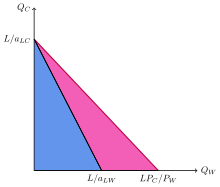
Comparative advantage is an economic concept that refers to the ability of a country or an individual to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to another country or individual. This means that the country or individual is able to produce the good or service more efficiently and at a lower cost than its trading partners.
The concept of comparative advantage was first introduced by economist David Ricardo in the early 19th century. He argued that countries should specialize in producing the goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, and then trade with other countries for the goods and services in which they do not have a comparative advantage. This specialization and trade would lead to increased efficiency and higher standards of living for all countries involved.
There are several factors that contribute to a country's comparative advantage. One of these factors is natural resources. A country that is endowed with an abundance of natural resources, such as oil or fertile land, will likely have a comparative advantage in the production of goods and services that rely on these resources. Similarly, a country with a skilled and educated workforce may have a comparative advantage in the production of high-tech goods and services.
Another factor that influences comparative advantage is technology. A country that is more technologically advanced will have a comparative advantage in the production of goods and services that require advanced technologies. For example, a country with a well-developed information technology sector may have a comparative advantage in the production of software and other IT-related services.
In conclusion, comparative advantage is based on a country or individual's ability to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to its trading partners. This ability is influenced by factors such as natural resources, human capital, and technology. By specializing in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage, countries and individuals can increase efficiency and improve their standard of living.
What Is Comparative Advantage? (Benefits and Comparisons)

The company with the lower opportunity cost has a comparative advantage. When the lower-cost fisherman Ann produces more fish than she herself plans to consume—that is, catches fish that she intends to trade—Bob taps in to her greater efficiency at fishing. On the MathsGee, you can: 1. It is pointless for country A to sell goods to country B, whatever its labour-cost advantages, if there is nothing that it can profitably take back in exchange for its sales. Ask and answer questions 2.
How Does Globalization Impact Comparative Advantage?

But in the real world, there are multiple countries and products involved in a trade. Trade allows specialization based on comparative advantage and thus undoes this constraint, enabling each person to consume more than each person can produce. C Governments should actively protect domestic industries from imports and vigorously promote exports. Therefore, producing wine has a comparative advantage in Portugal over cloth. Modern comparative advantage has come a long way, though. Example 5 In Puerto Rico, one hour of labor can produce either ten bottles of wine or five pieces of cloth.
How to Calculate Comparative Advantage?

The opportunity cost of babysitting, on the other hand, is high. When a country or an economy has an absolute advantage, it is more efficient than other countries at producing a specific good or service. Though a company may have a comparative advantage without earning a competitive advantage, so the two aren't exclusive to each other. If Bob spends all of his working time gathering bananas, he gathers fifty bunches. In this case, you might wonder why they do that. In his writings, he discusses that to make wine in Portugal it takes the labour of 80 men. It can get more food from its neighbor by trading it for oil than it could produce on its own.
Comparative Advantage

But they insist that the special interests of these groups clash with the total national interest, and the most that comparative-advantage Nations do, of course, maintain see. To learn about how we use your data, please Read our Privacy Policy. The benefit of comparative advantage is the ability to produce a good or service for a lower opportunity cost. They may channel additional labor, capital and natural resources toward the production of this specific good or service to take advantage of a lower opportunity cost and improve their profit margins. You may disable these by changing your browser settings, but this may affect how the website functions. A comparative advantage gives companies the ability to sell goods and services at lower prices than their competitors, gaining stronger sales margins and greater profitability.
6 Comparative Advantage Examples

Understanding how to calculate comparative advantage is crucial for any type of business. Countries who have a comparative advantage producing a specific good or service often choose to specialize in this area since it is more efficient and cost-effective than producing other goods and services. Less-developed countries have benefited from globalization by leveraging their comparative advantage in labor costs. The United States can produce 40 aircraft or 100 cars. The wine price in country A, for example, can be expected to fall as larger and larger supplies of imported wine become available. It has received singularly little attention from the economists of the Continent, and sometimes has been discussed by them as one of those subtleties that have little bearing on the facts of industry. The labour time required to produce a unit of either cost of production labour time country A country B wine 1 unit 1 hour 2 hours cloth 1 unit 2 hours 6 hours As compared with country A, country B is productively inefficient.
Comparative advantage

With one exception, there will always be at least one commodity that a low-productivity country such as B can successfully export. As a result, some developing countries have been able to progress more quickly in terms of job growth, educational attainment, and infrastructure improvements. Consider this hypothetical situation where the two neighboring countries the United States and Mexico both produce cars and aircraft. Some companies may have customers who experience miscommunications due to language barriers when they're speaking with representatives at Indian call centers. The countries specialize in producing goods and services that they can produce more efficiently with lower opportunity costs than the other goods and services.