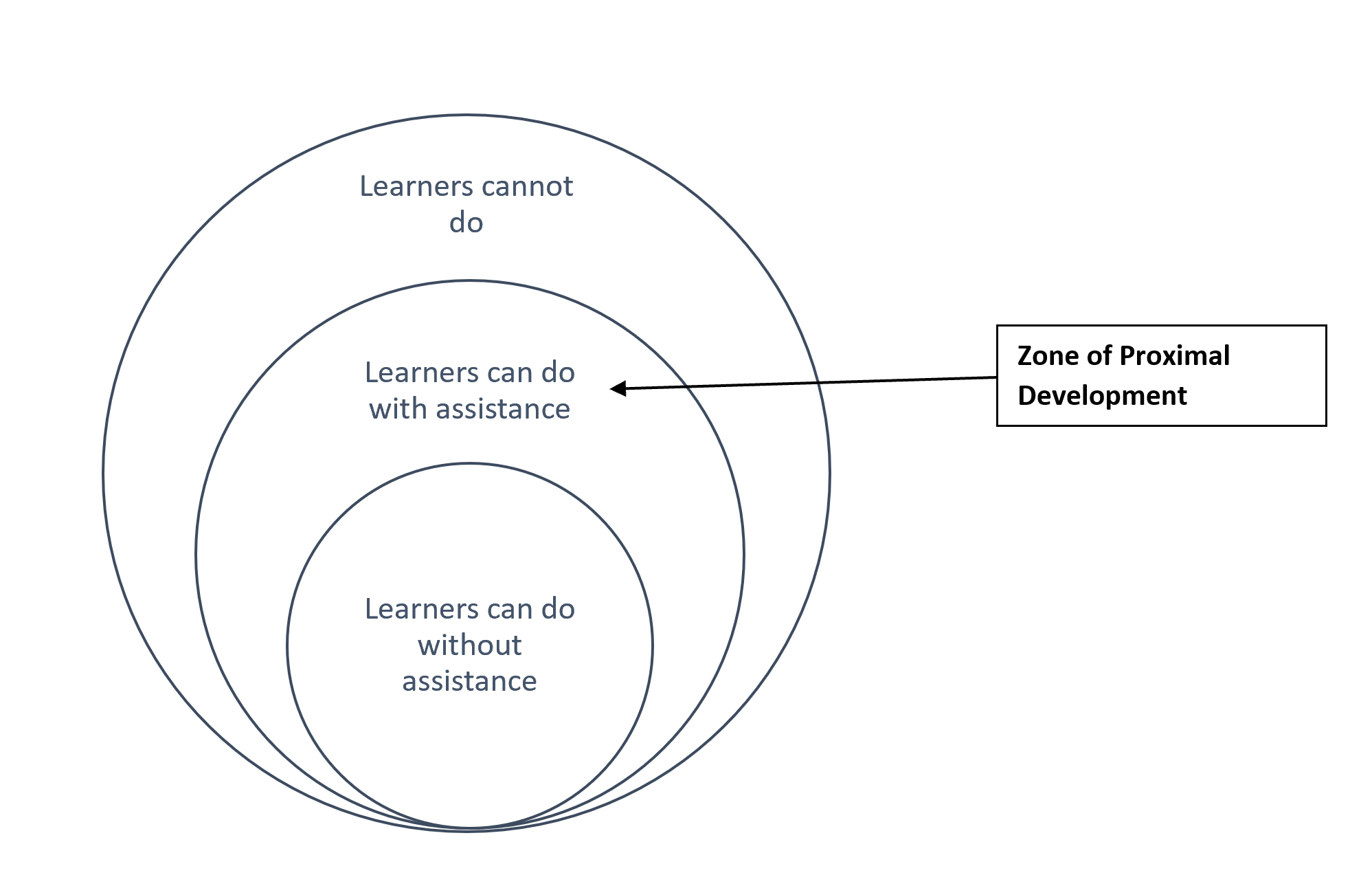
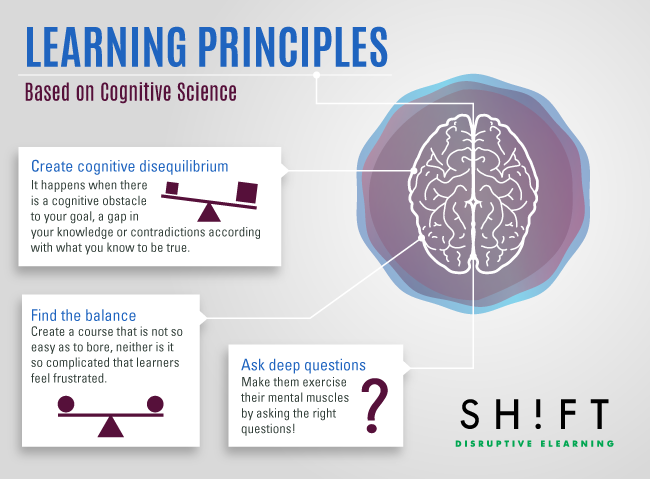
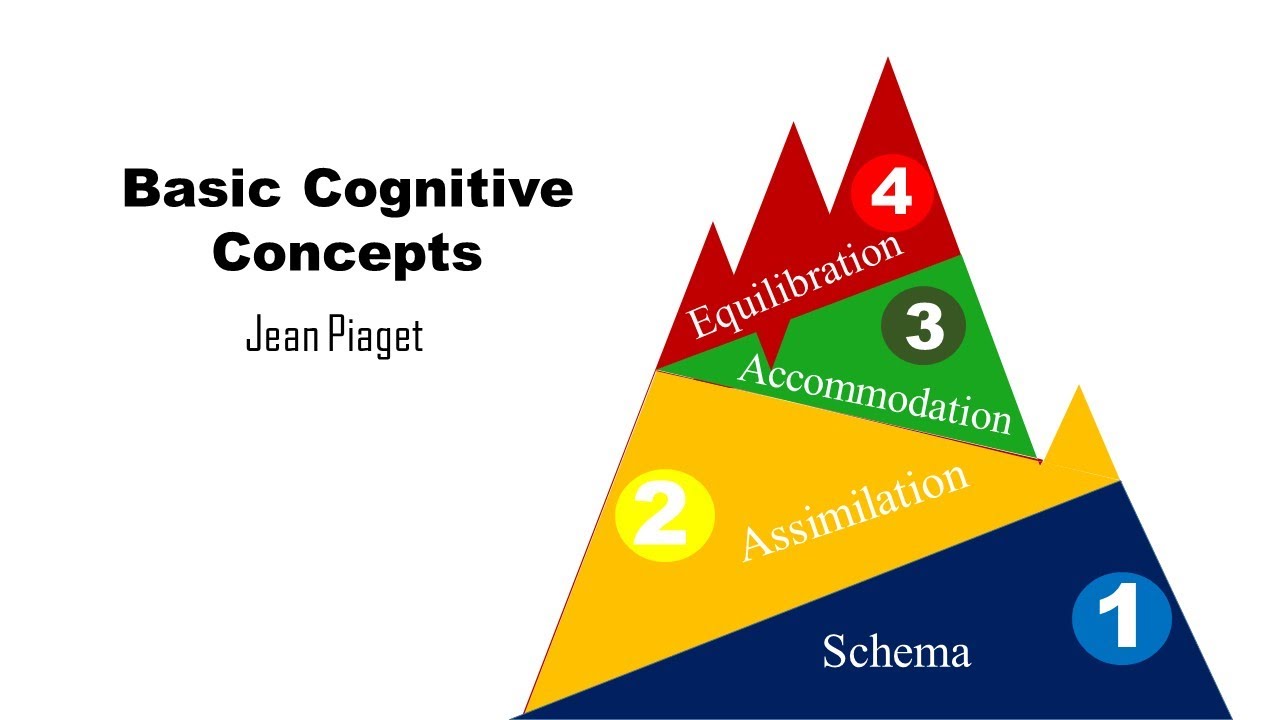
Cognitive disequilibrium is a state of discomfort or confusion that occurs when an individual's existing beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors are challenged by new information. It is a natural and necessary part of the learning process, as it forces individuals to reassess and potentially revise their understanding of the world.
Cognitive disequilibrium can be triggered by a variety of stimuli, including encountering new ideas, experiences, or perspectives that contradict one's existing beliefs. It can also be triggered by a lack of understanding or a gap in one's knowledge or skills.
The process of resolving cognitive disequilibrium involves actively seeking out new information, reflecting on one's beliefs, and potentially modifying or adjusting them in light of the new information. This process, known as assimilation, is essential for personal and intellectual growth.
However, cognitive disequilibrium can also be a source of stress and anxiety. It can be difficult to accept that one's beliefs may be incorrect or that there are multiple valid viewpoints on a given topic. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their own reactions to cognitive disequilibrium and to approach it with an open and curious mindset, rather than becoming defensive or resistant to change.
Cognitive disequilibrium can also be used as a teaching tool in education. By presenting students with new information or perspectives that challenge their existing beliefs, educators can encourage critical thinking and facilitate the assimilation process. This can help students develop a more nuanced and flexible understanding of the world around them.
In conclusion, cognitive disequilibrium is a normal and necessary part of the learning process. It can be a source of discomfort or anxiety, but it can also be an opportunity for personal and intellectual growth. By approaching it with an open and curious mindset, individuals can learn to embrace and resolve cognitive disequilibrium in a way that helps them better understand and navigate the world.