An "about me" speech is a short, personal introduction that allows you to share information about yourself with your audience. It can be used in a variety of contexts, such as at a job interview, during a presentation, or as a way to introduce yourself to a group of new people.
There are a few key elements to include in an "about me" speech. First, you should start by introducing yourself and giving your name. You can also provide a brief overview of your background, including where you grew up, your education, and any notable achievements or experiences.
Next, it's important to highlight your interests and hobbies. This can help to give your audience a sense of who you are as a person and what you enjoy doing in your free time. It's also a good idea to mention any skills or expertise you have, as this can help to show your audience what you are capable of and how you might be able to contribute to a group or project.
Finally, you should conclude your "about me" speech by sharing your goals and aspirations. This can be a great way to motivate and inspire your audience, as well as to give them a sense of what you are working towards.
Here's an example of an "about me" speech:
Hi, my name is [Name] and I'm from [City/State]. I grew up in a small town and always had a love for learning. I received my bachelor's degree in [Field of Study] from [University] and have since worked in a variety of roles related to my field of study. In my free time, I enjoy hiking, reading, and playing the piano. I'm also an avid fan of science fiction and fantasy novels.
One of my biggest passions is using my skills and expertise to make a positive impact in the world. I believe that education is the key to unlocking our full potential and I'm always looking for new ways to contribute to my community. My goal is to eventually become a teacher and inspire the next generation of leaders and innovators.
Thank you for taking the time to get to know me. I'm excited to be a part of this group and hope to contribute in any way that I can.
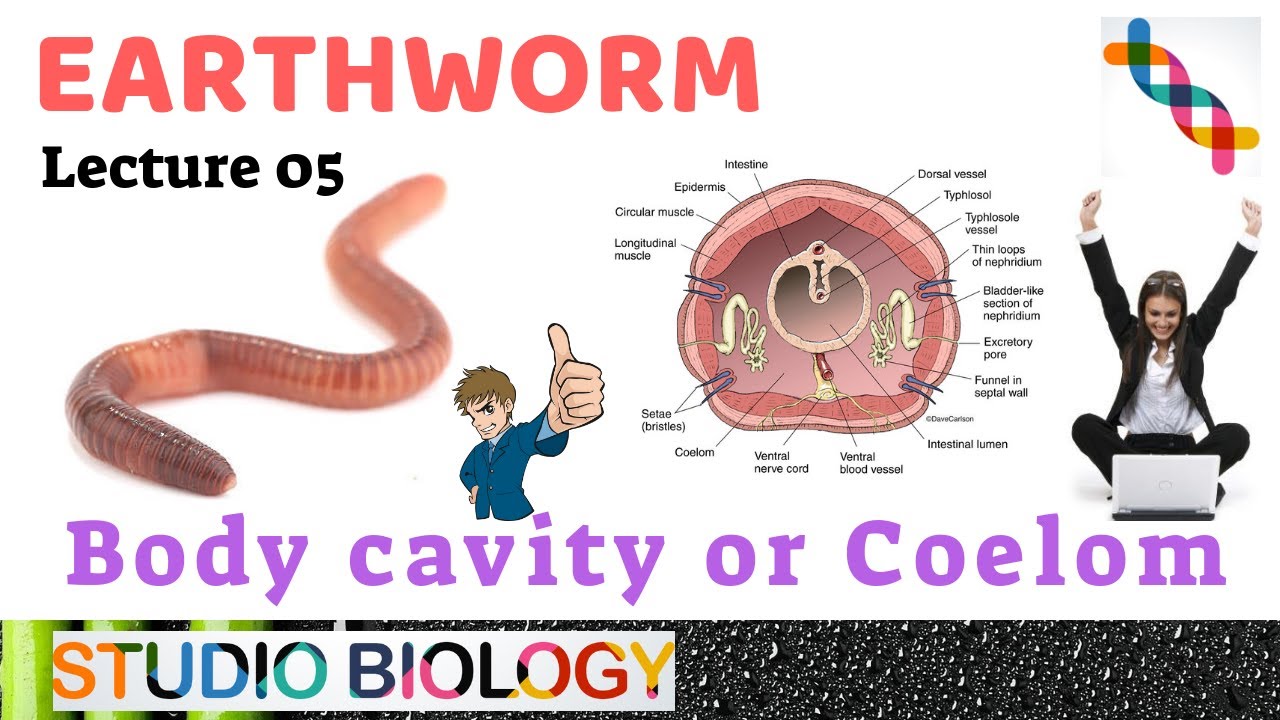
Explain the body cavity or coelom in animals.
