Amylase is a type of enzyme that plays a key role in the digestion of carbohydrates. It is found in the saliva of mammals, as well as in the pancreas and small intestine, and is responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars that can be absorbed and used by the body for energy.
The structure of amylase is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the enzyme. These amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds, forming a long chain. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape and function of the enzyme, as well as its ability to bind to specific substrate molecules.
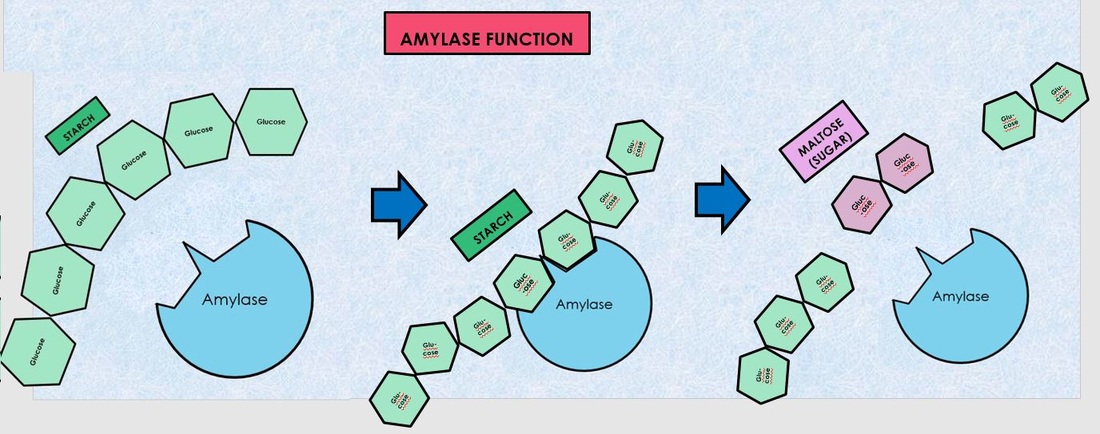
Amylase is a type of hydrolase enzyme, which means it breaks down chemical bonds by adding water molecules to them. In the case of amylase, it breaks down the bonds between glucose molecules in complex carbohydrates, such as starch, to produce simpler sugars like maltose and glucose.
Amylase has a specific structure that allows it to bind to starch molecules and break down the bonds between the glucose units. The enzyme contains a specific pocket or active site, where the substrate molecule fits and is broken down. The active site is made up of specific amino acids that interact with the substrate and facilitate the chemical reaction.
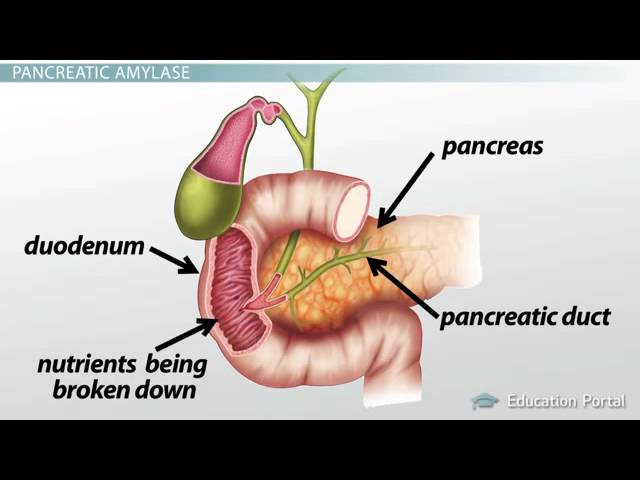
The function of amylase is to digest carbohydrates, which are an important source of energy for the body. When we eat foods that contain carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and potatoes, the amylase in our saliva begins breaking down the complex carbs into simpler sugars. The amylase from the pancreas and small intestine continues this process, breaking down the carbs into even simpler sugars that can be absorbed by the body and used for energy.
In summary, amylase is a type of enzyme that plays a crucial role in the digestion of carbohydrates. It has a specific structure, consisting of a sequence of amino acids that determines its shape and function, and an active site where it binds to and breaks down complex carbs into simpler sugars. The function of amylase is to aid in the digestion of carbs and provide the body with energy.
Amylase and Cellulase Structure and Function
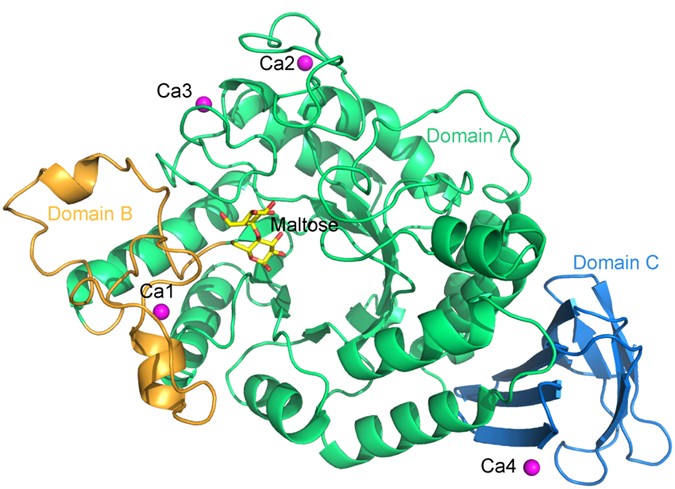
The amylase chain is made up of 496 amino acids. What is the function of trypsin? Within hepatocytes it joins with glucuronic acid to form conjugated bilirubin, which is water-soluble. They are widely used in the production of value-added food ingredients and food processing for improving the functional, nutritional and flavor properties of proteins. When the chain folds due to intermolecular interactions, the result is three distinct areas called domain A, domain B, and domain C. Originally it was called distaste, but the name was eventually changed in the early 1900s. What are the products of pepsin? Tightly folded polypeptide chains cause these globular shapes.
