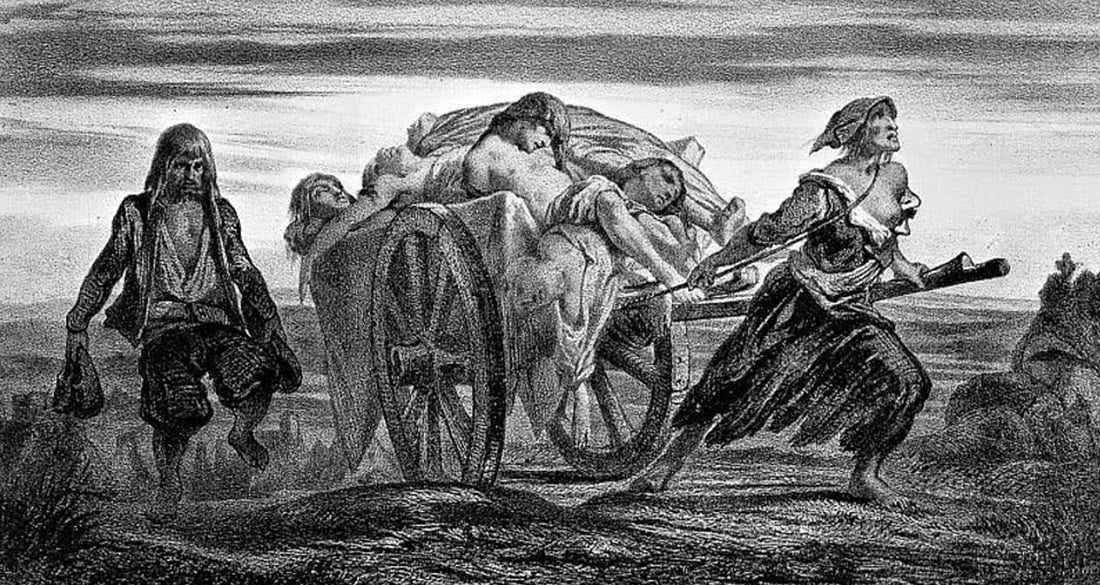
The Black Death, also known as the Great Plague or the Bubonic Plague, was a pandemic that devastated Europe during the 14th century. It is estimated that the Black Death killed up to 75-200 million people, which was roughly between 30-60% of Europe's population at the time. The Black Death had a profound impact on European society and led to significant cultural, economic, and social changes.
The Black Death is believed to have originated in Central Asia and spread westward along trade routes and through the movement of infected rodents. The plague was transmitted through fleas that lived on the bodies of rats and other small mammals, and it could be transmitted to humans through bites or through the inhalation of infected particles. The symptoms of the Black Death included fever, chills, weakness, and the appearance of painful, swollen lymph nodes known as buboes. The disease could progress to more severe forms, such as septicemic plague or pneumonic plague, which affected the blood and respiratory system, respectively. The mortality rate for the Black Death was extremely high, with some estimates suggesting that as many as 75% of those who contracted the disease died.
The Black Death had a profound impact on European society, as it decimated the population and disrupted the social and economic systems of the time. The shortage of labor led to an increase in wages for workers, and the declining population led to a decrease in land values. The Black Death also had cultural consequences, as it contributed to the decline of feudalism and the rise of centralized states. In addition, the Black Death had a significant impact on the arts, as many artists and intellectuals died during the pandemic, leading to a decline in artistic and intellectual output.
The Black Death had a lasting impact on Europe, and its effects can still be seen today. The pandemic changed the course of European history and shaped the world we live in today. It serves as a reminder of the devastating power of disease and the importance of preparedness and prevention in the face of public health crises.