Classification of dental cements. Dental cement 2022-10-21
Classification of dental cements
Rating:
5,1/10
1458
reviews
Dental cements are a type of material that are used in dentistry to hold various dental restorations in place. These cements can be classified into several different categories based on their intended use and the properties they possess. Some of the main categories of dental cements include:
Luting cements: These cements are used to hold dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and inlays, in place. They are designed to be strong and durable, and are typically made from a combination of resin and glass ionomer.
Liner cements: These cements are used to provide a protective layer between the tooth and a filling or other restoration. They are typically made from materials that are more forgiving and less likely to cause sensitivity, such as calcium hydroxide or zinc oxide.
Base cements: These cements are used to provide a foundation for a filling or other restoration. They are typically made from materials that are more forgiving and less likely to cause sensitivity, such as zinc oxide or calcium hydroxide.
Bonding agents: These cements are used to create a strong bond between a dental restoration and the tooth. They are typically made from a resin that is activated by light or heat, and are used in conjunction with a bonding agent.
Temporary cements: These cements are used to hold temporary restorations in place, such as crowns or bridges, until the permanent restoration can be placed. They are typically made from a material that is easy to remove, such as zinc oxide.
Each of these different types of dental cements has its own unique properties and characteristics, and is used for specific purposes in dentistry. It is important for dentists to be familiar with the various types of cements available and to choose the appropriate cement for each specific situation.
45. Dental Cements
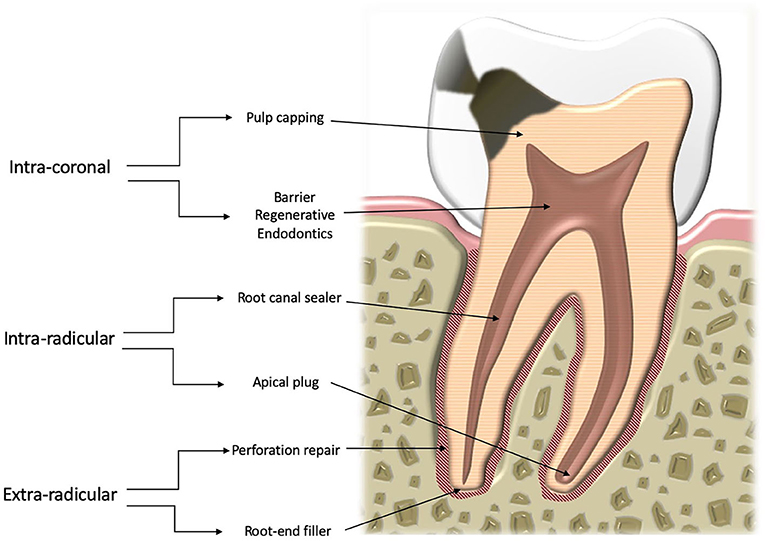
Materials used to bond teeth or materials to teeth Dental cements have a wide range of dental and orthodontic applications. Examples of water-based cements are glass ionomer, resin-modified glass ionomer, zinc phosphate, and zinc polyacrylate. Normally a patch test done by dermatologists will be used to diagnose the condition. Using this technique helps to eliminate the hydraulic issues associated with placement because of the precision of the fit of the restoration to the abutment. In 2005, he was awarded Diplomate status on the American Board of Aesthetic Dentistry. These were discussed in Permanent Cements Permanent cements are luting agents that are used for the long-term cementation of cast restorations such as inlays, crowns, bridges, laminate veneers, and orthodontic fixed appliances.
Next
dental cements Flashcards

RMGI cements are excellent to use when moisture control is a problem. . Be sure to fluff the powder in the bottle before dispensing the powder in the measuring scoop. A sable brush Figure 26 was then used to remove the majority of the excess cement. It is acceptable to clear away excess resin-modified glass ionomer cement when it reaches the gel stage or after complete setting.
Next
23: Cements

This type of dental material is designed to act as an adhesive to hold the indirect restoration to the tooth structure. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Pub. In the past most contained eugenol, but there are now eugenol-free oil-based cements. These cements truly form a micromechanical bond to both tooth structure on one side and restorative material on the other side. James Earl , 1950-, Vinson, LaQuia A. To err on the side of caution, some recommend avoiding desiccation of the dentin surface of the preparation before cementation 12 to decrease the likelihood of postoperative sensitivity after cementation. While mixing and setting the zinc phosphate it gives off an exothermic reaction.
Next
Dental cement

