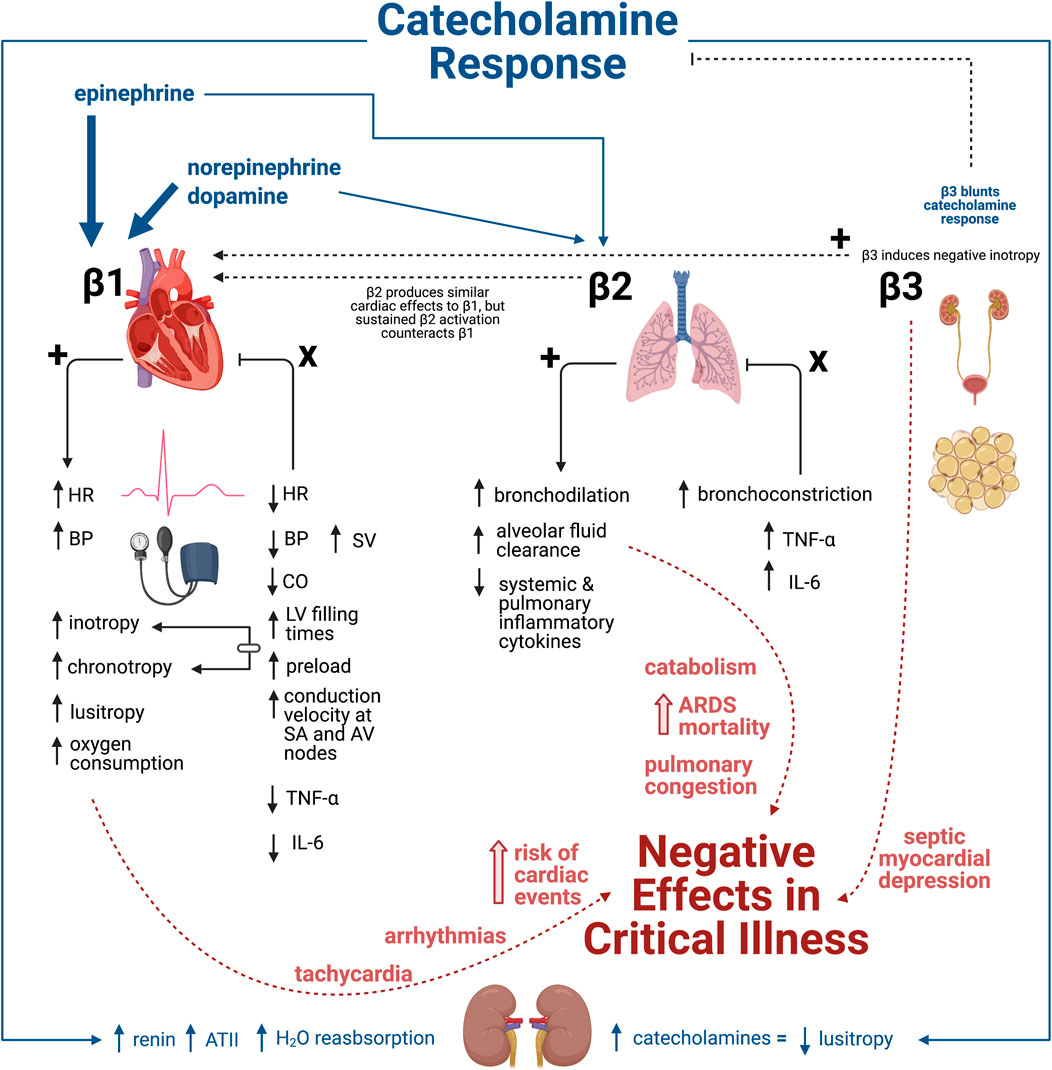
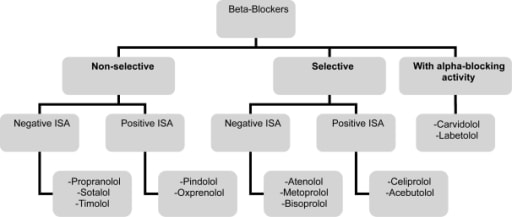
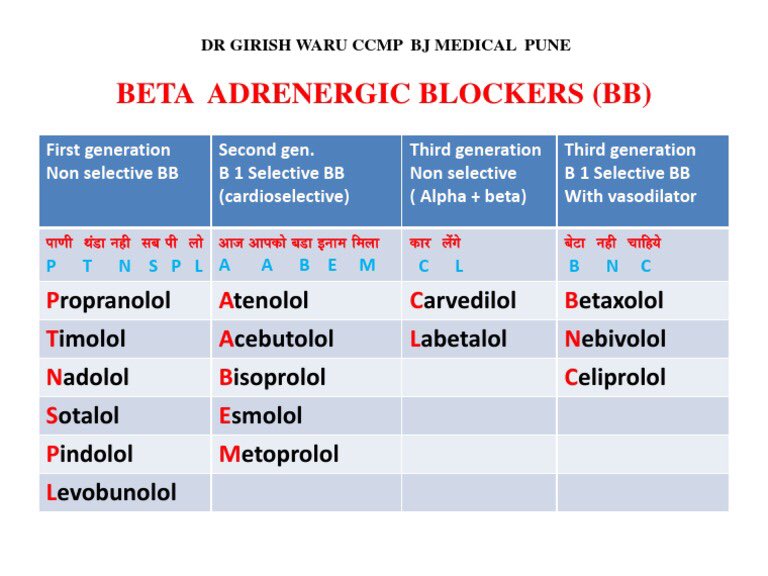
Beta blockers are a class of medications that are used to treat a variety of conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. These drugs work by blocking the effects of the hormone adrenaline, which can help to reduce the heart rate and blood pressure. There are two main types of beta blockers: selective and nonselective.
Selective beta blockers, also known as beta-1 blockers, specifically target the beta-1 receptors in the heart and blood vessels. These receptors are responsible for increasing the heart rate and blood pressure in response to stress or physical activity. By blocking these receptors, selective beta blockers can help to reduce the heart rate and blood pressure, which can be beneficial in conditions such as hypertension or angina.
Nonselective beta blockers, on the other hand, block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. Beta-2 receptors are found in various parts of the body, including the lungs, blood vessels, and smooth muscle tissue. In addition to their effects on the heart and blood vessels, nonselective beta blockers can also affect the function of these other tissues. This can lead to side effects such as difficulty breathing and a decreased ability to exercise.
There are several differences between selective and nonselective beta blockers. One of the main differences is their mode of action. Selective beta blockers only target the beta-1 receptors in the heart and blood vessels, while nonselective beta blockers block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. This means that selective beta blockers may have a more targeted effect on the heart and blood vessels, while nonselective beta blockers may have a wider range of effects on the body.
Another difference between the two types of beta blockers is their potential for side effects. Nonselective beta blockers have a higher risk of side effects because they affect a wider range of tissues in the body. These side effects can include difficulty breathing, a decreased ability to exercise, and an increased risk of developing diabetes. In contrast, selective beta blockers generally have a lower risk of side effects, although they can still cause side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, and low blood pressure.
In conclusion, selective and nonselective beta blockers are two different types of medications that are used to treat a variety of conditions, including high blood pressure and angina. While both types of beta blockers work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, selective beta blockers only target the beta-1 receptors in the heart and blood vessels, while nonselective beta blockers block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. This difference in mode of action can result in different side effect profiles and potential risks for each type of beta blocker.