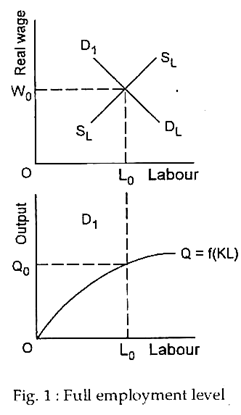
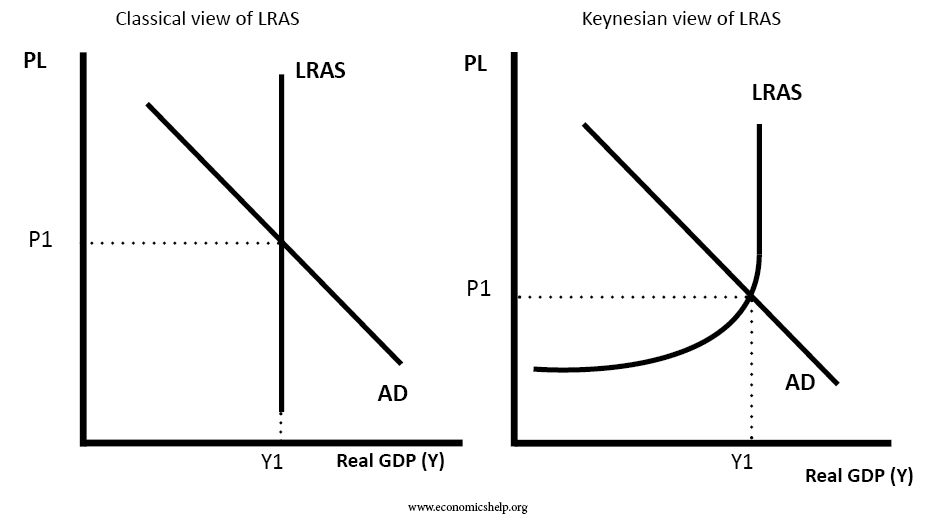
Classical demand theory is a fundamental concept in economics that helps to explain how consumers make purchasing decisions based on the price of a good or service. According to this theory, the demand for a particular product is determined by its price, and as the price of a product increases, the demand for it will decrease. This relationship is known as the law of demand.
One of the key assumptions of classical demand theory is that consumers are rational actors who seek to maximize their utility, or satisfaction, from the goods and services they consume. In this view, consumers weigh the costs and benefits of purchasing a particular product and decide whether or not to purchase it based on the perceived value they will receive from it.
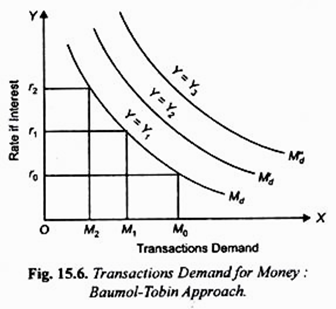
In order to understand how consumers make these decisions, classical demand theory posits that there are several factors that influence demand for a product. These include the price of the product itself, the prices of related products, the income of the consumer, and the consumer's tastes and preferences.
For example, consider a consumer who is deciding whether or not to purchase a new car. The price of the car will be a major factor in this decision, as the consumer will need to weigh the cost of the car against their budget and other financial considerations. The consumer may also consider the prices of other, related products, such as car insurance and maintenance costs, as well as their own income and other financial resources. Finally, the consumer's personal tastes and preferences will also play a role in their decision, as they may prefer certain brands or features over others.
Classical demand theory also helps to explain how changes in these factors can affect the demand for a product. For instance, if the price of a car increases, the demand for it may decrease, as consumers may decide that the higher price is not worth the perceived value they would receive from the car. Similarly, if the income of a consumer increases, they may be more willing to purchase higher-priced goods and services, as they have more disposable income available to them.
In conclusion, classical demand theory is a crucial concept in economics that helps to explain how consumers make purchasing decisions based on the price of a product and other factors such as related prices, income, and personal preferences. Understanding this theory can help businesses and policymakers make informed decisions about pricing and other strategies to increase demand for their products and services.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aggregatedemand.asp_final-e854e9e6631242ffb8b00c6a76d7cbb9.png)