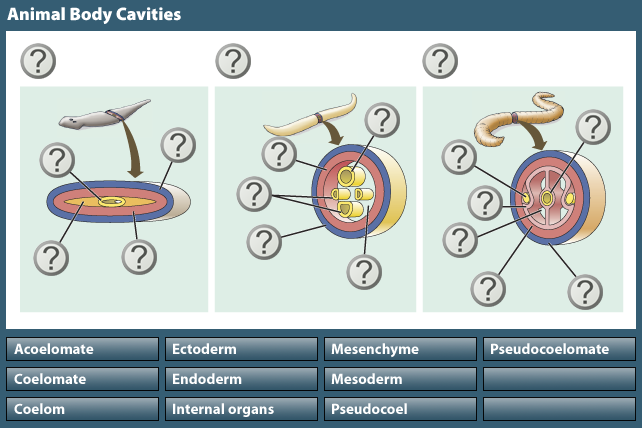
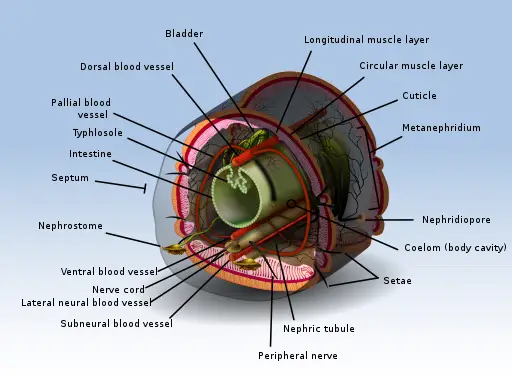
Triplobastic animals have 3 cell layers in their bodies, Ectoderm Outer layer Mesoderm middle layer and Endoderm inner layer. In some animals, such as worms, the coelom acts as a skeleton. Although the coelomic cavity is not found in adult human individuals it is seen in embryonic stages. The peritoneal cavity present in the abdomen and similar spaces around other organs such as lungs, heart are parts of the coelom. Function The coelom has numerous functions, the first of which involves acting as a cushion for the internal organs of the organism. Their third muscle type, called parenchymal muscle running through the vertical plane of their bodies, connecting the top tissue to the bottom can be contracted to create a wave-like motion down the length of their body.
ORGANIZATION OF COELOM
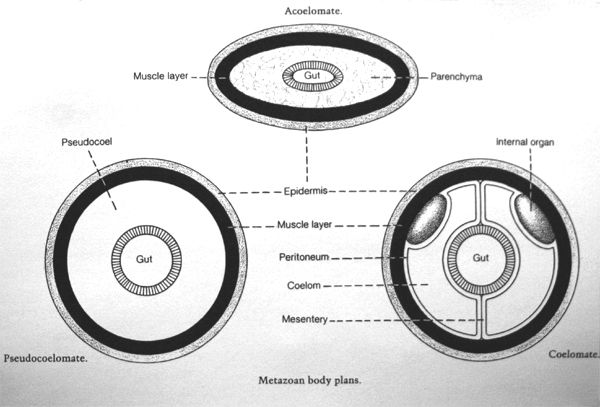
The coelom of an earthworm comprises phagocytes, mucus-secreting cells, yellow cells, and circular cells with a nucleus. This leads to the formation of pouches or pocket-like structures that form a cavity. Eucoelomate: Animals that have a true coelom. During the accident, the coelom, or your body cavity, helped to prevent further damage by cushioning your organs. When they meet and fuse, they completely separate the endoderm and ectoderm. This incapacitates thephysiological lower esophageal sphincter,allowing the contents of the stomach to reflux into the esophagus.
