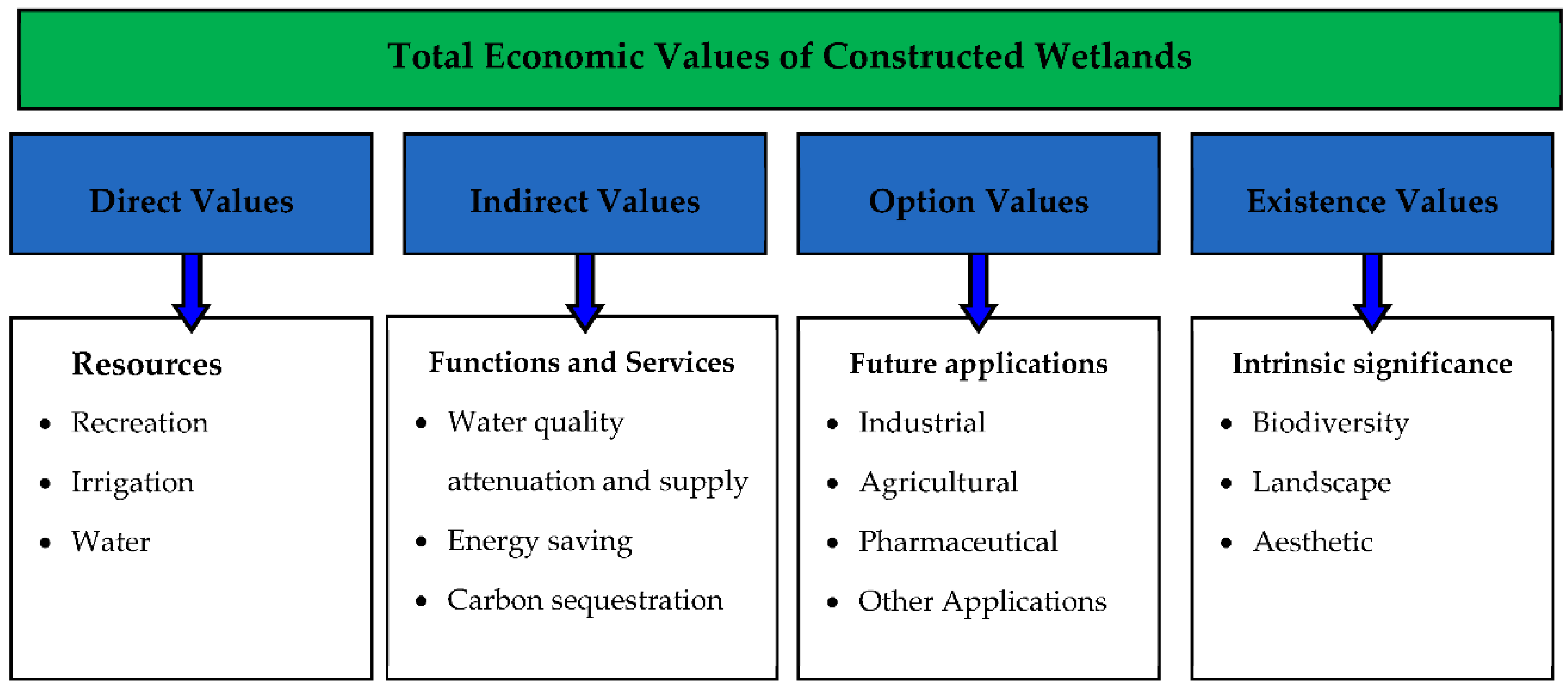
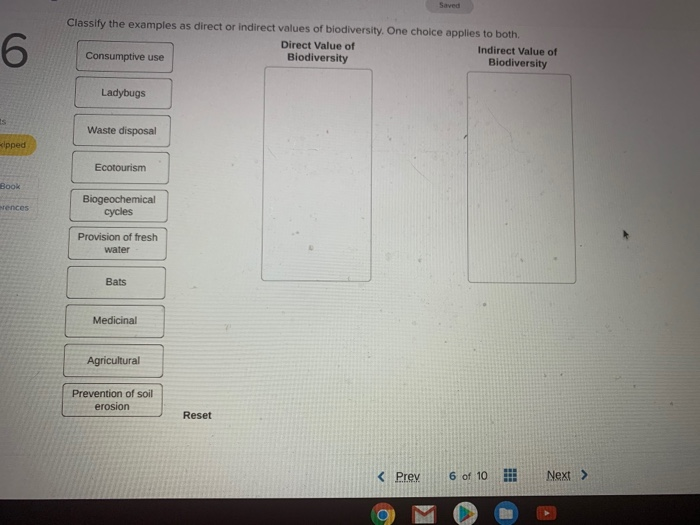
Biodiversity, or the variety of plant and animal life in a given area, is often valued for its intrinsic worth and the ecological functions it performs. However, biodiversity also has a number of indirect values that are often overlooked or underappreciated. These values can be grouped into three categories: cultural, economic, and social.
Cultural values refer to the non-material benefits that people derive from biodiversity, such as aesthetic enjoyment, spiritual fulfillment, and the sense of place and connection to nature that it provides. For example, people may visit natural areas to view wildlife, take photographs, or participate in recreational activities like hiking and birdwatching. These activities contribute to the cultural value of biodiversity and can also have positive impacts on mental health and well-being.
Economic values refer to the tangible benefits that biodiversity provides to human society, such as the goods and services it produces. For example, biodiversity is the source of many of the world's food crops, and it also supports industries like forestry, agriculture, and fishing. In addition, biodiversity can provide economic benefits through ecotourism, which relies on the presence of unique and diverse plant and animal life to attract visitors.
Social values refer to the intangible benefits that people derive from biodiversity, such as the sense of community and social cohesion that it can foster. For example, people may come together to participate in conservation efforts or to enjoy nature together, which can strengthen social bonds and foster a sense of community. Biodiversity can also play a role in traditional cultural practices and rituals, which can help to preserve cultural identity and transmit cultural knowledge from one generation to the next.
Overall, the indirect values of biodiversity are diverse and multifaceted, and they highlight the many ways in which biodiversity enriches human society and culture. Protecting biodiversity is not only important for the health of the planet, but also for the well-being of people and the communities they live in.