Pepsin is an enzyme that plays a key role in the digestion of proteins in the human body. It is produced and secreted by the chief cells of the stomach, and is found in high concentrations in the gastric juice that is produced by the stomach.
The main function of pepsin is to break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids, which can then be absorbed and used by the body for various purposes. It does this by hydrolyzing the peptide bonds that hold the amino acids in a protein molecule together. This process is known as proteolysis.
Pepsin is activated by hydrochloric acid (HCl), which is also produced by the stomach. HCl helps to create an acidic environment in the stomach that is ideal for pepsin to function optimally. The pH of the stomach is typically around 2, which is much more acidic than the pH of the rest of the digestive system. This low pH is necessary for pepsin to work effectively, as it is only active at pH values below 6.
Pepsin is activated by HCl in the stomach, and begins to break down proteins as soon as they enter the stomach. This process is important because it helps to make the proteins more accessible to the other enzymes in the digestive system, which can then break them down further into their individual amino acids.
In addition to its role in protein digestion, pepsin has also been shown to have other functions in the body. It has been suggested that pepsin may play a role in immune system function, and may also have anti-inflammatory effects.
Overall, the function of pepsin in gastric juice is essential for the proper digestion and absorption of proteins in the human body. Without pepsin and the other enzymes in the digestive system, the body would be unable to effectively break down and utilize the proteins that it consumes, leading to malnutrition and other health problems.
Pepsin Function, Production & Mechanism

What functional groups must be present to confer this pI on pepsin? How many amino acids does pepsin have? The gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus. Immediately following a meal, pepsin and HCI secretion are increased. The strong acidity of the stomach denatures the proteins from ingested food, thereby increasing the exposure of the peptide bonds of protein. This facilitates consumption of large quantity of food. After being endocytosed, the enzyme sticks to laryngeal cells, depletes their defenses, and intensifies internal damage. Gastric juice has a low PH and naturally highly acidic and watery. Following a meal, kidney excretes more of alkaline urine for short period to maintain the pH of blood.
What group does pepsin belong to?
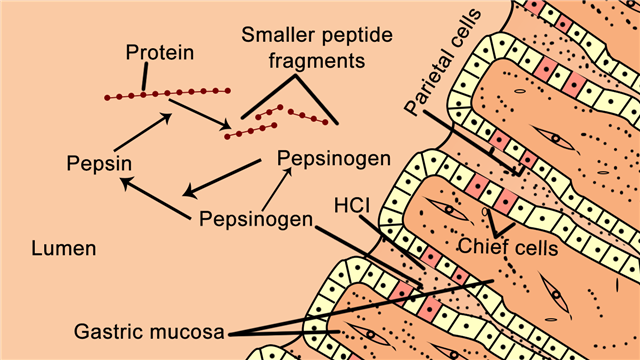
Since the primary function of pepsin is related to protein digestion, a lack of pepsin will lead to some disorders. Pepsinogen reacts with stomach acid, or hydrochloric acid, and becomes the active enzyme — pepsin. Gastric juice helps in the excretion of some heavy metals, alkaloids, and toxins. Pepsin shows maximum activity at pH 2. Acid in the pyloric antrum b. This is nothing but conversion of soluble caseinogen into insoluble calcium caseinate.
Pepsin

The cardiac gastric glands are located at the very beginning of the stomach; the intermediate, or true, gastric glands in the central stomach areas; and the pyloric glands in the terminal stomach portion. Besides activating pepsinogen into pepsin, hydrochloric acid, or gastric acid, it also helps unfold the protein that still has its 3D structure. Movements of the stomach help in mixing the food with the gastric juice. This juice is highly acidic because of its hydrochloric acid content, and it is rich in enzymes. One of the pepsin applications is in the food industry, wherein the enzyme is used for curdling milk in cheese-making. The parietal cells or the oxyntic cells that secrete the hydrochloric acid.