Platyhelminthes: Body Cavity & Movement

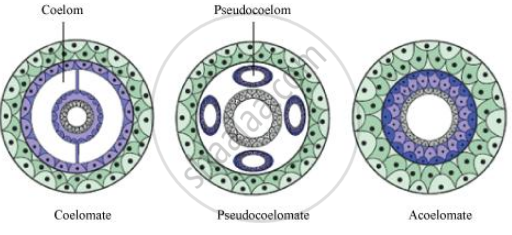
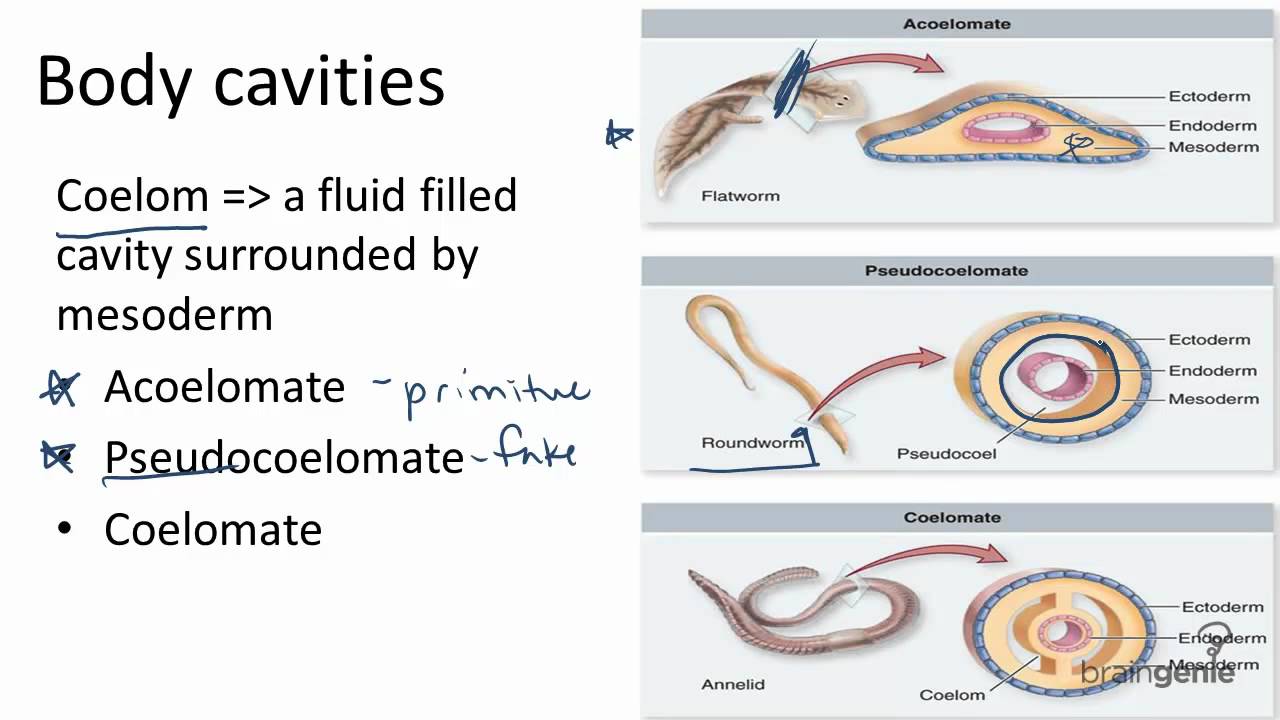
What are the two types of coelomic cavity? A coelom is a hollow, fluid-filled cavity found in many living things, where it acts as a protective cushion for their internal organs. The advantages of the coelom in animals include the fact that the coelom, a cavity filled with fluid around the organs, provides a hydrostatic skeleton to aid movement, and allows for more efficient circulation of nutrients and removal of wastes. During the accident, the coelom, or your body cavity, helped to prevent further damage by cushioning your organs. Porifera, Coelenterata and Flatworms Platyhelminthes. It forms from the three germinal layers during embryonic development. Coeloms arise in two different ways.