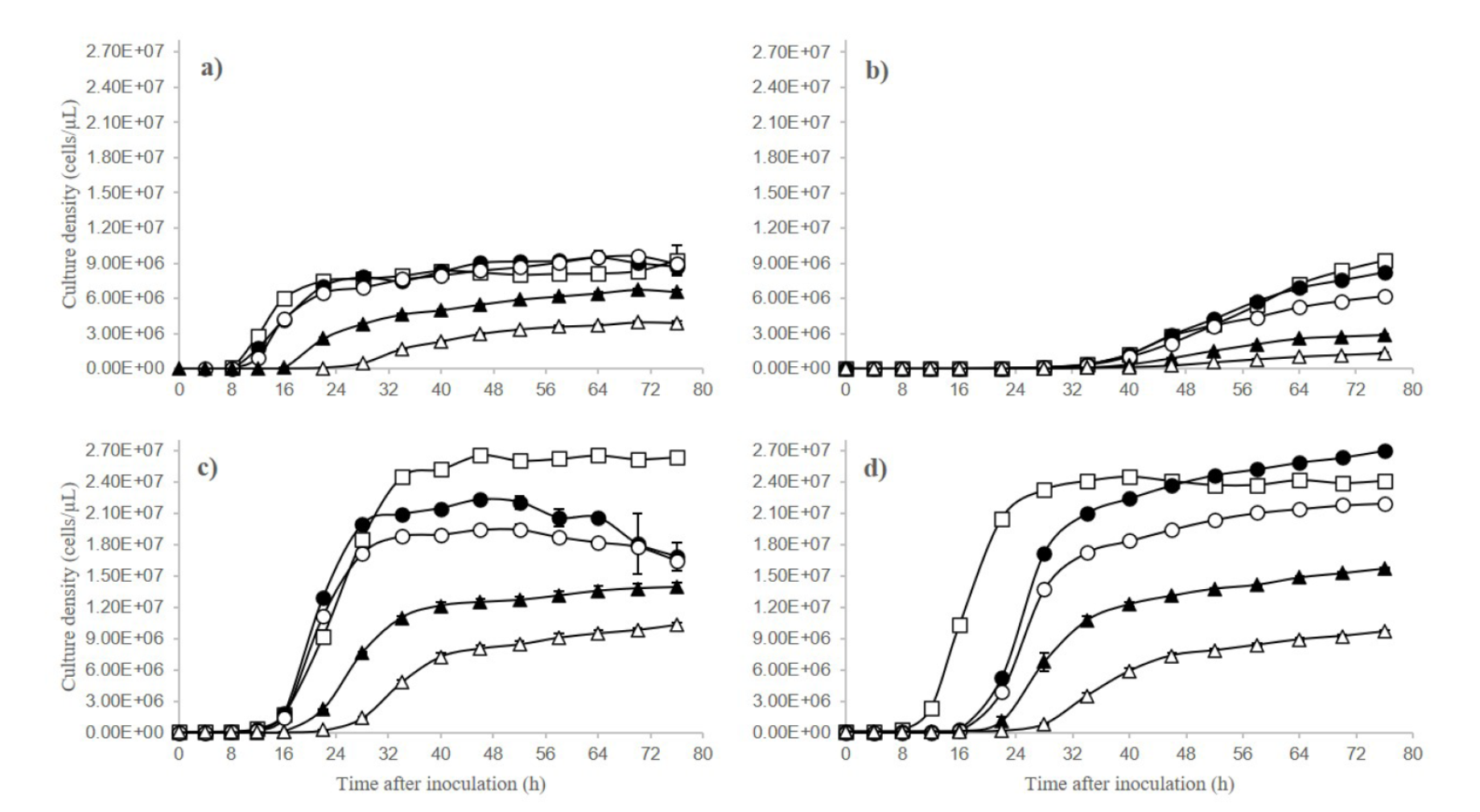
Yeast is a type of single-celled fungus that plays a crucial role in the production of various fermented products such as bread, beer, and wine. During the process of fermentation, yeast converts sugars present in the dough or must (juice extracted from grapes or other fruits) into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The type of sugar used in the fermentation process can affect the yield and quality of the final product.
One type of sugar commonly used in fermentation is glucose, a simple sugar that is easily metabolized by yeast. Glucose is a primary source of energy for yeast cells and can be found in a variety of natural sources such as fruits, honey, and corn syrup. When glucose is fermented by yeast, it produces a moderate amount of ethanol and carbon dioxide, resulting in a balanced flavor and alcohol content in the final product.
Another type of sugar commonly used in fermentation is sucrose, a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose. Sucrose is commonly found in cane sugar and beet sugar and is often used in the production of beer, cider, and mead. During the fermentation process, sucrose is broken down into its component sugars, glucose and fructose, which are then metabolized by the yeast. The use of sucrose in fermentation can lead to a higher alcohol content and a sweeter flavor in the final product.
Fructose, a simple sugar found in fruits and honey, can also be used in fermentation. When fermented by yeast, fructose produces a high yield of ethanol and a sweet flavor in the final product. However, fructose is more difficult for yeast to metabolize than glucose and may result in a slower fermentation process.
Lactose, a sugar found in milk, is not commonly used in fermentation as it is not easily metabolized by yeast. Lactose requires the enzyme lactase to be broken down into its component sugars, glucose and galactose, which can then be fermented by yeast. The use of lactose in fermentation may result in a slower and less efficient process.
In conclusion, the type of sugar used in the fermentation process can have a significant effect on the yield and quality of the final product. Glucose and sucrose are commonly used sugars in fermentation and produce moderate to high yields of ethanol and a balanced to sweet flavor in the final product. Fructose can also be used in fermentation, but it may result in a slower process and a sweeter flavor. Lactose is not commonly used in fermentation due to its difficulty in being metabolized by yeast.