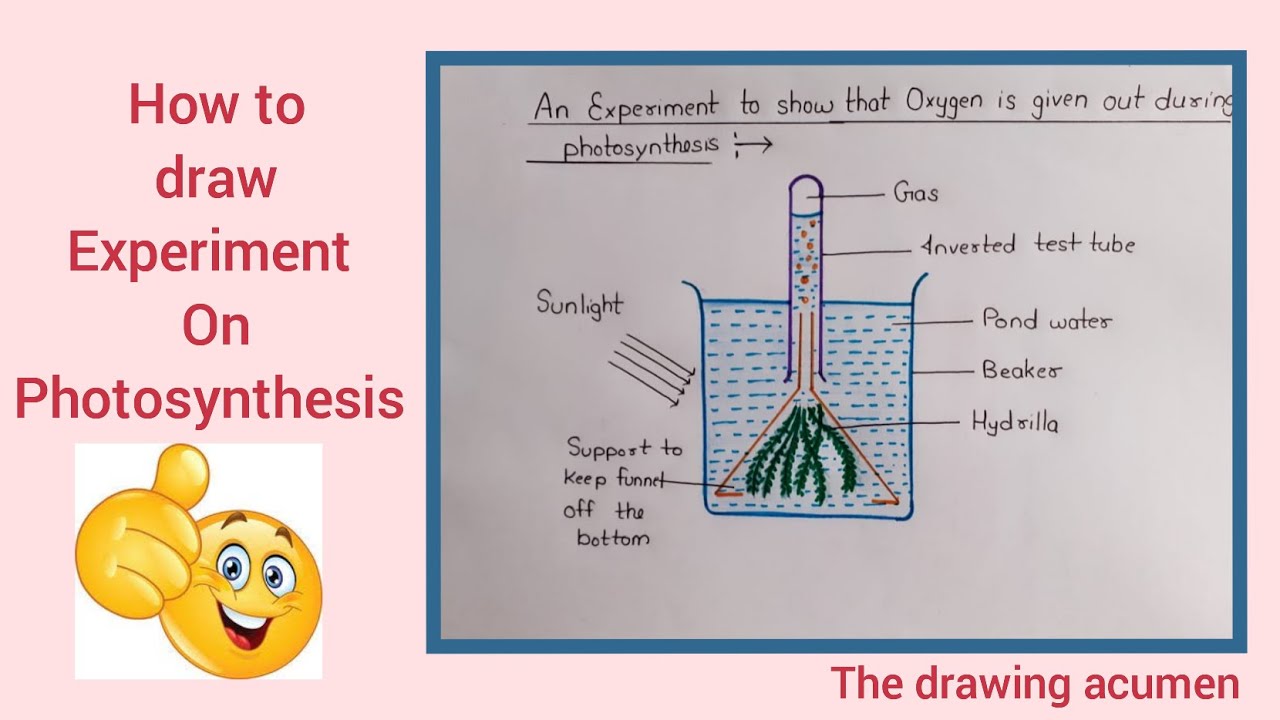
Hydrilla, also known as Hydrilla verticillata, is a submerged aquatic plant native to Asia and widely introduced as an ornamental plant in the United States. It is an invasive species that has caused significant ecological and economic damage in many parts of the world due to its ability to outcompete native plants and form dense monocultures. Despite its negative impacts, hydrilla is a fascinating plant that has adapted to life in aquatic environments through unique mechanisms of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy through the production of glucose. In terrestrial plants, photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which contain pigments called chlorophylls that absorb light energy. The energy is used to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen through a series of chemical reactions.
Hydrilla, like other aquatic plants, also performs photosynthesis in its chloroplasts, but it has adapted to its submerged environment in several ways. One adaptation is the presence of additional pigments called carotenoids and xanthophylls, which absorb light at different wavelengths and help the plant absorb more light energy. These pigments are particularly important in low light conditions, such as in deep water or during cloudy weather, when light intensity is reduced.
Another adaptation of hydrilla is its ability to perform a type of photosynthesis called "C4 photosynthesis." This type of photosynthesis is more efficient than the "C3 photosynthesis" used by most terrestrial plants, as it allows the plant to better capture and use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. C4 photosynthesis involves the separation of the carbon dioxide fixation and glucose synthesis steps, which allows the plant to better regulate the concentration of carbon dioxide in the chloroplasts and improve the efficiency of photosynthesis.
In addition to these adaptations, hydrilla has also developed mechanisms to overcome the challenges of living in an aquatic environment. For example, it has a highly developed system of vascular tissue that transports water and nutrients throughout the plant, and it has the ability to take up nutrients directly from the water through its roots. It also has a flexible stem and the ability to regenerate from small fragments, which allows it to survive in fluctuating water levels and adapt to different aquatic environments.
In conclusion, hydrilla is a fascinating plant that has adapted to life in aquatic environments through unique mechanisms of photosynthesis. Its ability to perform C4 photosynthesis, absorb light at different wavelengths, and transport water and nutrients throughout the plant make it well-suited to life in the water. However, its invasive nature and ability to outcompete native plants has made it a major threat to many aquatic ecosystems, and efforts are being made to control and manage its spread.