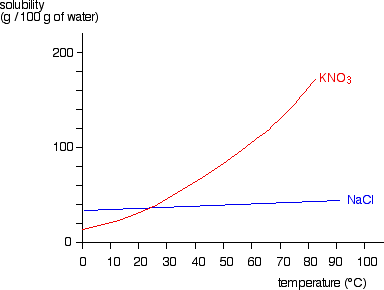
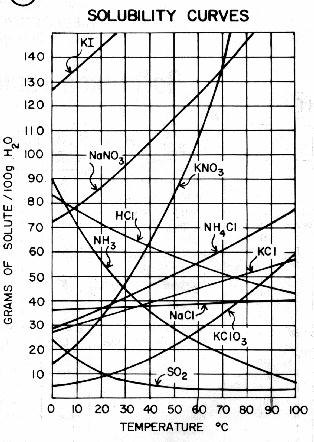
Solubility is the amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a solvent to form a homogeneous solution. It is an important concept in chemistry and is affected by various factors, including temperature. In this essay, we will explore how solubility changes with temperature and the underlying principles behind this phenomenon.
As a general rule, solubility increases with temperature. This means that as the temperature of the solvent increases, the amount of solute that can be dissolved in it also increases. This is due to the fact that the kinetic energy of the particles in the solvent increases with temperature, allowing them to break the attractive forces between the solute particles and dissolve them more easily.
One example of this is the solubility of gases in liquids. Gases are generally more soluble in liquids at higher temperatures because the increased kinetic energy allows the gas particles to more easily overcome the attractive forces between the liquid particles and dissolve into the solvent. This is why carbonated beverages are more fizzy when they are cold – the solubility of the gas (usually carbon dioxide) in the liquid is lower at lower temperatures.
On the other hand, solubility of solids in liquids generally decreases with temperature. This is because the solute particles become more energetic as the temperature increases, and they are able to break the attractive forces between themselves and the solvent more easily. As a result, they tend to come out of solution and form a solid precipitate.
There are some exceptions to these general trends. For example, the solubility of certain gases, such as oxygen, in water decreases with temperature. This is because the solubility of gases in water is also influenced by the solute-solvent interactions, and the solubility of oxygen in water decreases as the temperature increases due to the increased repulsive forces between the oxygen and water molecules.
In summary, solubility is affected by temperature, with solubility generally increasing with temperature for gases in liquids and decreasing with temperature for solids in liquids. Understanding the relationship between solubility and temperature is important in a variety of fields, including chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.