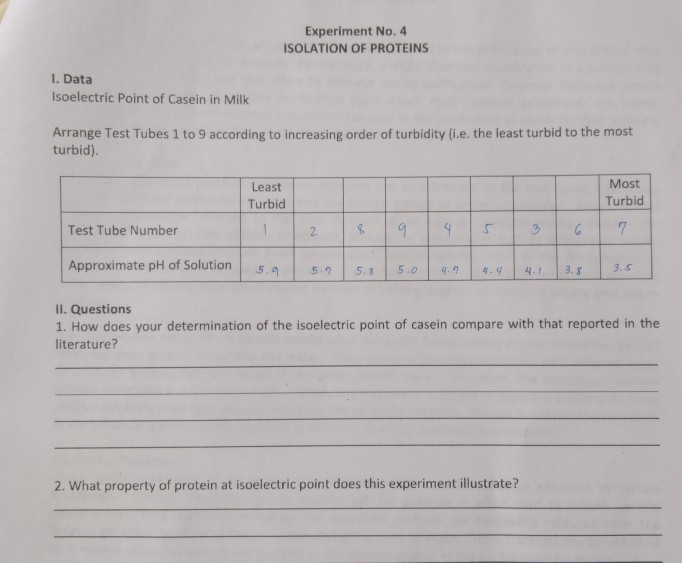
The isoelectric point (pI) of a substance is the pH at which it has a net zero charge. For proteins, this means that the number of positively charged amino acids is equal to the number of negatively charged amino acids, resulting in a neutral charge overall. The isoelectric point can be important in various applications, including protein purification, enzyme activity, and food processing.
Milk is a complex mixture of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, and other substances, and it is not uncommon for milk proteins to have an isoelectric point. In fact, milk contains several different types of proteins, each with its own unique isoelectric point.
One of the main proteins found in milk is casein, which makes up about 80% of the protein content. Casein has an isoelectric point of around 4.6, which means that it has a negative charge at pH values below 4.6 and a positive charge at pH values above 4.6. Casein is a phosphoprotein, which means that it contains phosphorous in its structure. The negatively charged phosphorous groups contribute to the overall negative charge of casein at pH values below 4.6.
The other main protein found in milk is whey protein, which makes up the remaining 20% of the protein content. Whey protein has a higher isoelectric point than casein, at around pH 6.5. This means that it has a positive charge at pH values below 6.5 and a negative charge at pH values above 6.5.
The isoelectric point of milk is influenced by the pH of the milk, which is typically around 6.5-6.7. At this pH, both casein and whey proteins are negatively charged. This can be important in food processing, as the negative charge of milk proteins can help them bind to each other, forming a stable structure. For example, in the production of cheese, the negative charge of milk proteins can help them coagulate and form a solid curd.
In summary, milk is a complex mixture of proteins, each with its own unique isoelectric point. The isoelectric point of milk is influenced by the pH of the milk, which is typically around 6.5-6.7. The isoelectric point of milk proteins can be important in various applications, including protein purification, enzyme activity, and food processing.
Isoelectric Focusing of Bovine Milk Caseins
New bonds are formed, one of the salt type, where calcium is active, and the second of the hydrophobic type. Add equal volume of water to the skimmed milk. The series of reactions, occurring between amino groups of amino acid residues and aldehyde groups from milk carbohydrates, is called the Maillard reaction or browning reaction. It is, however, clear that this repulsion is not sufficient to stabilize the proteins. To determine the pI that is the pH value at which the estimated charge is zero, we estimated an initial pH at which the overall charge of the protein is positive and one where the charge is negative.
Isoelectric Precipitation of Proteins

See PECTIN Food Use. PROTEIN IDENTIFICATION There are two methods that are commonly used to identify proteins: Edman Degradation and Mass Spectrometry. The salting-out phenomenon is often related to the interaction between ions and water molecules, since at higher salt concentrations, there would be no more exposed charged residues without the corresponding counter-ion condensation. Streptavidin contains no carbohydrates, which if present can bind nonspecifically to lectin-like substances found in normal tissue from kidney, liver, brain, and mast cells. At low pH, the proteins are positively charged, and are strongly attracted to a negatively charged surface. After a weak denaturation, proteins can sometimes revert to their original state, with restoration of their biological functions.
Formula for isoelectric point? Explained by FAQ Blog
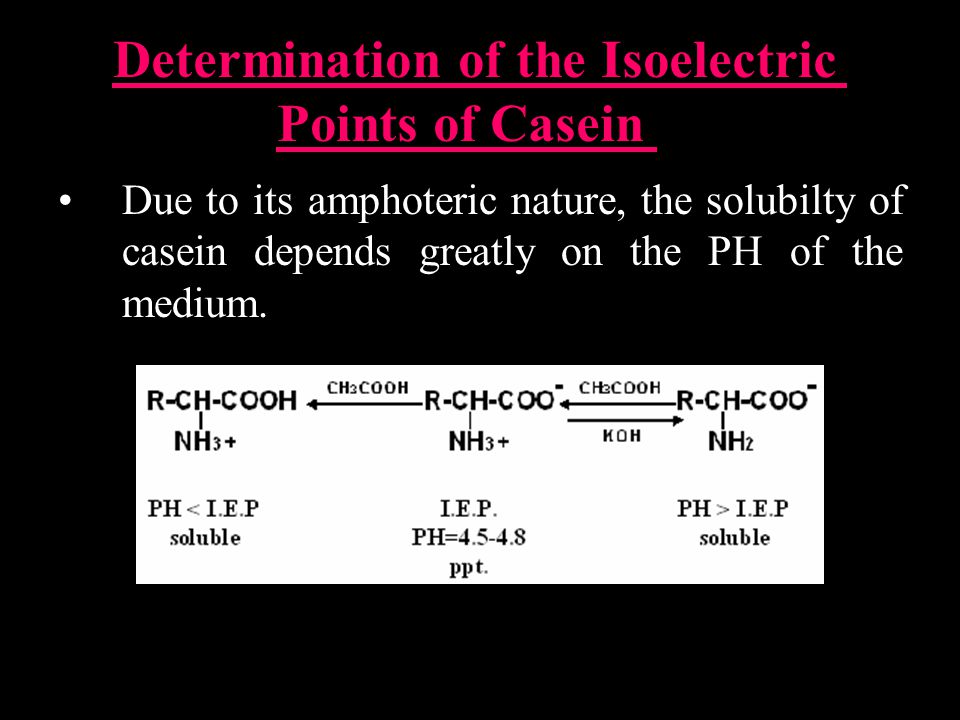
The vial is sealed with a screw cap, and the sample is re-extracted an additional hour while stirring at 1500rpm. The following description refers mainly to precipitation of micellar casein. Transfer the skimmed milk into a 500 ml glass beaker. Usually, an increase in temperature results in an increase in solubility for nonbiological solutes and, while the same tendency is observed for protein solubility, the opposite behavior, known as retrograde behavior, is not rare. Minimum solubility values for any salt are at a pH of 5. We believe the more sour it is, then the pH level would be lower leading for it to be more acidic, so buttermilk would be the most acidic.