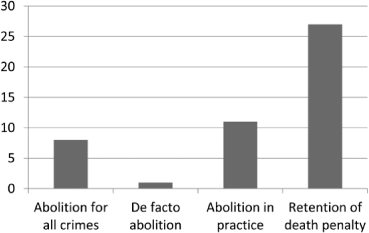
The juvenile death penalty, or the execution of individuals who were under the age of 18 at the time of their crime, has been a controversial and divisive issue for decades. On one hand, proponents of the juvenile death penalty argue that it is a necessary tool for deterrence and retribution, and that some crimes are so heinous that they merit the ultimate punishment. On the other hand, opponents of the juvenile death penalty argue that young people are still developing and are less culpable for their actions, and that the death penalty is an inhumane and ineffective form of punishment.
One argument in favor of the juvenile death penalty is that it serves as a deterrent to other young people who may be considering committing similar crimes. Some proponents argue that the threat of the death penalty can prevent future crimes by sending a strong message that society will not tolerate such actions. However, research on the deterrent effect of the death penalty is mixed, and some studies have even found that it may actually increase the rate of violent crime. Additionally, it is difficult to determine whether a potential offender was deterred by the threat of the death penalty or by other factors, such as the fear of being caught or the desire to lead a law-abiding life.
Another argument in favor of the juvenile death penalty is that it is a way to hold young people accountable for their actions and to provide justice for the victims of their crimes. Some proponents argue that certain crimes, such as murder or terrorism, are so serious that they deserve the ultimate punishment. However, others argue that the death penalty is not an effective way to provide justice or closure for victims, and that it often serves more as a form of revenge than as a means of addressing the underlying causes of crime.
There are several arguments against the juvenile death penalty. One argument is that young people are still developing and are less culpable for their actions than adults. The brain continues to develop and mature throughout adolescence and into young adulthood, and young people may not have the same level of impulse control, judgment, or understanding of the consequences of their actions as adults do. This suggests that they may be less morally responsible for their actions and less deserving of the death penalty.
Another argument against the juvenile death penalty is that it is an inhumane and ineffective form of punishment. The death penalty is often criticized for its inherent cruelty and the suffering it causes to both the condemned individual and their loved ones. Additionally, there is a risk of executing innocent people, as the criminal justice system is not perfect and mistakes can be made. There have been several cases in the United States where individuals who were sentenced to death were later found to be innocent, highlighting the potential for wrongful convictions.
In conclusion, the juvenile death penalty is a complex and controversial issue, with valid arguments on both sides. While some people believe that it is necessary for deterrence and retribution, others argue that young people are less culpable for their actions and that the death penalty is inhumane and ineffective. Ultimately, the decision of whether to use the juvenile death penalty should be guided by a consideration of these competing factors and a determination of what is in the best interests of society as a whole.

:format(webp)/https://www.thestar.com/content/dam/thestar/news/canada/2022/12/10/horrible-murders-flawed-trials-and-two-hangings-at-midnight-60-years-ago-marked-the-end-of-capital-punishment-in-canada/_1turpin_hanging_protest_turn_secondary.jpg)