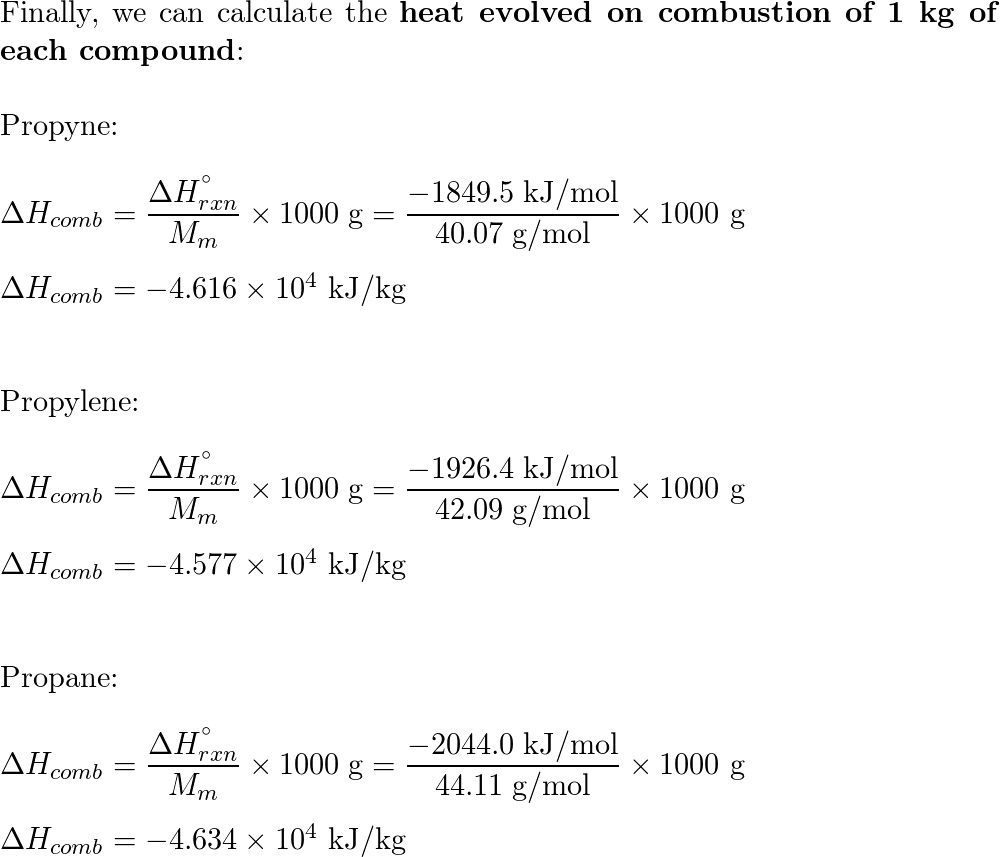Heat evolved during combustion is the heat energy that is released during the process of burning a substance. This process is also known as exothermic reaction, as it releases heat to the surroundings.
Combustion is a chemical reaction that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. It is a common occurrence in our daily lives, as we rely on combustion to provide heat and light for our homes, cook our food, and power our vehicles.
The heat evolved during combustion is a measure of the energy released during the reaction. It is typically measured in units of energy per unit of mass, such as calories or joules per gram. The heat of combustion can be determined by measuring the temperature change of the surroundings during the reaction.
The heat of combustion is an important property of a substance, as it can be used to determine the amount of energy that can be obtained from burning it. For example, fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are commonly used to generate electricity, and the heat of combustion is used to calculate the amount of electricity that can be produced from a given amount of fuel.
There are several factors that can affect the heat of combustion of a substance. One of the main factors is the chemical composition of the substance. Different substances have different chemical bonds, and the energy required to break these bonds can vary significantly. As a result, different substances will release different amounts of heat during combustion.
Another factor that can affect the heat of combustion is the amount of oxygen available for the reaction. If there is not enough oxygen present, the reaction may not be complete, and the heat of combustion will be lower. On the other hand, if there is excess oxygen, the reaction may be more complete, and the heat of combustion will be higher.
In conclusion, heat evolved during combustion is the heat energy released during the process of burning a substance. It is an important property of a substance and is used to determine the amount of energy that can be obtained from burning it. The heat of combustion can be affected by the chemical composition of the substance and the amount of oxygen available for the reaction.