Each manufacturer uses a slightly different system for sectioning the powder. B, Porcelain-metal fixed partial denture being cemented with resin-modified glass ionomer cement FujiCEM, GC America, Alsip, Illinois using an active force when cementing by having the patient bite down on a saliva ejector. The chemical makeup for polycarboxylate cement comes in a liquid made up of polyacrylic acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid, tartaric acid and water, while the powder is made up of zinc oxide, magnesium oxide, aluminum oxide, and different reinforcing fillers. The front or anterior teeth incisors, canine require aesthetics more than strength and it is the opposite in the posterior or the molars. Classification of Resin Cements.
Next
Classification of Dental cements based on their uses
This adheres to the enamel, dentin, and metallic materials. The following categories outline the main uses of cements in dental procedures. The setting reaction produces an end product called zinc eugenolate which readily hydrolyses producing free eugenol that causes adverse effects on fibroblast and osteoclast-like cells. FujiCEM in a paste-paste automix delivery system is shown in this photograph. Finger pressure was used for several seconds Figure 15 to extrude excess cement around the margins of the restoration.
Next
Dental Cements: An Overview

The teeth were prepared for a 5-unit PFM fixed partial denture bridge. Intermittent finger pressure was used to ensure that all the excess cement was expressed and the restoration was fully seated Figure 25. Again, proper resistance and retention form of the preparation is still more important for successful retention of any restorative material than the cement that is used for placement. Bonding property of two resin-reinforced glass-ionomer cements to zirconia ceramic. Retracted view of the preparations of teeth Nos. An RMGI cement FujiCEM was extruded from the cartridge with mixing tip directly into the abutments of the restoration. In some cases these cements are self-adhesive to dentin.
Next
5 Different Types of Dental Cements Essay Example

This was easily accomplished due to the thin film thickness 6 µm of the RMGI cement. It was originally polyacrylic acid and has changed over to polyalkenoate cement. However, setting can be completed fast when water is present. New metal and ceramic primers have been developed that have been reported to enhance bond strengths of cements to nonetchable substrates, such as zirconia and metal. E, Completed cementation of porcelain-metal crown.
Next
Classification of Resin Cements

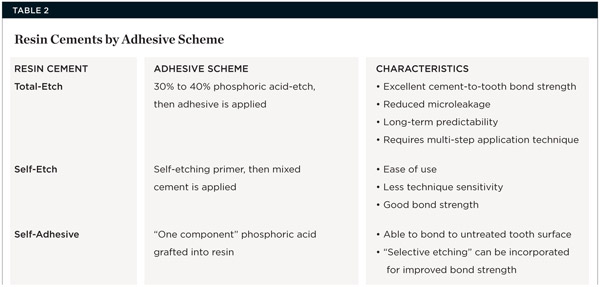
As long as 1. The second type of cement is Composite Resin Cement. A sonic or piezo scaler with water spray can also be used carefully to ensure complete cement removal from the sulcular areas. Zinc phosphate exhibits a very high compressive strength, average tensile strength and appropriate film thickness when applies according to manufacture guidelines. Glass ionomer has benefits such as it causes less trauma to the pulp; it has low solubility in the mouth, and adheres to a slightly moist tooth surface, etc. Preparations with less than ideal cervico-incisal height may require that additional bond strength that is afforded by the use of total-etch resin cements.
Next

Lowe graduated magna cum laude from Loyola University School of Dentistry in 1982 and served there as an assistant professor in operative dentistry until its closure in 1993. The preparations can be dried using a cotton pledget so that a small amount of moisture remains on the surface. Some manufacturers divide the powder into equal parts, whereas others divide the powder into progressively smaller increments. This type of cement adheres to enamel, dentin, and metallic materials. J Am Dent Assoc. Allergic Reaction Associated with the use of Eugenol Containing Dental Cement in a Young Child. Powder-to-Liquid Ratio Incorporating too much or too little powder will alter the consistency of the cement.
Next







