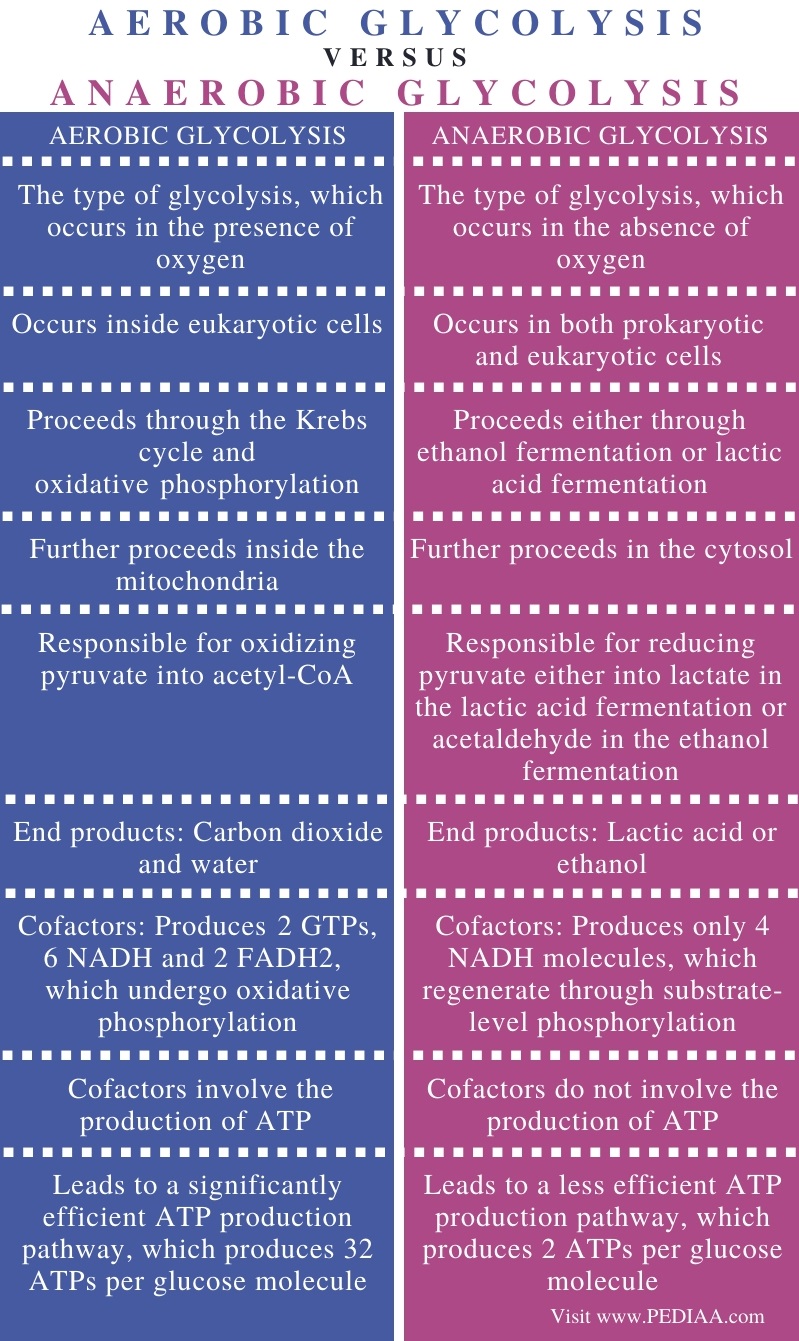
Aerobic respiration is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the cells of organisms and is essential for the production of energy. It involves the breakdown of glucose, a simple sugar, into smaller molecules through a series of chemical reactions that release energy. The final product of aerobic respiration is a combination of water, carbon dioxide, and energy.
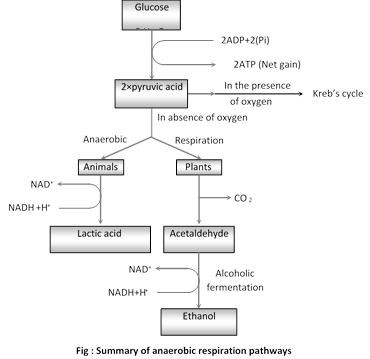
Aerobic respiration begins with the process of glycolysis, in which glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. This process occurs in the cytosol, or fluid-filled region, of the cell and does not require oxygen. However, the energy produced during glycolysis is relatively low compared to the energy that can be obtained through the complete breakdown of glucose.
To obtain the maximum amount of energy from glucose, the pyruvate produced during glycolysis must be further broken down through the process of aerobic respiration. This process takes place in the mitochondria, the energy-producing structures within cells.
During aerobic respiration, pyruvate is converted into a molecule called acetyl-CoA and enters the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA then undergoes a series of reactions known as the citric acid cycle, or the Krebs cycle, which results in the production of ATP, the energy-carrying molecule used by cells.
The citric acid cycle also produces carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. The carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere through the process of respiration, while the water is a product of the chemical reactions that occur during the citric acid cycle.
Overall, the final product of aerobic respiration is a combination of water, carbon dioxide, and ATP. The energy produced through this process is used by cells to power a wide range of functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and the synthesis of new molecules. Without aerobic respiration, living organisms would be unable to generate the energy needed to sustain life.