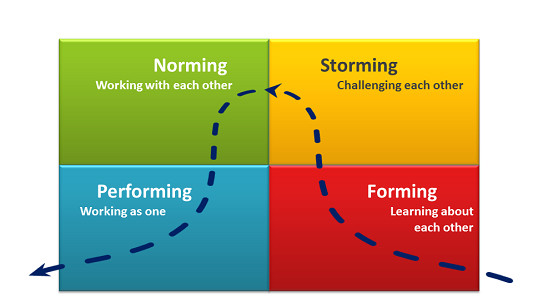
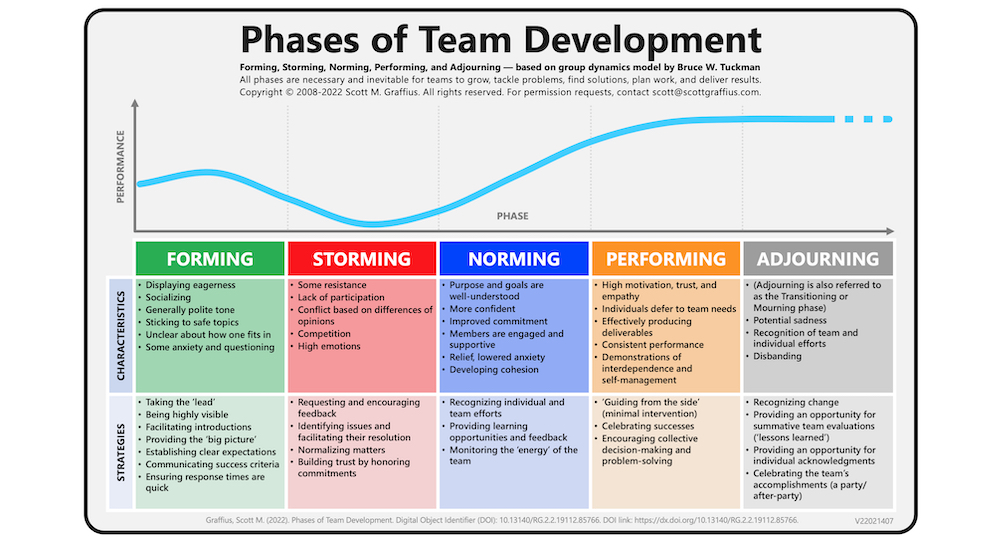
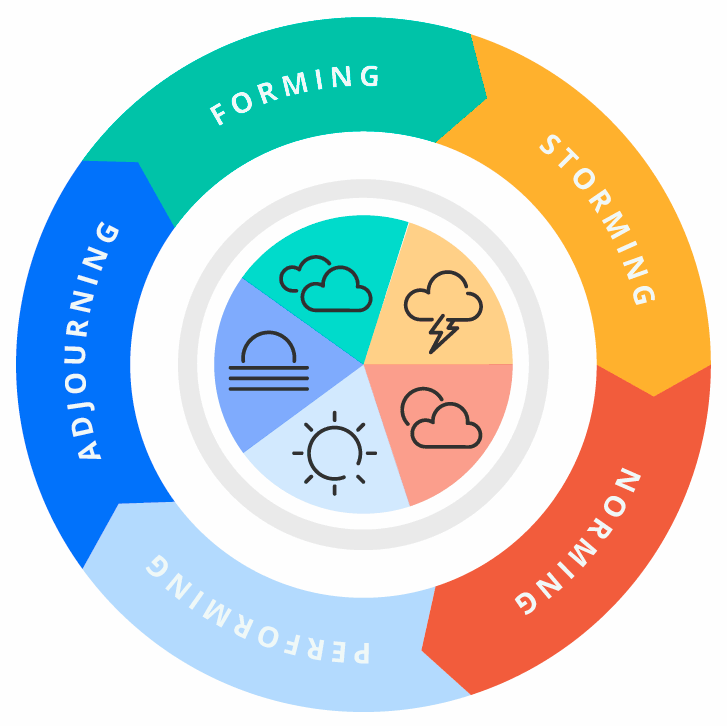
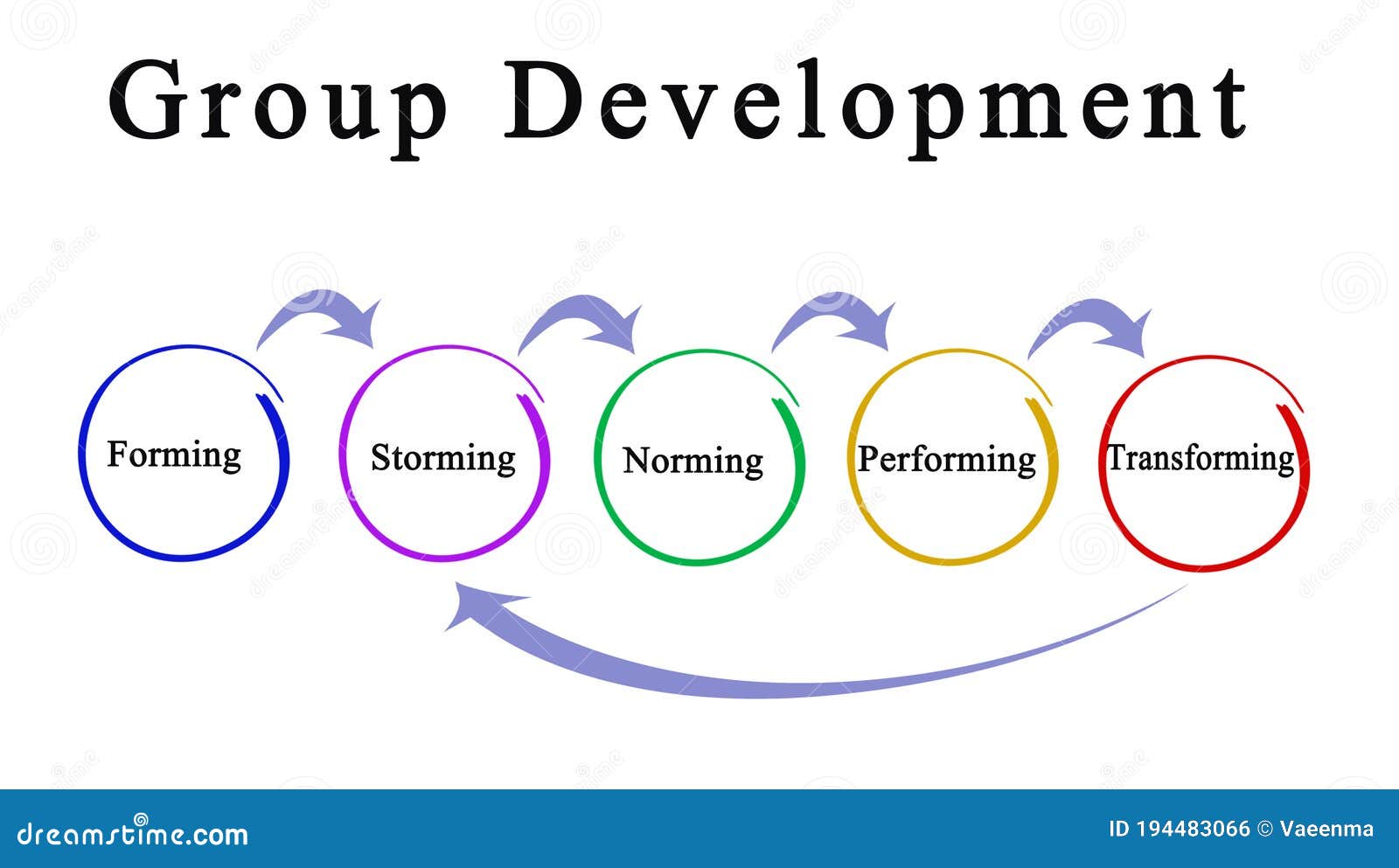
Forming, storming, norming, and performing are stages of group development, first proposed by psychologist Bruce Tuckman in 1965. These stages describe the typical progression of a group as it comes together, works through conflicts and challenges, establishes its norms and expectations, and becomes a high-performing team. Understanding and navigating these stages can be crucial for group leaders and members as they work towards achieving their goals.
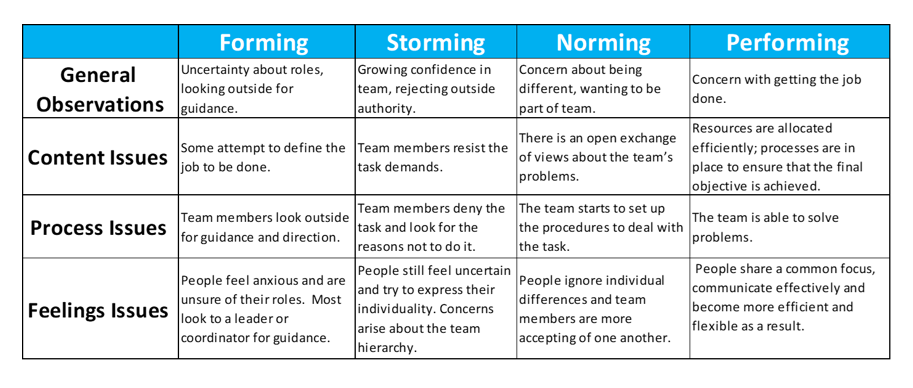
The first stage of group development is forming. During this stage, group members are just getting to know each other and establishing initial relationships. They may be somewhat tentative and reserved, as they are still getting a sense of the group dynamic and their own roles within it. At this point, the group is largely dependent on the leader for direction and guidance.
The second stage is storming. During this stage, group members may begin to challenge the leader and each other as they work to establish their roles and clarify their goals. There may be conflict and disagreement as group members assert their own ideas and perspectives. It is important for the leader to facilitate open communication and encourage healthy conflict resolution during this stage.
The third stage is norming. As the group begins to work through its conflicts and establish its norms and expectations, it enters the norming stage. Group members become more cohesive and begin to work together more effectively. They establish trust and respect for one another and develop a shared sense of purpose.
The final stage is performing. At this point, the group has developed a high level of trust, respect, and cooperation. It is able to work effectively and efficiently towards its goals, and is able to handle conflicts and challenges as they arise. The group has become a high-performing team.
It is important to note that these stages are not always linear, and a group may move back and forth between stages or skip certain stages altogether. It is also important for group leaders to be aware of these stages and to provide support and guidance as the group progresses through them. By understanding and navigating the stages of group development, leaders and members can work towards building a strong, cohesive, and high-performing team.




.png?format=1000w)