Conditioning theory is a psychological theory that explains how an individual's behavior can be modified through reinforcement or punishment. It is a fundamental concept in psychology that has been extensively studied and applied in various fields, such as education, marketing, and behavioral therapy.
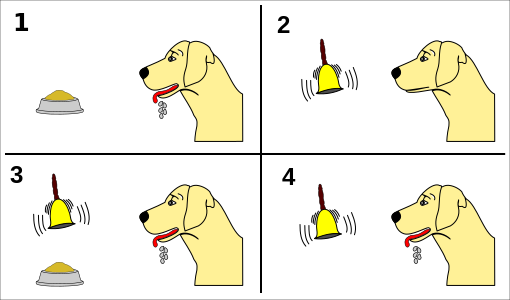
There are two main types of conditioning: classical conditioning and operant conditioning. Classical conditioning, also known as Pavlovian conditioning, was first described by Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist. In his famous experiment, Pavlov conditioned a dog to salivate at the sound of a bell by ringing the bell just before presenting the dog with food. Over time, the dog learned to associate the sound of the bell with the arrival of food, and eventually, it would start salivating at the sound of the bell alone, even if there was no food present.
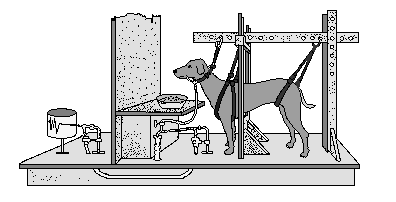
Operant conditioning, on the other hand, is a form of learning in which the consequences of an individual's behavior determine the likelihood of that behavior occurring again in the future. B.F. Skinner, an American psychologist, developed the concept of operant conditioning. In his experiment, he placed a rat in a box with a lever that, when pressed, would dispense a food pellet. The rat learned to press the lever to get food, and this behavior increased the more the rat was reinforced with food.
Both classical and operant conditioning involve the use of reinforcement and punishment to modify behavior. Reinforcement is any consequence that increases the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future, while punishment is any consequence that decreases the likelihood of a behavior occurring again in the future. Reinforcement can be either positive or negative. Positive reinforcement involves adding a desirable consequence to increase the frequency of a behavior, while negative reinforcement involves removing an aversive consequence to increase the frequency of a behavior. Punishment can also be either positive or negative. Positive punishment involves adding an aversive consequence to decrease the frequency of a behavior, while negative punishment involves removing a desirable consequence to decrease the frequency of a behavior.
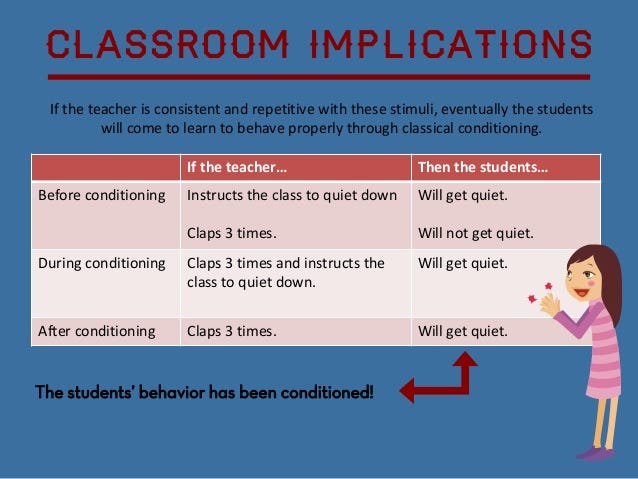
Conditioning theory has many practical applications. In education, it can be used to teach new skills or behaviors, such as reading or arithmetic. In marketing, it can be used to encourage consumers to purchase a product or service. In behavioral therapy, it can be used to help individuals overcome phobias or addictions.
Overall, conditioning theory is a powerful tool for understanding and modifying human behavior. It provides insight into how individuals learn and how their behaviors can be changed through reinforcement and punishment. By understanding this theory, we can better understand and predict human behavior, which has numerous practical applications in various fields.