Amylase: Definition, Example and Structure
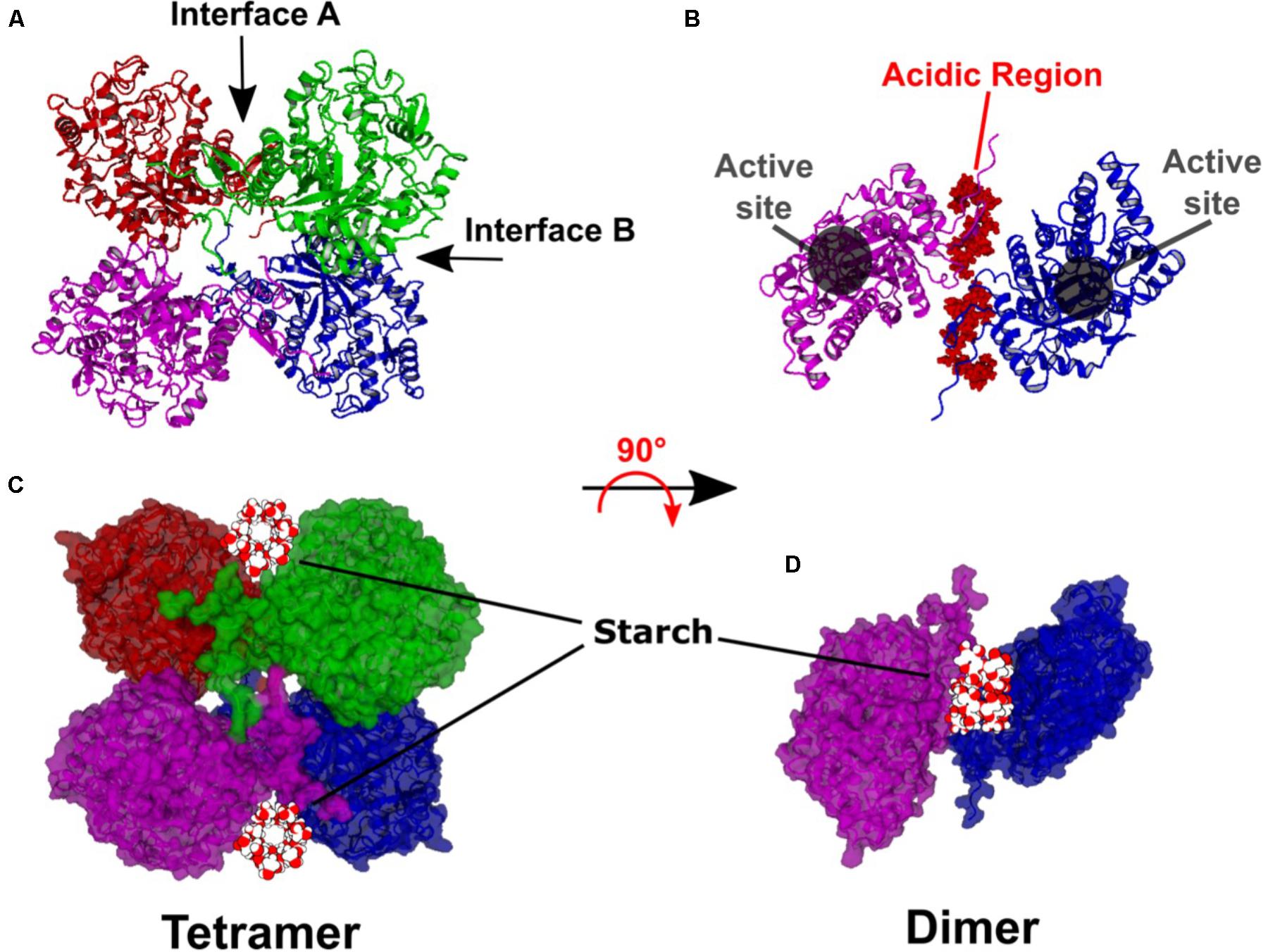
What is the end product of amylase? Parietal cells within the stomach lining secrete hydrochloric acid that lowers the pH of the stomach. This is the reason for long fermented doughs such as sourdough. The amylase enzyme collides with starch molecules and forms an enzyme-substrate complex. This test measures the amount of amylase in the blood or urine or sometimes in peritoneal fluid, which is fluid found between the membranes that cover the abdominal cavity and the outside of abdominal organs. The same enzyme can be used to form smaller molecules from a larger molecule or to do the opposite. The resulting products of amylase acting on starch, referred to as dextrins, are -1,4-linked glucose dimers maltose , -1,4-linked glucose trimers maltotriose , and branched oligosaccharides of 6 to 8 glucose units that contain both -1,6 and -1,4 linkages limit dextrins.
Salivary Amylase Function & Structure
Amylose consists of a linear, helical chains of roughly 500 to 20,000 alpha-D-glucose monomers linked together through alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds. ANS: D The liver has hemostatic functions. In: The enzymes, vol 5. What is the main function of salivary amylase? Amylase- Its clinical significance: a Review of the Literature. Thickness perception of starch-thickened products during eating has been linked to starch viscosity and salivary amylase activity. Furthermore, the traditional classification is related to the stereochemistry of their reaction products, so these proteins with enzymatic activity are also classified as α-amylases, β-amylases or γ-amylases. It breaks down complex carbohydrates into smaller, simple sugars, making them more accessible for the body to digest.